Elek test Principle
In vitro, the Elek test can be described as an test of immunoprecipitation (immunodiffusion) test that determines what specific strain of Corynebacterium Diphtheriae is toxic. An antitoxin test strip that contains diphtheria antitoxin is put on top of the Agar plate. Strains that are to be evaluated (patient’s isolate) identified as positive and negative toxigenic strains are streaked across the surface of the agar in a straight line across the plate, and at an angle with respect to the antitoxin strip.
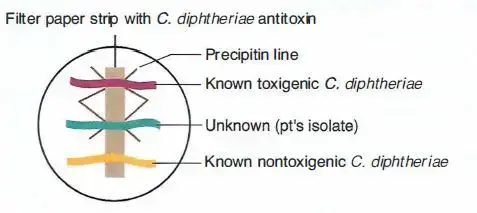
Antitoxin is released from the filter paper, while the toxin produced by strains that produce toxin are absorbed by development. In the area of equivalence, an equivalence line of precipitin is created.
Procedure of Elek test
- Mix one tube of melt nutrient agar to 2 ml of horse serum.
- Turn the tube around to mix the agar and serum. Don’t shake it.
- Put the mixture in an unsterilized dish.
- With forceps that have been lightly heated place the strip of anti-toxin impregnated filter papers in the middle of the dish, allowing it to sink under the surface of the agar.
- Let the agar set after which you can lift an edge of the lid. allow the plate to dry for about 30 minutes inside the incubator.
- If dry, inoculate using a strain that is toxinogenous C. diphtheriae. This is done by streaking one line of inoculum over the paper strip and plate in a straight line with the paper strip.
- Repeat this process for approximately 1 inch from C. diphtheriae spores with an inoculum test strain.
- The plate should be incubated for 24 hours, and then check the outcomes.
Result of Elek test
After 24 hours of incubation at 37°C, plate is examined with transmitted light for the presence of Incubation for 24hrs at 37degC The plate is then assessed using transmitted light for evidence of lines of fine precipitin that are at a 45 degrees angle towards the lines.
Positive Test: Precipitin lines form at zone of equivalence, test organism is toxigenic.
If toxin is generated by the strain that is tested it diffuses to the side of the streak. The antitoxin is released through the filter paper. at the point where the toxin and antitoxin come together (at the point of similarity) the precipitin line is formed.
The control strain can create a precipitate that will then coalesce with the precipitate from the test strain, forming an identity line
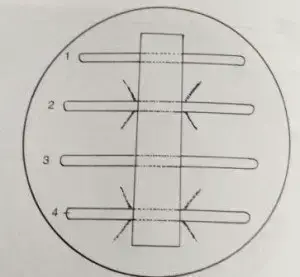
Check out this image Try to figure out the meaning yourself prior to reading the following explanation:
- Line 1 is a negative control
- Line 2 is the positive control
- Line 3 is a test organism that is a nontoxigenic strain C. diphtheriae
- Line 4 is a test organism that is a toxigenic strain of C. diphtheriae