Difference Between Virus and Viroids
In this article we will discuss about Differences Between Viroids and Prions.
Virus
- Viruses are minuscule infectious entities that consist of nucleic acid, which may be either RNA or DNA, encased in a protein coat and occasionally enveloped by a lipid layer. They possess the unique ability to replicate solely within living host cells, commandeering the cellular machinery for their reproduction.
- Viruses demonstrate a form of obligate intracellular parasitism, devoid of metabolic machinery and organelles, which renders them inactive outside of host cells and wholly reliant on host systems for the processes of genome replication and protein synthesis.
- Viruses are categorized based on their nucleic acid type and strandedness, replication mechanisms, capsid symmetry, the presence or absence of an envelope, and host range, adhering to ICTV taxonomy, which includes realms such as Riboviria among others.
- Viruses hold significant relevance in the fields of medicine and biology, as they are responsible for a diverse array of diseases, impact ecological and evolutionary dynamics through the facilitation of horizontal gene transfer, and function as essential instruments in molecular biology research and biotechnology, including gene therapy and vaccine development.
- In ecological contexts, viruses play a crucial role in regulating microbial populations, contributing to biogeochemical cycles by recycling organic matter through mechanisms such as the viral shunt. They are the most abundant biological entities in environments like oceans, significantly influencing nutrient flows and the dynamics of ecosystems.
- The notion of viruses originated from filtration experiments conducted in the late 19th century by Dmitri Ivanovsky in 1892 and Martinus Beijerinck in 1898. They characterized a “contagium vivum fluidum” responsible for tobacco mosaic disease and determined that the infectious agent could traverse filters designed to capture bacteria.
- The advancements of electron microscopy in the 1930s, which allowed for the visualization of virions, the introduction of plaque assays in the 1950s for quantifying animal viruses, and the emergence of molecular biology techniques in the latter part of the 20th century have significantly clarified viral structure, replication strategies, and pathogenic mechanisms, thereby solidifying virology as a separate scientific discipline.
- The exploration of viruses is advancing with the identification of giant viruses, the emergence of novel viral families via metagenomics, and the rise of new pathogens. This highlights the persistent necessity for research into viral diversity, host interactions, and effective strategies for disease control and prevention.
Viroid
- Comprising only a short, circular, single-stranded RNA molecule usually 246–467 nucleotides long, viroids are the smallest known plant pathogens.
- Different from viruses, they are “naked” RNA agents lacking a protein coat (capsid).
- Their RNA folds into a highly base-paired, rod-like secondary structure with areas of paired nucleotide stems and loops, so giving stability and functional domains.
- Viroids cannot carry metabolic or replicative activities on their own and do not encode any proteins.
- Sometimes involving self-cleaving (ribozyme) activity, they replicate independently in host plant cells using the RNA polymerase II of the host by a rolling-circle mechanism.
- There two main families of viroid:
- Pospiviroidae (non-self-cleaving, nuclear-replicating)
- Avsunviroidae (self-cleaving via hammerhead ribozymes, chloroplast-replicating)
- No animal or human infections are known; they infect flowering plants, transferred mechanically, by pollen, seeds, grafting, or tools.
- first identified in 1971 by Theodor O. Diener as the potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd), so signifying a significant expansion in knowledge of infectious RNA entities.
- Their RNA sequence and structure define viroid pathogenicity, which can cause different symptoms (stunting, leaf deformation, chlorosis), affect gene expression, and set RNA silencing in host plants active.
- In crops including potatoes, tomatoes, citrus, avocado, and coconut, they cause major agricultural losses.
- Providing understanding of RNA-based life origins and molecular biology, viroids could reflect evolutionary relics from a primordial RNA world.
