Hey, if you’re a student of microbiology then you’re familiar with the term Microsporum spp. but if you’re from another field I don’t think you’re familiar with the term.
If you are familiar then let me know in the comment section.
Now, let me explain you in a brief;
There are some skin infections in our daily life which are very common such as tinea capitis, tinea corporis, ringworm, etc. All of these skin infections are caused by fungal species, and Of these, Microsporum spp is the most responsible for these skin infections. These fungal infections or skin infections are also known as Cutaneous mycoses or dermatomycoses. These fungal diseases can be mild, but if not treated properly they can become a serious problem.
Now in this article, we will learn treatment, prevention, of Microsporum spp infections.
What is Microsporum spp?
- Microsporum spp is a genus of fungi, which is responsible for different types of skin infection such as, tinea capitis, tinea corporis, ringworm, and other dermatophytosis (fungal infections of the skin)
- They only affect all keratinized areas of the body (hair, skin and nails)
- Nail infection by Microsporum is rare.
- Microsporum spp reproduce by forming macroconidia and macroconidia on short conidiophores.
*macroconidia are referred to as large asexual reproductive structures and microconidia refers to smaller asexual reproductive structures.
- They can’t grow above 37°C, which is why they are restricted to the nonviable skin tissues.
- Microsporum spp. is a type of Zoonotic fungi, because they can transmit from animal to human, which is a serious problem.
- Microsporum spp. infection is not fatal. The main effects are aesthetic and will persist until treated with the appropriate medication.
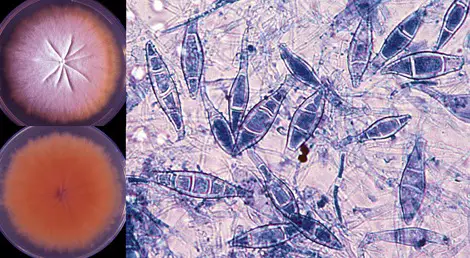
Species of Microsporum spp
There are present different species of Microsporum such as, Microsporum amazonicum, Microsporum audouinii, Microsporum boullardii, Microsporum canis, Microsporum canis var. Distortum, Microsporum cookei, Microsporum distortum, Microsporum duboisii, Microsporum equinum, Microsporum ferrugineum, Microsporum fulvum, Microsporum gallinae, Microsporum gypseum, Microsporum langeronii, Microsporum nanum, Microsporum persicolor, Microsporum praecox,, Microsporum ripariae, Microsporum rivalieri.
Taxonomic Classification of Microsporum spp.
| Kingdom | Fungi |
| Order | Onygenales |
| Phylum | Ascomycota |
| Family | Arthrodermataceae |
| Genus | Arthroderma |
Natural Habitats of Microsporum spp.
These filamentous keratinophilic fungi or Microsporum spp. are widely distributed in the world but some of them have restricted geographic distribution. Microsporum spp. can grow at room temperature of 25-27˚C . They can be found in ;
- Microsporum spp. Are naturally found in soil which is known as the geophilic species.
- They can be found in animals, which is known as the zoophilic species.
- They can be found in humans (skin, hair, and nails), which is known as the anthropophilic species.
Pathogenicity of Microsporum spp.
- Microsporum is responsible for dermatophytosis. The term Dermatophytosis is used to denote the infection in hair, skin or nails due to any dermatophyte species.
- Similar to other dermatophytes, Microsporum spp cause cutaneous diseases by degrading insoluble keratin substrates of hair, skin, and nails with the help of a particular class of extracellular proteolytic inducible enzyme called keratinase, which is synthesis by them.
- Microsporum spp normally infects skin and hair. Only except Microsporum persicolor which does not infect hair.
Clinical Significance or Symptoms of Microsporum spp.
The symptoms of Microsporum spp. Infection may vary based on the region that is affected, such as;
- In the case of hair infection, they can cause hair loss (ectotrix) or breakage (endotrix), Scaling on the scalp. i.e. tinea capitis, and tinea barbea.
- In skin infection they can cause lesions that may appear as circular or annular and elevated, producing a ringworm infection form.
- The nail infection may appear as discoloration, dystrophy, hyperkeratosis, and occasionally onycholysis.
- It can cause Itching in the affected area.
Transmission of Microsporum spp.
- Animal to Human: They can transmit from cats and dogs to humans through direct or indirect contact with the combs, brushes, hats, furniture, linens, etc. I.e. Cats and dogs are the main reservoir for Microsporum canis.
