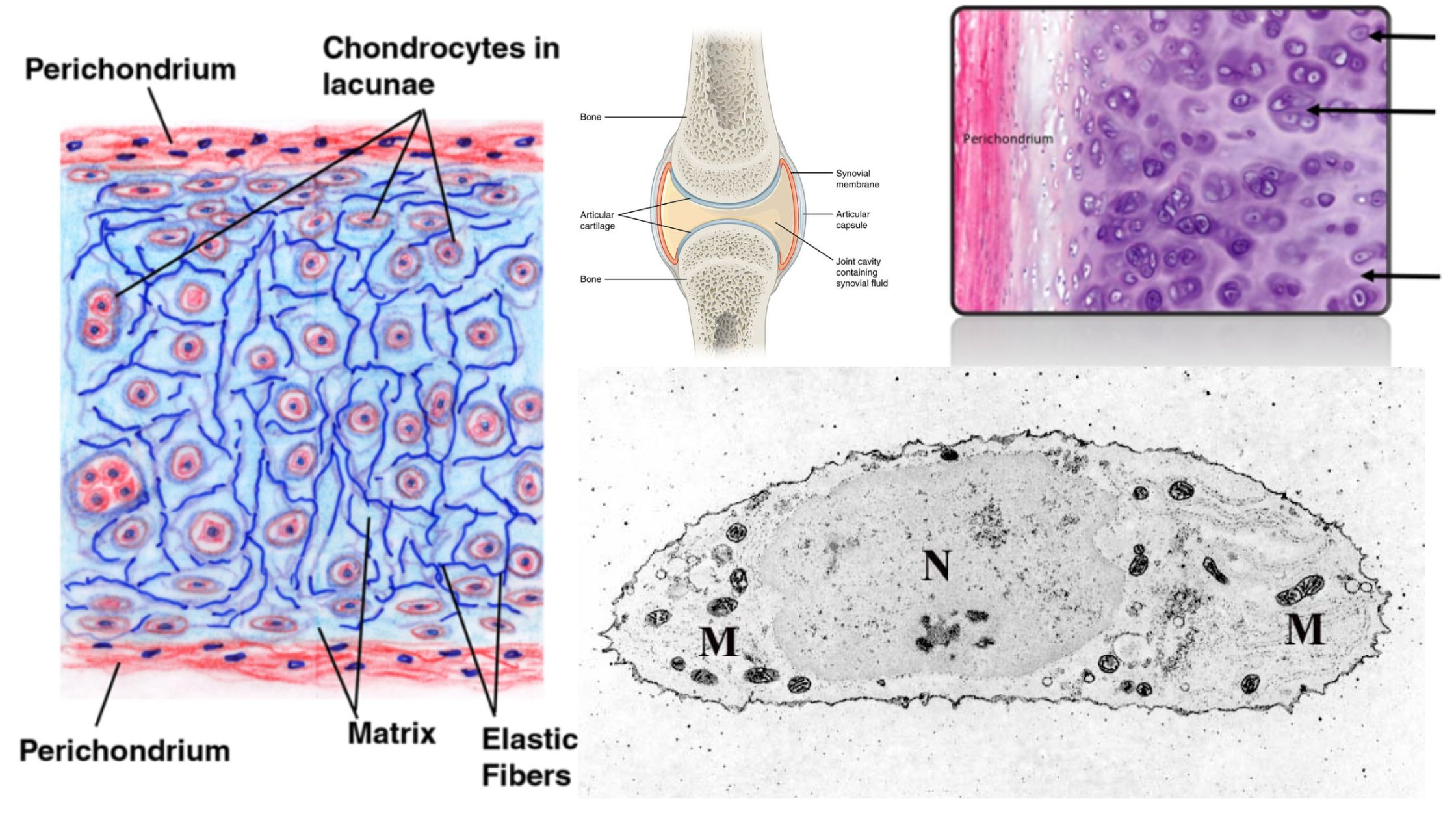
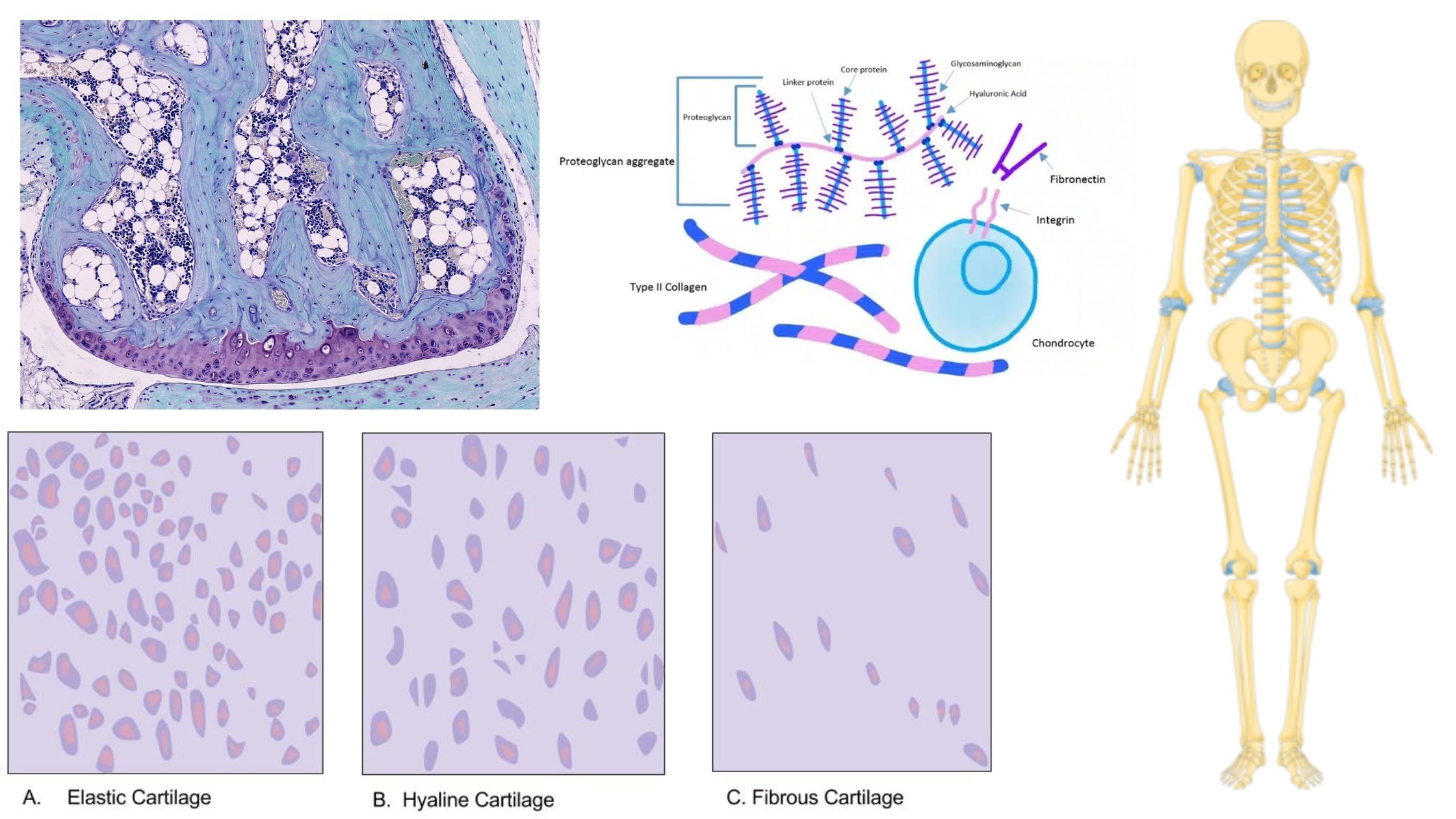
