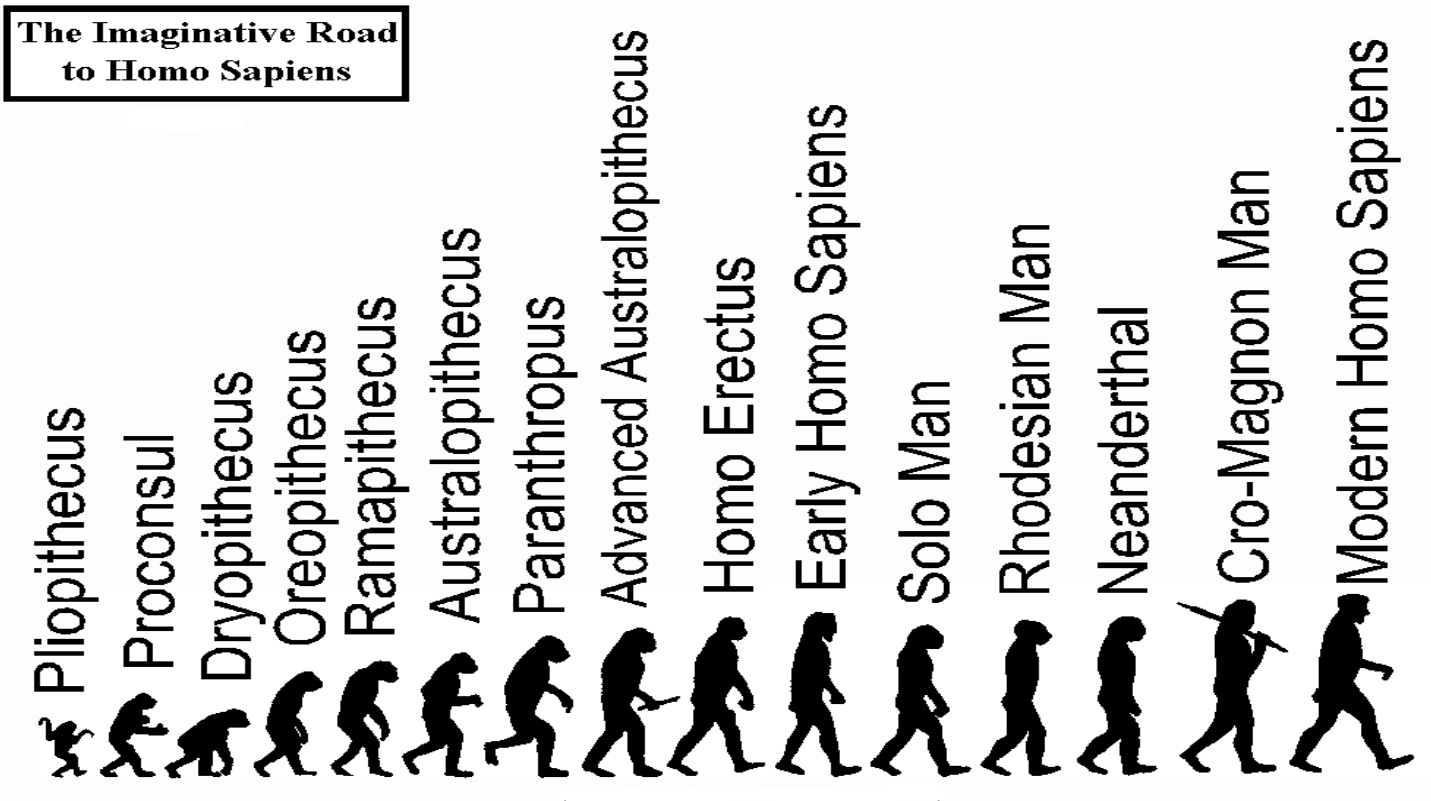
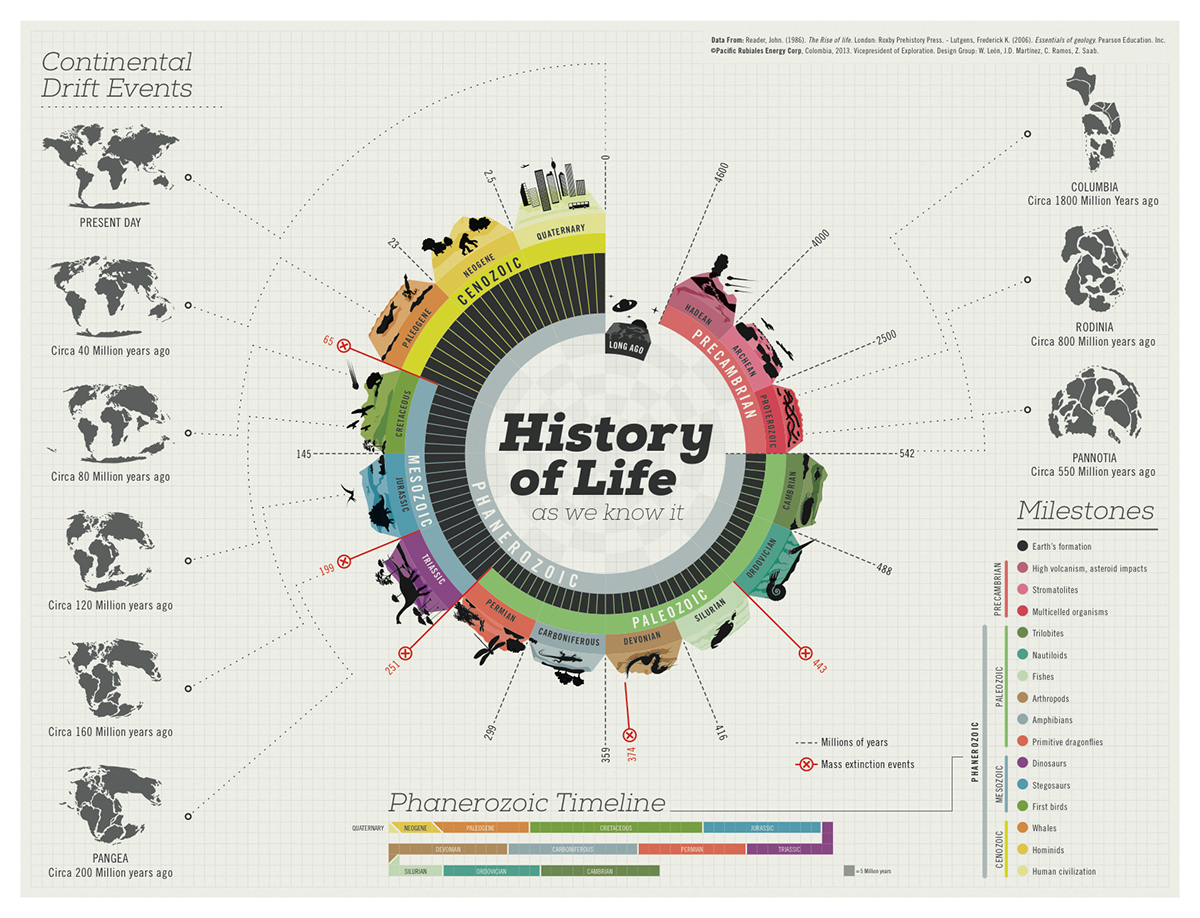
Macroevolution – Definition, Principle, Process, Features, Examples
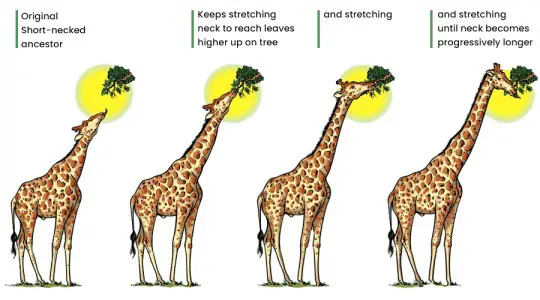
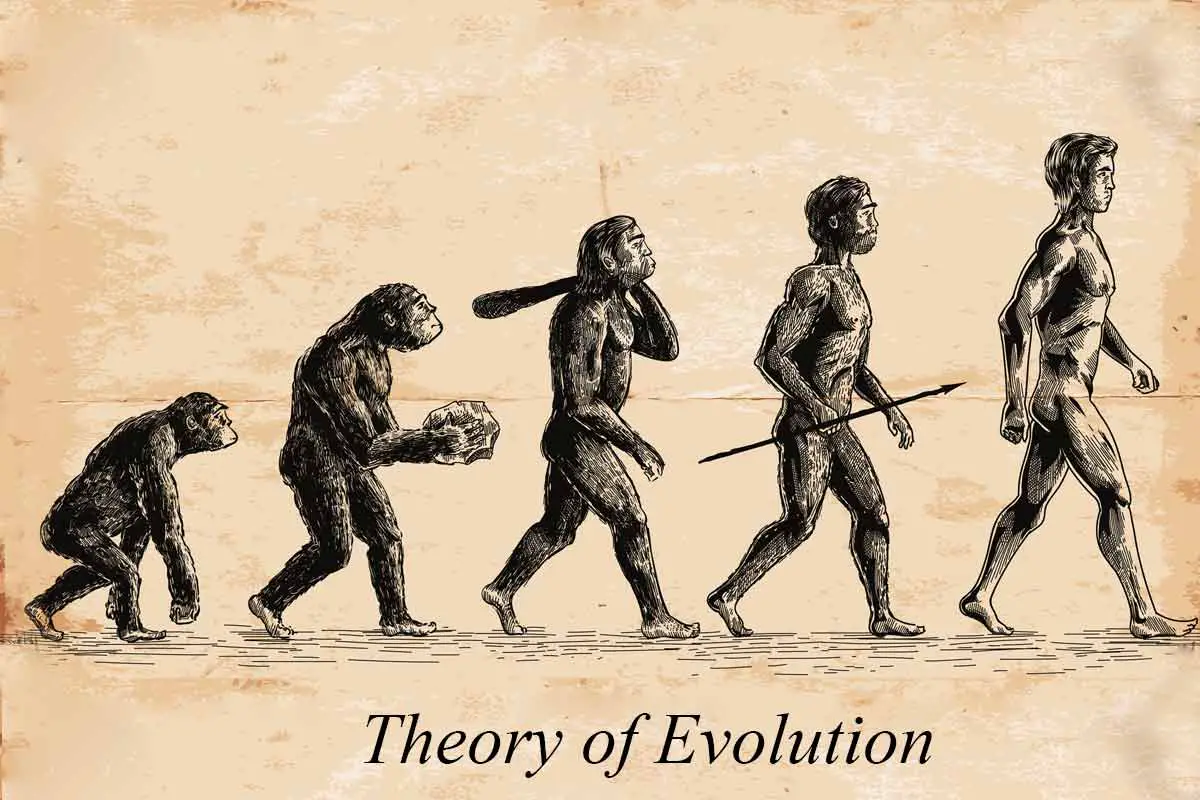
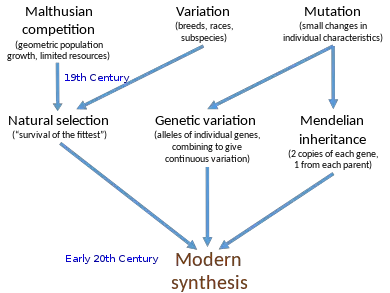
What is Macroevolution? Definition of Macroevolution Macroevolution refers to the large-scale evolutionary changes that occur above the level of species, involving the emergence of new taxa (genera, families, orders, etc.) and the diversification of life forms over long periods of time. It encompasses the study of patterns and processes that shape the biodiversity and relationships … Read more