- Human to Human: They can transmit from human to human through direct contact (sexual contact, kissing, etc) and indirect contact (bedding, clothes, etc). I.e. Antropophilic species are contagious between humans.
- They can transmit from soil to humans or animals.
Reproduction of Microsporum spp.
- Microsporum spp. reproduces asexually with the formation of macroconidia.
- Macroconidia is asymmetrical, spherically shaped, and has thick cell walls coarsely roughened.
- The interior portion of each macroconidium is typically divided into six or more compartments separated by broad cross-walls.
- Microsporum also produces microconidia that resemble those of many other dermatophytes and thus is not a useful diagnostic feature.
Morphological Characters of Microsporum spp.
- Macroscopic morphology characters
- The colonies of Microsporum appears as glabrous, downy, wooly, or powdery.
- The diameter of the colony varies between 1 to 9 cm after 7 days of incubation on Sabouraud dextrose agar at 25°C.
- The color of the Microsporum spp. colony varies depending on the species. It may be white to beige or yellow to cinnamon. From the reverse, it may be yellow to red-brown.
- In the Hair perforation test, they have the ability to grow on rice grains and also at 37°C provide useful hints to differentiate Microsporum spp. from each other.
- Microscopic morphology characters
- They produce septate hyphae, microaleurioconidia, and macroaleurioconidia.
- The Conidiophores are hyphae-like.
- Microaleuriconidia appears as unicellular, solitary, oval to clavate in shape, smooth, hyaline, and thin-walled.
- Macroaleuriconidia appears as hyaline, echinulate to roughened, thin- to thick-walled, typically fusiform (spindle in shape), and multicellular (2-15 cells).
- Microsporum spp. often have an annular frill.
* They have spindle-shaped macroconidia with echinulate to rough walls, which help them to distinguish from others.
Culturing of Microsporum spp.
Microsporum spp. Can grow in –
- Sabouraud dextrose agar, at 25˚C.
- In rice grain medium with pigmented peripheries.
- Trichophyton agar.
Detection or Diagnosis of Microsporum spp. Infections
- Microsporum spp. It can be detect from the soil by a mechanism called baiting. This method is used to attract Microsporum spp. from specific soil samples. In this method, involve preparation of the desired soil with keratinized molecules (hair fragments, nail clippings, etc) and waiting for colonization of fungus onto the material.
- In clinical reports, researchers used two methods, known as Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequencing and Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (Maldi-TOF) Mass Spectrometry to distinguished the species of the Microsporum gypseum complex.
- A potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of a skin scraping can be reviewed under the microscope to confirm the diagnosis of a fungus.
- Different species of Microsporum can be detected by examining the morphological characters of the colony in different culture media such as;
- Potato Dextrose Agar:
- Microsporum audouinii formed a pinkish-brown or salmon-colored fluffy colony
- Microsporum canis formed a bright yellow colony.
- Trichophyton Agar:
- M. canis produce a flat, white, suede-like to downy, with a yellow to pale yellow-brown reverse colony.
- M. audouinii formed a flat, white, suede-like to downy, with yellow-brown reverse colony with a furry texture.
- Rice Grain Agar:
- M. canis formed a white aerial mycelium with the production of yellow pigment.
- Potato Dextrose Agar:
- The periodic acid-Schiff stain also used for identifying Dermatophytic fungi in microscopic anatomy or microanatomy.
Treatment of Microsporum spp. Infection
- Topical treatment:
Fungal infections on skin can be treated with antifungal creams, which can take around two weeks, such as
- Clotrimazole containing creams such as, Cruex cream, Desenex cream, Lotrimin cream, lotion, and solution.
- Miconazole containing cream such as, Monistat-Derm cream.
- Ketoconazole containing cream, i.e. Nizoral cream.
- Econazole containing cream, i.e. Spectazole.
- Naftifine containing cream, i.e.Naftin.
- terbinafine containing cream, i.e. Lamisil cream and solution.
- For hair infection use Nizoral (ketoconazole) 2% Shampoo, it is an antifungal shampoo.
- Systemic treatment:
Some fungal infections can not be treated with topical treatment, they need to be treated with oral medications. Examples include scalp fungus and fungus of the nails. Oral medication takes about a three-month to cure the infection. Some example of oral medications are;
- griseofulvin (Fulvicin, Grifulvin, and Gris-PEG).
