What is Global Warming?
- Global warming refers to the gradual increase in the Earth’s surface temperature, a phenomenon that has been observed over the last century or so. While the concept itself is debated, the scientific community has accumulated substantial data confirming that the average temperature of the Earth is rising. This warming is not just a natural fluctuation but is significantly influenced by both human activities and natural processes.
- The primary driver of global warming is the greenhouse effect, a process where certain gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), absorb heat radiated from the Earth’s surface, preventing it from escaping into space. As the concentration of these gases has increased due to human activities, particularly since the Industrial Revolution, the Earth’s climate has been steadily warming.
- Human-induced factors are a major contributor to this rise in temperature. The burning of fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial activities have dramatically increased the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These activities not only release CO2 but also contribute to the release of other pollutants that exacerbate the warming process. The effects of these activities are clearly reflected in temperature records, which show that since 1850, the global temperature has increased by approximately 1°C, with the most substantial warming occurring after the mid-20th century.
- Recent data from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) underscores the importance of this issue. The rate of warming has accelerated, with five of the hottest years on record occurring since 2015. This dramatic shift in temperature patterns can have serious consequences, not only for the climate but also for ecosystems, weather patterns, and biodiversity.
- Besides natural causes such as volcanic activity and variations in solar radiation, human actions have significantly amplified the greenhouse effect. Industrial processes, agricultural practices, and transportation are key contributors to the buildup of greenhouse gases. These factors, combined with the rapid depletion of forests that once acted as carbon sinks, create a feedback loop where the planet continues to warm at an accelerated rate.
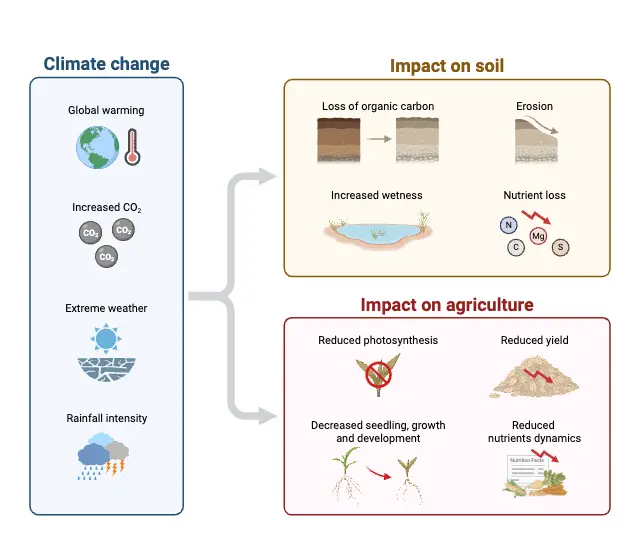
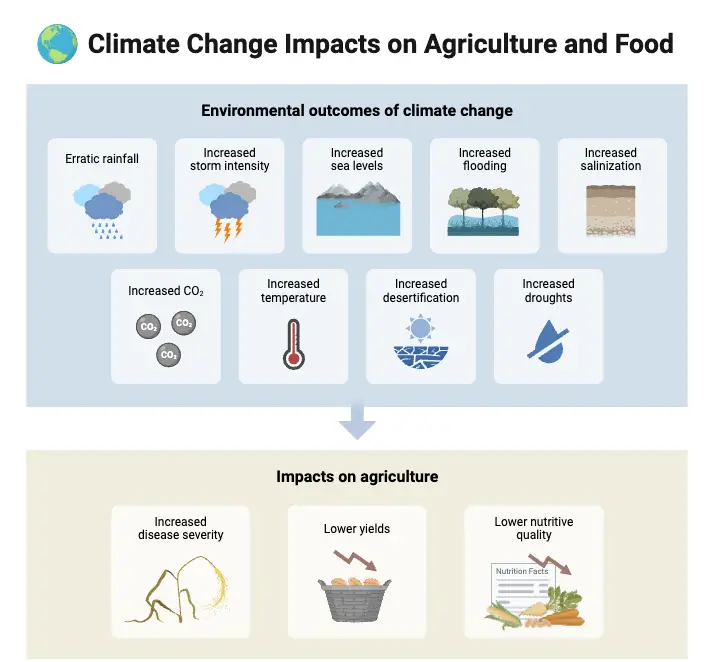
- The impacts of global warming are far-reaching. Rising temperatures contribute to the melting of ice caps and glaciers, causing sea levels to rise. This leads to coastal flooding, threatening populations in low-lying areas. Changes in weather patterns also result in more extreme events, such as heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall. These shifts affect agriculture, water supply, and ecosystems, ultimately impacting both human and animal life.
Definition of Global Warming
Global warming is the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily caused by the buildup of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane due to human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. This leads to climate changes and various environmental impacts.
