What is Double Beam Balance?
- In labs, a double beam balance is a mechanical device used for very accurate mass measurement with simplicity of use.
- Its two parallel beams allow the unknown mass to be balanced against calibrated sliding weights by use of a pan connected to either end.
- The instrument works on the concept of equilibrium; when the weights on one pan balance the object on the other, the system gets a zero reading suggesting the mass of the object.
- Its design usually follows the Roberval balance principle, therefore assuring that the beam stays level and precise even if weights are not exactly positioned at the center.
- Popular in educational environments and quality control labs, double beam balances are prized for their simplicity and longevity.
- In comparative weighing, when the emphasis is on mass differences between two things rather than an absolute value, they shine.
- Though they offer exact measurements, the smallest weight increase on the sliding weights limits the degree of precision.
- Their mechanical character removes the requirement for electrical power, therefore strengthening basic ideas of physics including leverage and equilibrium for students and scientists.
Double Beam Balance Principle
- Operating on the law of moments, a twin beam balance guarantees the system finds equilibrium by counteracting the torque generated by the unknown mass with that of measured weights.
- It has two horizontal beams pivoted at a central fulcrum with a pan connected to either end to allow any mass differential to produce a detectable spinning effect.
- The idea is based on classical physics; balance results when the moments on both sides equal each other; the moment (or torque) is the product of a mass and its distance from the pivot.
- One pan holds the thing to be weighed; adjustable sliding weights are added to the opposing pan until the beam is exactly horizontal, therefore signaling that the total weight of the sliding masses equal that of the object.
- This comparison approach reduces direct reliance on local gravitational fluctuations as both sides of the balance are equally impacted, therefore producing great measurement precision.
- Especially helpful in exact laboratory measurements, the sliding weights—marked on a graduated scale—allow precision adjustments and help to detect even tiny mass variations.
- Applying basic ideas of lever mechanics and equilibrium, the twin beam balance acts as a teaching tool showing fundamental physics ideas and offering consistent mass determination.
Purpose of Double Beam Balance
- Comparative weighing makes most use of the twin beam balance, which allows exact mass difference between two things to be found.
- In labs, it is extensively used for very accurate measurement of tiny amounts of powders, chemicals, and compounds for scientific research.
- In learning environments, it is a useful tool for illustrating the ideas of lever mechanics and equilibrium, therefore supporting fundamental physics ideas.
- Furthermore crucial in quality control procedures across many sectors is the device, which guarantees constant and accurate mass measurements in production and research.
- Its mechanical construction, free of reliance on electrical power, making it a consistent choice in settings with erratic or absent power sources.
- Furthermore fit for regular usage in laboratory and field applications is its strong structure and simplicity of maintenance.
Parts of double beam balance
A double beam balance is a mechanical mass measuring equipment with many important components:
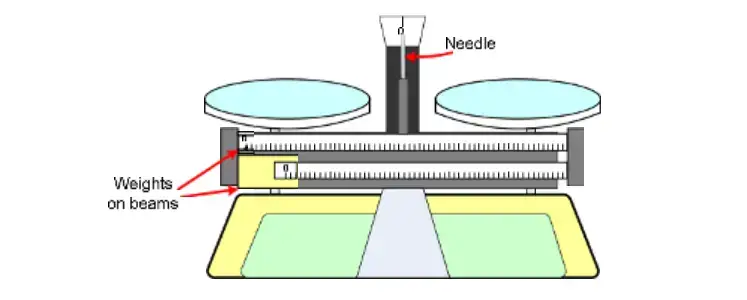
- Pans: Two stainless steel platforms on either side of the balance where items and counterweights are put.
- Beams: Two horizontal beams with sliding weights (poises) for delicate balancing changes.
- Fulcrum: The fulcrum supports the beams and allows them to move freely, allowing the balance to estimate mass by comparing pan weights.
- Pointer: A needle that indicates beam equilibrium, usually zero when the masses on both pans are equal.
- Base: A robust cast alloy foundation that supports the construction and assures stability during measurements.
- Zero Adjustment Knob: A spring-loaded zero adjustment used to calibrate the balance before use for precise measurements.
- Magnetic dampening System: Some versions use magnetic dampening to decrease vibrations and steady the pointer for faster, more accurate readings.
Operating Procedure of double beam balance
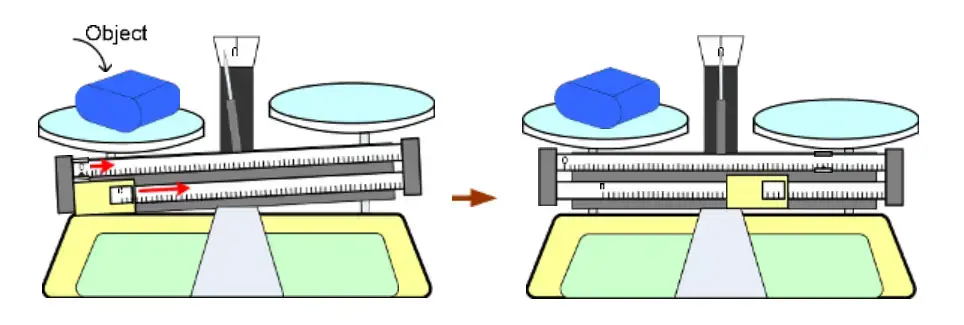
- Starting with an empty balance, check that the pointer sits at zero to guarantee the instrument is free from residual weights and correctly calibrated.