- Terbinafine.
- itraconazole (Sporanox).
- fluconazole (Diflucan).
Drug Resistance of Microsporum spp.
- Microsporum gyseum shows resistance against ketoconazole as well as against miconazole and clotrimazole in certain strains.
- Microsporum canis is a TRF-resistant strain, which shows resistance to terbinafine (TRF).
Prevention and Control of Microsporum spp. Infection
- Do not share your clothing, towels, hairbrushes, combs, hair accessories, sports gear, or other personal-care items with others.
- Avoid direct contact with infected animals and related fomites.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes to minimize sweat and moisture, which can help in the prevention of fungal infections.
- Wash hands after taking care of pets, or animals.
Common Species of Microsporum spp.
Microsporum canis
| Description: | 1. Microsporum canis is a zoophilic dermatophyte 2. asexual fungus. 3. “canis” implies dogs |
| Habitat: | Cats and dogs are the main sources |
| Infection: | Ringworm in humans, especially children. Invades hair, skin and rarely nails. |
| Morphology: | 1. Colonies of Microsporum canis appear as flat, spreading, white to cream-colored, with a dense cottony surface which may show some radial grooves. 2. The color of the Colonies usually has a bright golden yellow to brownish-yellow reverse pigment. 3. There also present some non-pigmented strains. 4. The Macroconidia of Microsporum canis usually appears as spindle-shaped with 5-15 cells, verrucose, thick-walled and often have a terminal knob, 35-110 x 12-25 µm. 5. |
| Confirmatory Tests: | 1. On Rice Grains, ti shows Good growth of white aerial mycelium with the production of yellow pigment and reveals numerous macroconidia and microconidia under microscopic observation. 2. Form Bright yellow color on Potato Dextrose Agar. 3. On Vitamin Free Agar (Trichophyton Agar No.1) it shows Good growth indicating no requirements of special nutrient, with the formation of flat, white, suede-like to downy, with a yellow to pale yellow-brown reverse. 4. Show Positive results within 14 days in Hair Perforation Test. |
| Diagnosis: | perform both Wood’s lamp examination and microscopic analyses of suspected areas. |
| Treatment: | systemic therapy with griseofulvin, itraconazole or terbinafine. |
Microsporum nanum
| Description: | 1. Microsporum nanum belong from the family Arthrodermataceae. 2. Microsporum nanum is both zoophilic and geophilic. 3. causes infection in dead keratinized tissues such as skin, hair, and nails. |
| Habitat: | Animals such as pigs and sheep are the natural host |
| Infection: | Microsporum nanum infections include tinea capitis, tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea faciei. |
| Morphology: | M. nanum produces a thin, powdery, and soft fibrous colony that appears white at the center becoming light yellowish-brown towards the colony margin on Sabouraud’s Dextrose agar at 25 °C. |
| Confirmatory Tests: | The reverse side appears brownish-orange in young colony and reddish-brown in older colony. |
| Diagnosis: | perform both Wood’s lamp examination and microscopic analyses of suspected areas. |
| Treatment: | Griseofulvin, clotrimazole, miconazole, enilconazole and many herbal treatments, such as extracts from Azadirachta indica, essential oil from Curcuma longa[ and Eucalyptus pauciflora have been reported to be effective in inhibiting the fungus. |
Microsporum audouinii
| Description: | 1. Microsporum audouinii is an anthropophilic fungus 2. colonizes keratinized tissues (primarily hair) causing infection. 3. They can grow in neutral pH, range from 6.8-7.0 and room temperature. 4. growth is strongest in the hexoses. 5. growth is weakest in maltose, sucrose, lactose and galactose. |
| Habitat: | Microsporum audouinii often found in soil that is rich in keratinous material. |
| Infection: | Tinea capitis (scalp ringworm) and Tinea corporis, in prepubescent children (starting at 6 months) and rarely affect adults. |
| Morphology: | 1. Colonies are flat, spreading, greyish-white to light tan-white in colour, and have a dense suede-like to the downy surface, suggestive of mouse fur in texture. 2. Macroconidia and microconidia are rarely produced, most cultures are sterile or produce only occasional thick-walled terminal or intercalary chlamydospores. 3. Macroconidia may resemble those of M. canis but are usually longer, smoother and more irregularly fusiform in shape. 4. Microconidia, when present, are pyriform to clavate in shape and are similar to those seen in other species of Microsporum, Lophophyton and Nannizzia. |