Causes of Global Warming
Global warming is primarily driven by both human and natural causes. Each factor contributes to the increase in Earth’s temperature in different ways. Below is an organized look at the major contributors:
Human-Induced Causes
- Deforestation
Trees absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) and release oxygen, maintaining a balance in the atmosphere. When forests are cleared for agriculture, urban development, or logging, less CO2 is absorbed. This loss of carbon sinks leads to more CO2 in the air, contributing to global warming. - Vehicle Emissions
Vehicles, whether used for short or long distances, burn fossil fuels, releasing large amounts of CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions accumulate and trap heat, raising global temperatures. - Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Widely used in air conditioners, refrigerators, and aerosol propellants, CFCs are chemicals that contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer. The ozone layer acts as a shield against harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. As the ozone thins, more UV radiation reaches Earth, raising temperatures and exacerbating global warming. - Industrial Development
The rise of industrialization has led to increased emissions from factories and power plants. These industries release greenhouse gases such as CO2, methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to warming. - Agricultural Practices
Farming activities, such as livestock farming and rice paddies, release significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, agricultural land-use changes can release stored carbon from the soil, adding to the greenhouse gas burden. - Overpopulation
A growing global population leads to more human activity. More people means more energy consumption, more vehicles, and more emissions. The increased CO2 from human respiration, along with the higher demand for resources, amplifies global warming.
Natural Causes
- Volcanic Activity
Volcanoes can significantly impact the climate. The ash and gases released during eruptions, particularly CO2 and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can linger in the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing temporary or even long-term increases in global temperatures. - Water Vapor
Water vapor is a naturally occurring greenhouse gas. However, as temperatures rise, more water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and rivers. The additional moisture in the atmosphere can trap more heat, further accelerating the warming process. - Melting Permafrost
Permafrost is frozen soil found in cold regions, which contains greenhouse gases like methane and CO2 that have been trapped for centuries. As global temperatures rise, permafrost thaws, releasing these gases into the atmosphere and contributing to the ongoing increase in global temperatures. - Forest Fires
Forest fires, whether natural or human-caused, release large amounts of CO2 and particulate matter into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to the greenhouse effect, intensifying global warming.
Each of these causes, whether human-induced or natural, plays a role in the gradual warming of the planet. While natural factors like volcanic eruptions and water vapor have always been part of Earth’s climate system, the overwhelming impact of human activities since the industrial revolution has accelerated global warming at an unprecedented rate.
Effects of Global Warming
Global warming is significantly altering the planet’s climate, leading to a series of environmental and health issues. The rise in temperature is just the beginning of a wide-ranging impact, from melting glaciers to disrupted ecosystems and natural habitats.

- Rising Temperatures
- Earth’s temperature has been steadily climbing since 1880, with a rise of about 1°C.
- This shift is a primary driver behind the melting of glaciers and the subsequent rise in sea levels.
- Coastal regions are especially vulnerable to flooding and erosion as a result of this rise in sea levels.
- Threats to Ecosystems
- Coral reefs are under increasing stress due to higher global temperatures.
- Warmer waters harm coral reefs, which are already fragile and vital to marine biodiversity.
- The health of these ecosystems is crucial, as they support countless species of plants and animals.
- Climate Imbalance
- Global warming is contributing to unpredictable and extreme weather patterns across the globe.
- Some regions face prolonged droughts, while others experience frequent floods.
- This disruption in typical weather patterns leads to imbalances that affect agriculture, infrastructure, and daily life.
- Spread of Diseases
- Higher temperatures and shifting humidity levels are altering the habitats of disease-carrying mosquitoes.
- These changes are causing the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue to new regions, threatening public health.
- As these vectors expand their range, the global burden of infectious diseases grows.
- Increase in Mortality Rates
- Natural disasters such as floods, tsunamis, and heatwaves are becoming more frequent and severe due to global warming.
- These events often lead to higher death tolls, particularly in vulnerable populations.
- Additionally, the spread of diseases following such calamities adds to the strain on healthcare systems.
- Loss of Natural Habitats
- As the climate changes, many plants and animals are losing their natural habitats.
- Some species are forced to migrate to new areas, but many are unable to adapt or find suitable environments, leading to extinction.
- The shift in habitat also affects biodiversity, disrupting food chains and ecosystems worldwide.
- https://www.studyiq.com/articles/global-warming/
- https://www.newscientist.com/question/what-is-global-warming/
- https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/weather/climate-change/effects-of-climate-change
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Effects_of_climate_change
- https://ourworldindata.org/climate-change
- https://www.livescience.com/37057-global-warming-effects.html
- https://www.weforum.org/stories/2022/06/climate-change-weather-extreme-health/
- https://www.oliverwyman.com/our-expertise/insights/2024/jan/quantifying-climate-change-impact-on-human-health.html
- https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/11/6/e046333
- https://www.sciencing.com/5-causes-global-warming-8232444/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/climate-change-heat-and-health
- https://byjus.com/biology/global-warming/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/global-warming
- https://wwf.org.au/what-we-do/climate/causes-of-global-warming/
- https://climate.nasa.gov/causes.amp