- Set the thing to be weighed on one pan—usually the left—then make sure it is centered to prevent unequal weight distribution.
- Add the adjustable sliding weights gradually to the other pan until the indication needle comes back to zero, therefore indicating equal torques on both sides.
- Many twin beam balances include separate scales for various increment ranges, so use the smaller weight for precise tuning and the larger sliding weight for coarse adjustments.
- Let a moment follow every change for the beam to settle; mechanical dampening may cause the pointer to need time to steady.
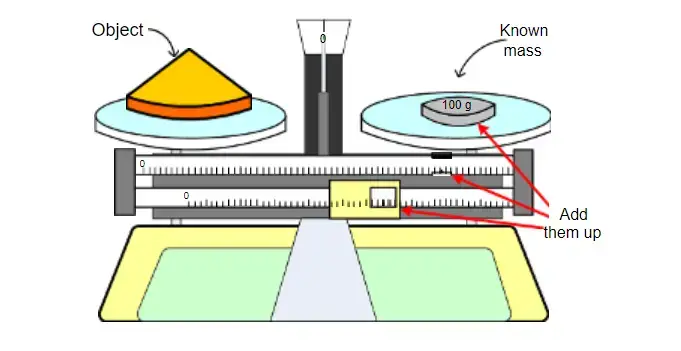
- Read the figures indicated on the sliding weights once balance is attained to find the object’s overall mass.
- Add extra known masses and compute the total weight for things more than the capacity of the conventional weights.
- Throughout the process, keep the surroundings clear of drafts and vibrations to avoid outside disturbances influencing the measurement accuracy.
Advantages
- Operating without electrical power, the twin beam balance is a simply mechanical device that guarantees dependable performance even in places with erratic power sources.
- It is perfect for exact laboratory tests and comparison weighing as its basic design based on equilibrium ideas produces rather consistent measurements.
- The precision calibration made possible by the changeable sliding weights helps to detect minute mass variations necessary for jobs like relative weight of molecules.
- Offering long-term cost effectiveness in both industrial and educational environments, the double beam balance is sturdy and low-maintenance thanks to a strong structure and few moving components.
- By showing fundamental physics ideas like lever mechanics and torque, it is a great teaching tool that strengthens theoretical knowledge by means of real-world example.
- Its accuracy in comparison weighing guarantees constant and precise mass readings free from external influence in quality control and research applications.
Limitation
- The balance’s resolution is limited by its sliding mechanism’s lowest weight, therefore small mass discrepancies may go unnoticed.
- It is less accurate for sub-gram or microgram readings since it is designed for comparison weighing.
- In contexts with untrained users, operator error in reading or changing sliding weights can cause errors.
- The gadget is sensitive to air currents, vibrations, and uneven surfaces, which can upset equilibrium and cause inaccurate results.
- Regular maintenance is needed to maintain precision due to mechanical wear, especially at the pivot and knife-edge fulcrum.
Usage of Double beam balance
- Labs use it to measure powders, liquids, and chemicals by comparing unknown samples to calibrated weights.
- In quality control and regular testing, it is used for comparison weighing to estimate item masses.
- It teaches balance, torque, and lever mechanics through hands-on demonstrations.
- It checks measurement consistency and ensures reliable and accurate findings in experiments.
- It may calibrate other instruments by giving an accurate mass measurement reference, which is vital in analytical operations.
- This mechanical device works without electricity, making it perfect for fieldwork and unpredictable power supply.
- It helps with accurate mixture composition, where even slight mass changes might effect results.
Difference Between a Triple Beam Balance & Double Beam Balance
| Feature | Triple Beam Balance | Double Beam Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Features a single pan and three beams with sliding weights that measure in specific increments (e.g., 100g, 10g, and 1g), allowing fine adjustments. | Consists of two pans on either side of a central fulcrum, functioning like a seesaw, where the mass of an object is determined by balancing it against a known mass. |
| Measurement Method | Uses sliding weights along three beams to achieve balance, with mass determined by summing the values indicated on each beam. | Involves placing the object to be weighed on one pan and adding known masses to the other until equilibrium is reached, comparing the unknown mass to known standards. |
| Precision | Offers high accuracy, often measuring to the nearest 0.1 gram, making it suitable for laboratory use. | Provides reliable but less precise measurements, as accuracy depends on the availability and calibration of known masses. |
| Usage | Commonly used in schools and laboratories for precise measurements in physics and chemistry experiments. | Used in quality control and comparative weighing situations where the exact mass is not as critical. |
| Advantages | Allows for fine adjustments and precise measurements without additional weights; durable and easy to use once calibrated. | Simple design with no need for sliding weight calibration; useful for comparative measurements and can accommodate larger objects. |
Video Guide for Double beam balance
Reference
- https://www.cannondigi.com/parts-and-function-of-double-beam-balance/
- https://www.sciencing.com/difference-balance-double-beam-balance-8512350/
- https://www.labnics.com/beam-balance/nddb-100
- https://www.uniconinstruments.com/balances.htm
- https://www.shivsons.com/product/double-beam-balance/
- https://www.labotronics.com/double-beam-balance
- https://www.labotronics.com/catalog/double-beam-balance/lb-10dbb
- https://www.labmate.com/double-beam-balance
- https://hirophysics.com/Labsheet/balance/balance.html
- https://www.labdex.com/beam-balance/lx10dbb