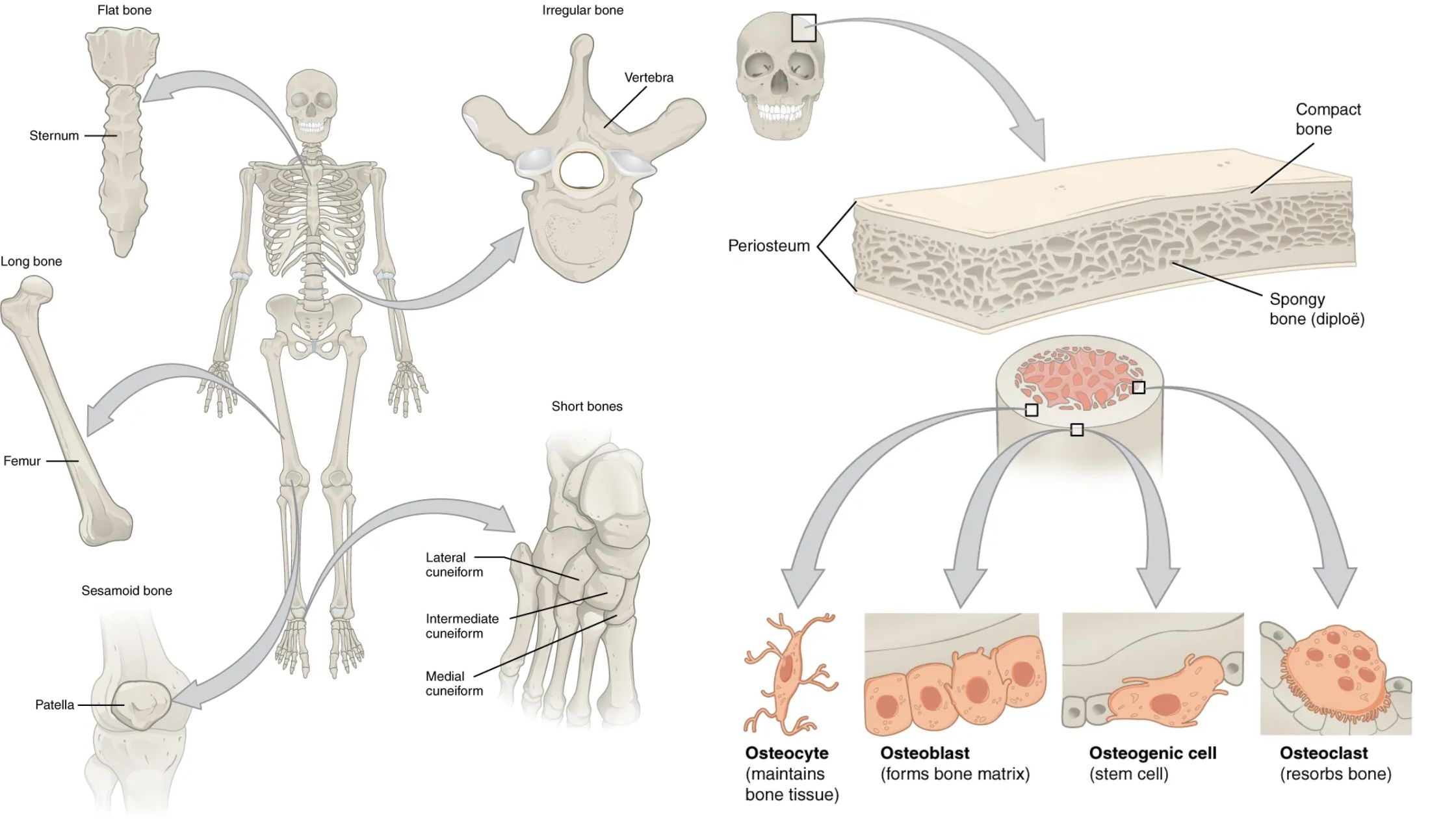
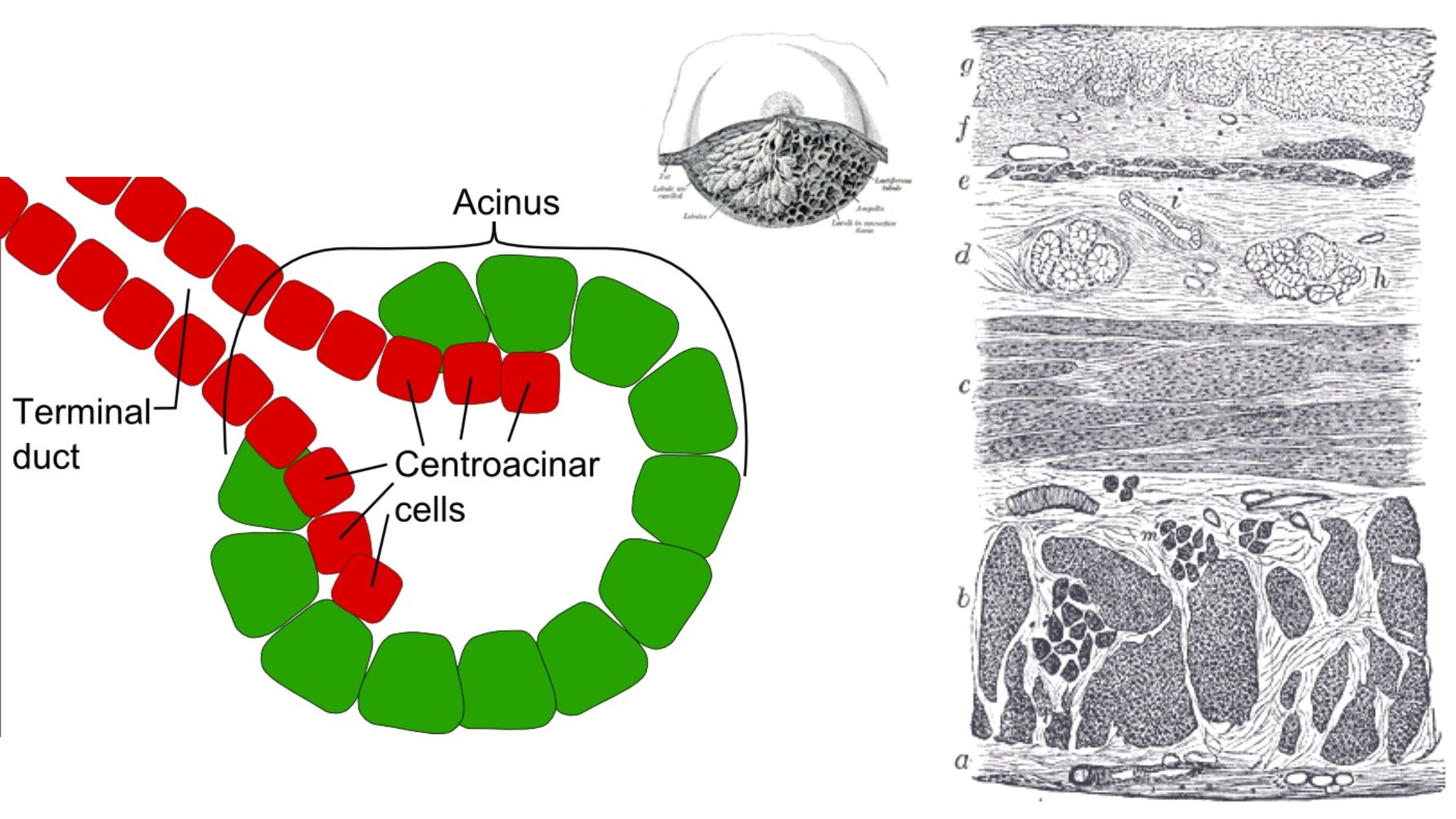
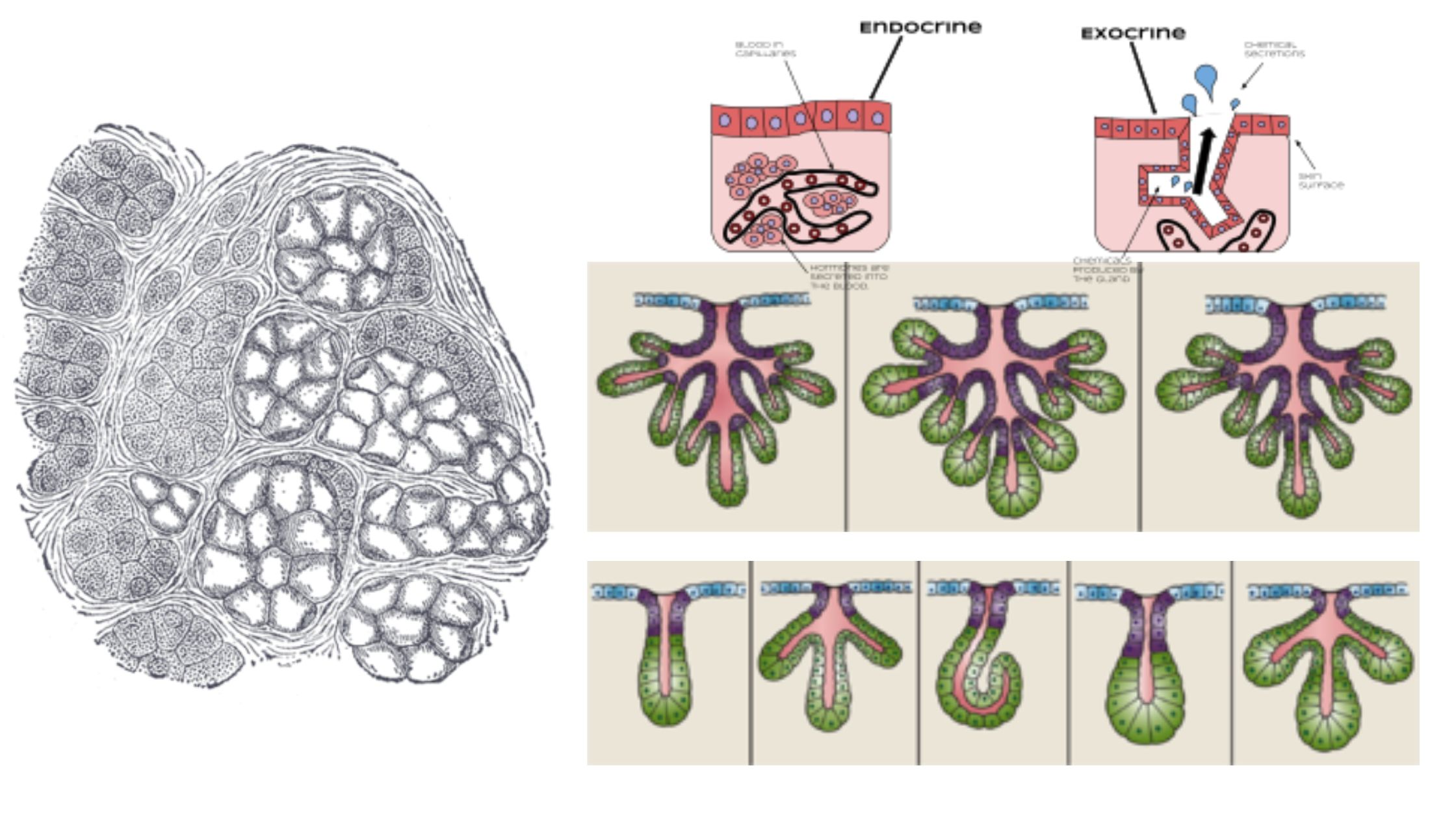