| Confirmatory Tests: | 1. On Rice Grains, it shows Very poor or absent, usually being visible only as a brown discoloration. 2. Form Salmon to pinkish-brown (M. canis is bright yellow) on Reverse Pigment on Potato Dextrose Agar. 3. On Vitamin Free Agar (Trichophyton Agar No.1) it shows Good growth indicating no requirements of special nutrient, with the formation of flat, white, suede-like to downy, with a yellow to pale yellow-brown reverse. 4. Show Negative results within 28 days in Hair Perforation Test. 5. only M. audouinii shows a rapid pH change to alkaline (purple colour) on BCP Milk Solids Glucose Agar. |
| Diagnosis: | 1. Direct microscopy with 10% KOH 2. Performing a wet mount would show ‘racquet shaped hyphae’ |
| Treatment: | griseofulvin, and other drugs, itraconazole, fluconazole, and terbinafine can be used. |
Microsporum ferrugineum
| Description: | 1. Microsporum ferrugineum is an anthropophilic fungus 2. colonizes keratinized tissues (primarily hair) causing infection. 3. They can grow in neutral pH, range from 6.8-7.0 and room temperature. 4. growth is strongest in the hexoses. 5. growth is weakest in maltose, sucrose, lactose and galactose. |
| Habitat: | Microsporum audouinii often found in soil that is rich in keratinous material. |
| Infection: | causing epidemic juvenile tinea capitis in humans. |
| Morphology: | 1. Two colony types may be observed. The first type is glabrous, heaped, wrinkled and often has furrows and folds. color is yellow to rust from the front and a dull orange pigmentation is observed from the reverse. 2. The second type is flat, spreading and leathery to downy. The color is white. 3. microconidia or macroconidia are not produced. 4. colony diameter of 0.5-1 cm on Sabouraud dextrose agar incubated at 25°C for 7 days. 5. Long, straight, thick-walled, hypersegmented hyphae are often present. |
| Confirmatory Tests: | 1. In vitro hair perforation test is negative. 2. Urease activity is positive. 3. produces pale yellow colonies on Lowenstein-Jensen medium. |
| Diagnosis: | 1. Direct microscopy with 10% KOH 2. Performing a wet mount would show ‘racquet shaped hyphae’ |
| Treatment: | Use antifungal drugs |
Microsporum fulvum
| Description: | 1. It’s a wildly-distributed dermatophyte species in the Fungi Kingdom. 2. It is recognized as an opportunistic fungal pathogen 3. M. fulvum is referred to as part of the Microsporum gypseum complex. 4. Microsporum fulvum is classified as a teleomorphic species as it sexually reproduces. |
| Habitat: | Microsporum fulvum common within soil environments and grows well on keratinized material, such as hair, nails and dead skin. |
| Infection: | M. fulvum has been reported in cases of dermatophytosis, cutaneous mycoses on any keratinized tissue (dead skin). |
| Morphology: | 1.The fungus propagates sexually reproductive asci that are 5-7 microns large with up to 8 spores, which are densely packed with ascospores. 2. macroconidia are also formed and appear in large clusters (up to 8 microns in diameter) with hyphae branches. macroconidia are fusoid-shaped with tapered ends and have very thin walls. 3. Microconidia are drop-shaped and are observed with sparse, irregular hyphae. |
| Diagnosis: | 1. baiting can be used to attract Microsporum fulvum to specific soil samples. 2. Performing a wet mount would show ‘racquet shaped hyphae’ |
| Treatment: | 1. proper hygienic practices assist with prevention of infection. 2. Anti-fungal (terbinafine) drugs may be prescribed. |
Reference
- https://mycology.adelaide.edu.au/descriptions/dermatophytes/microsporum/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536909/
- https://www.msdsonline.com/resources/sds-resources/free-safety-data-sheet-index/epidermophyton-floccosum/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsporum
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsporum_fulvum
- https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1413-86702014000200181
- https://www.bode-science-center.com/center/relevant-pathogens-from-a-z/microsporum-spp.html
- https://drfungus.org/knowledge-base/microsporum-canis/
- https://www.viroxanimalhealth.com/hubfs/VAH_Resources_/PDFs/Factsheet_MicrosporumCanis_April2016.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsporum_canis#Diagnosis
- https://microbenotes.com/microsporum-spp/