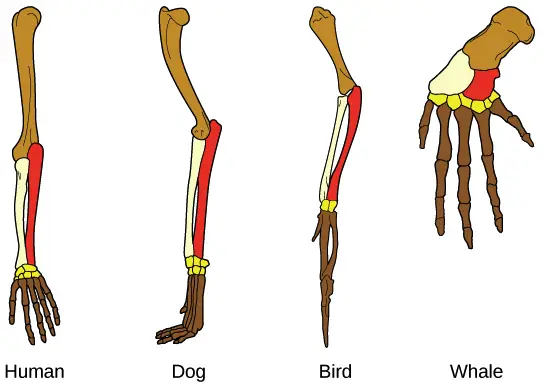
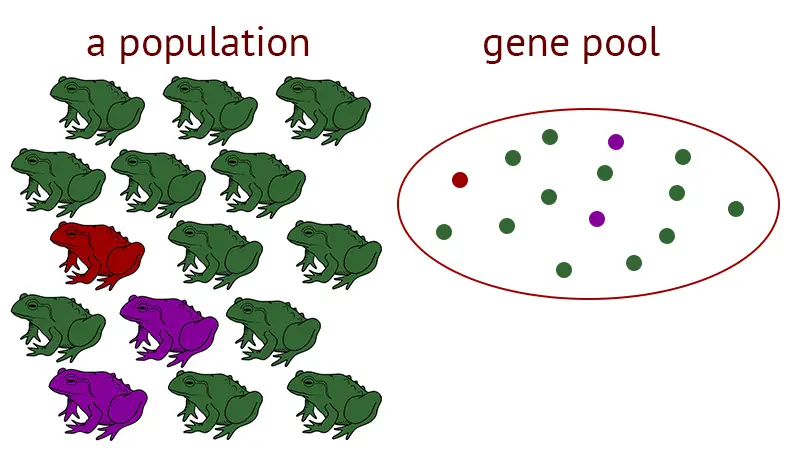
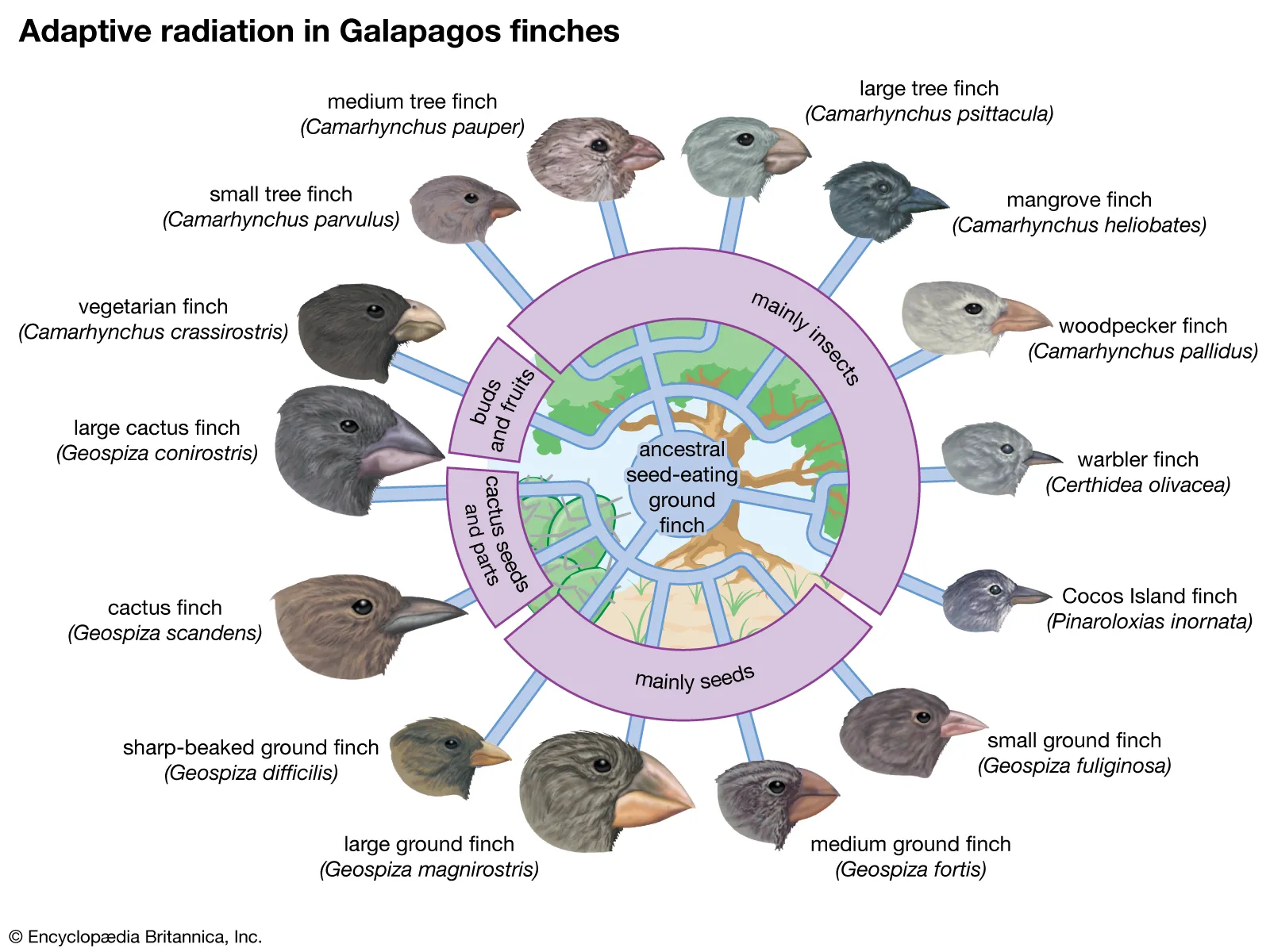
Learning Behaviour – Definition, Types, Examples
What is Learning Behaviour? Learning by Animals Learning in animals is a fascinating subject that has captivated the attention of animal behaviorists. Understanding how animals learn and the mechanisms involved has been a topic of extensive research. Heyes (1994) has identified three commonly recognized types of experiences that can result in learning. The first type … Read more