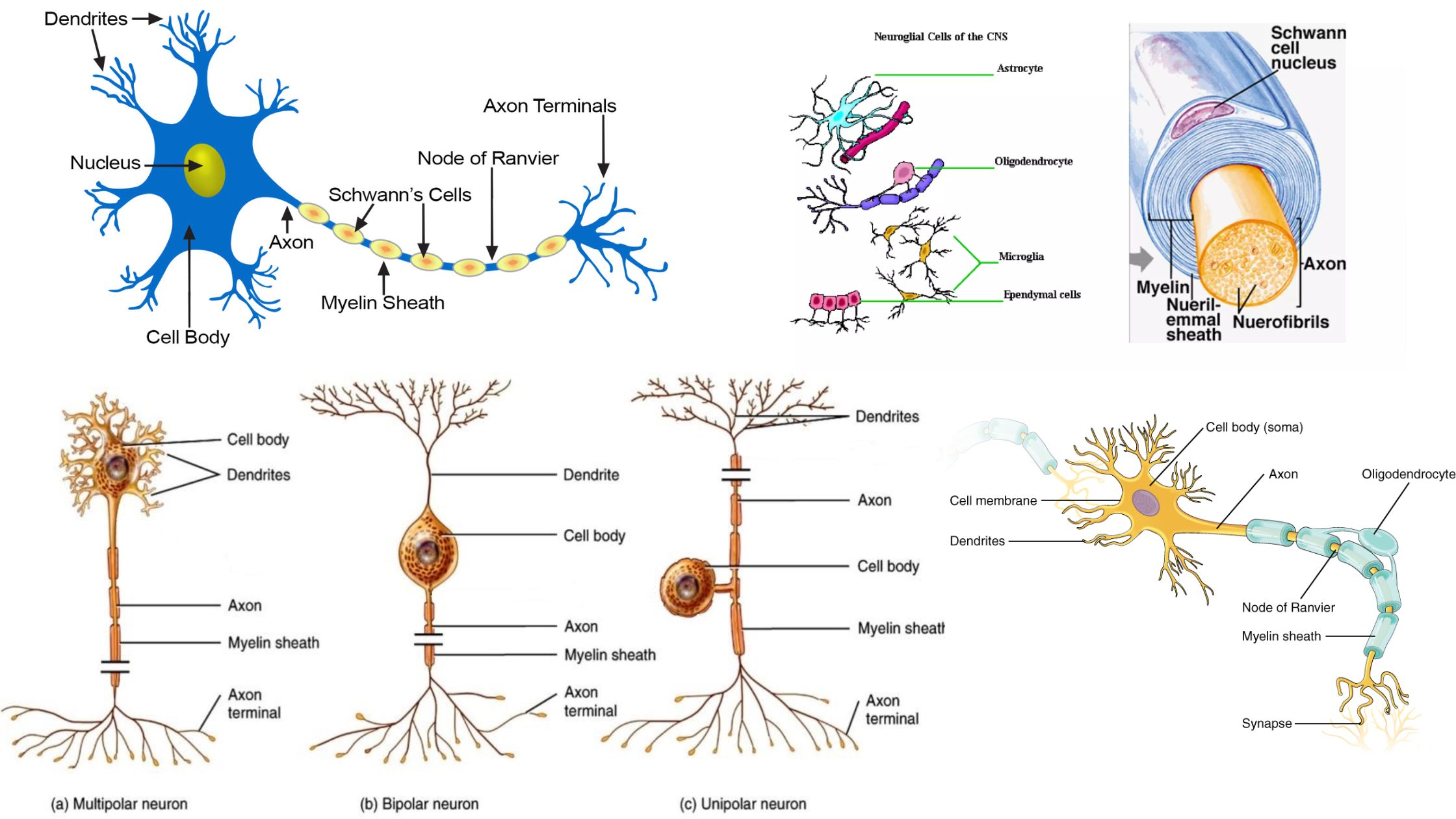
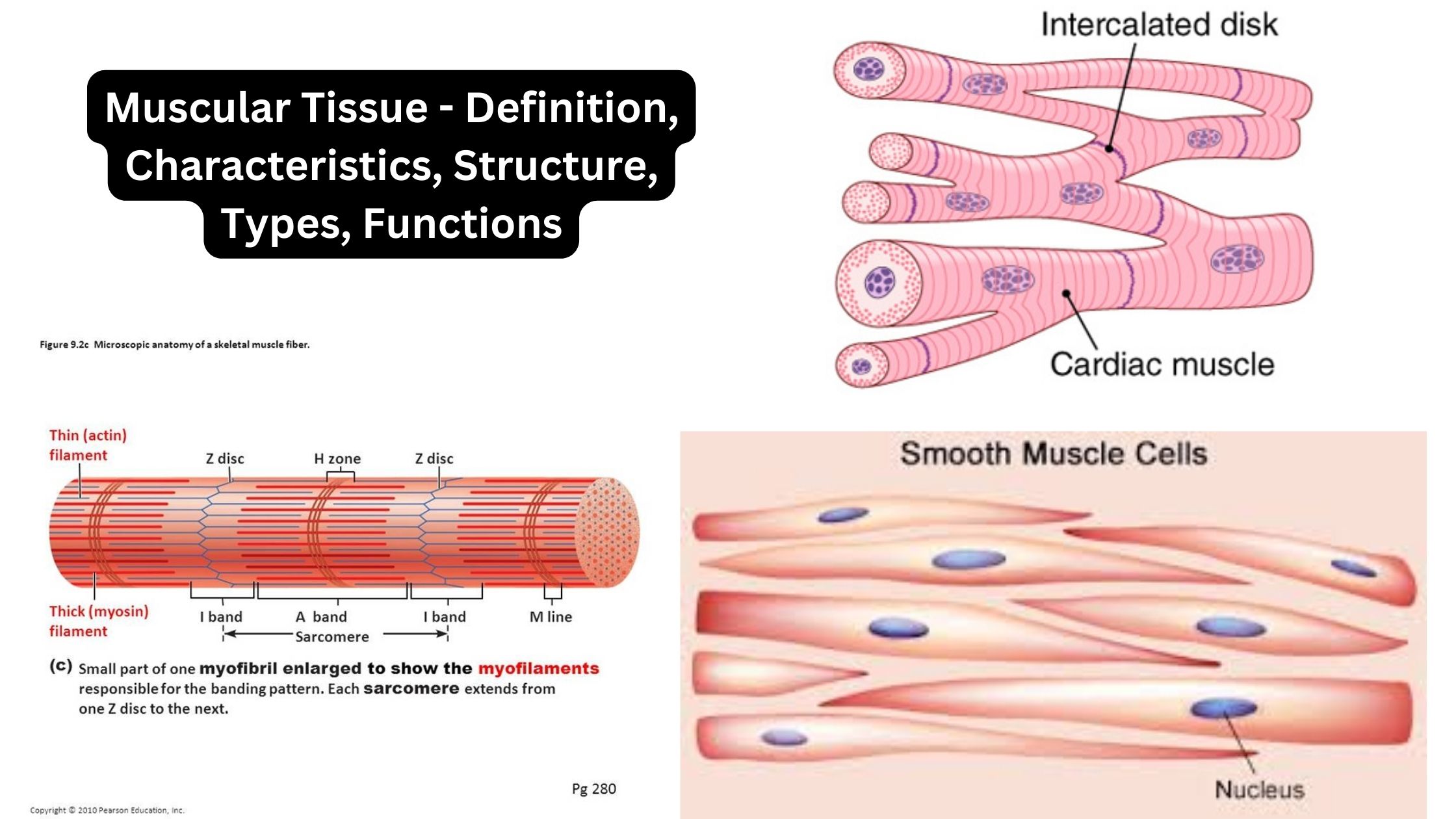