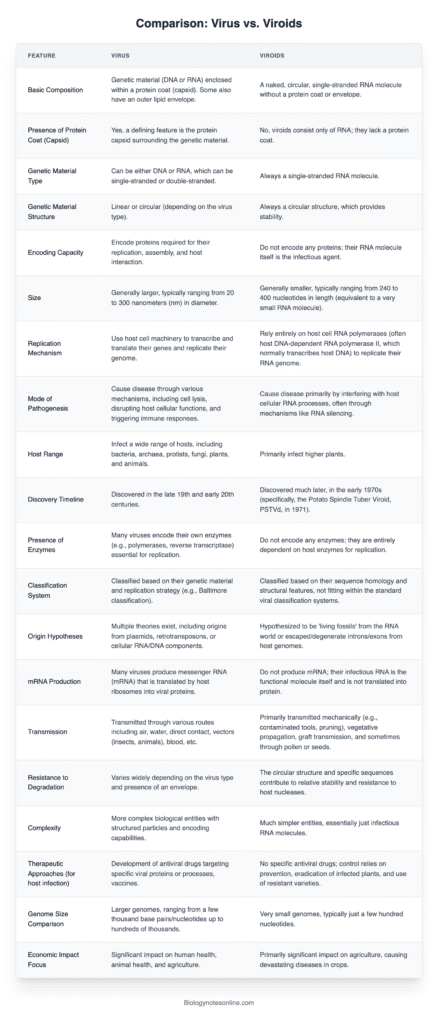
Difference Between Virus and Viroids – Virus Vs. Viroids
| Feature | Virus | Viroid |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Material | DNA or RNA, single- or double-stranded, linear or segmented | Small circular single-stranded RNA molecule |
| Capsid/Coat | Protein coat (capsid); some have additional lipid envelope acquired from host membranes | No protein coat or capsid; naked RNA |
| Size | Generally 20–300 nm (can range from ~20 nm to >400 nm); larger than viroids | Extremely small: ~246–467 nucleotides (~1–2 nm diameter RNA circle) |
| Structure | Nucleic acid enclosed in protein capsid; some enveloped with host-derived lipid bilayer; capsid symmetry often icosahedral or helical | Naked circular RNA with extensive intramolecular base-pairing forming secondary structures |
| Coding Capacity | Encode one or more proteins (capsid proteins, polymerases, regulatory proteins); may carry enzymes like reverse transcriptase | No protein-coding capacity; entirely noncoding RNA |
| Host Range | Infect animals, plants, bacteria, fungi, archaea; wide diversity of hosts | Primarily infect plants (angiosperms); one human-associated viroid-like agent (hepatitis D virus requires helper virus) |
| Replication Mechanism | Hijack host machinery; replication strategies vary by genome type (e.g., rolling circle in some DNA viruses, reverse transcription in retroviruses, RNA-dependent RNA replication for RNA viruses) | Autonomous replication via host RNA polymerase II (nuclear viroids) or RNA polymerases in chloroplasts (some); rolling-circle mechanism without protein synthesis |
| Transmission | Diverse: direct contact, aerosols, bodily fluids, vectors (arthropods), seeds (for plant viruses), vegetative propagation, fomites | Mechanical contact, vegetative propagation of plants, seed or pollen transmission in some cases; no vector proteins (spread via tools, contact) |
| Disease and Pathogenicity | Cause wide range of diseases in animals (e.g., influenza, HIV) and plants (mosaic, necrosis); pathogenicity via host-cell disruption, immune responses, oncogenesis | Cause specific plant diseases (e.g., potato spindle tuber disease, citrus exocortis); economic impact in agriculture; human disease only via hepatitis D viroid in presence of hepatitis B virus |
| Detection and Cultivation | Detected via culture in cell lines, embryonated eggs, plaque assays, molecular methods (PCR, sequencing, serology); require living host cells for propagation | Detected by molecular assays (RT-PCR, northern blotting); cannot be cultured independently as they lack protein coat and do not form particles |
| Origin and Discovery | Discovered late 19th century (Tobacco mosaic virus infectivity studies); taxonomy governed by ICTV; diverse evolutionary origins and adaptations | Discovered 1971 by Theodor Diener (potato spindle tuber viroid); classified in families Pospiviroidae and Avsunviroidae; represent simplest known infectious agents |
| Examples | Tobacco mosaic virus, influenza virus, HIV, bacteriophage T4, herpesviruses | Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd), Citrus exocortis viroid, Hop stunt viroid |
Well written