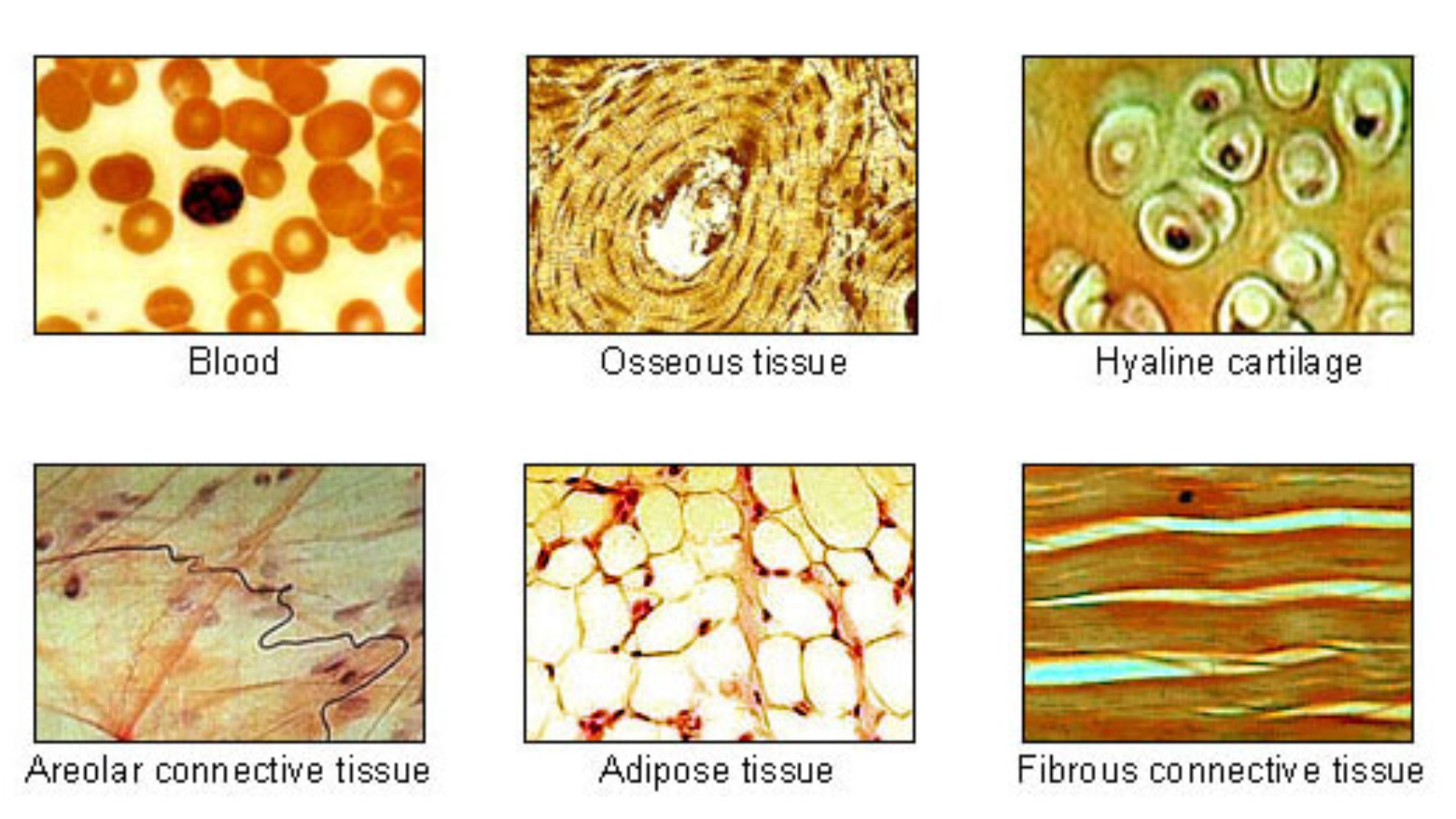
Hyaline Cartilage – Definition, Structure, Functions
What is Hyaline Cartilage? Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in various parts of the human body, characterized by its glossy and smooth appearance. Here are some key points about hyaline cartilage: Overall, hyaline cartilage serves as an important connective tissue in the body, contributing to the proper functioning and structure of … Read more