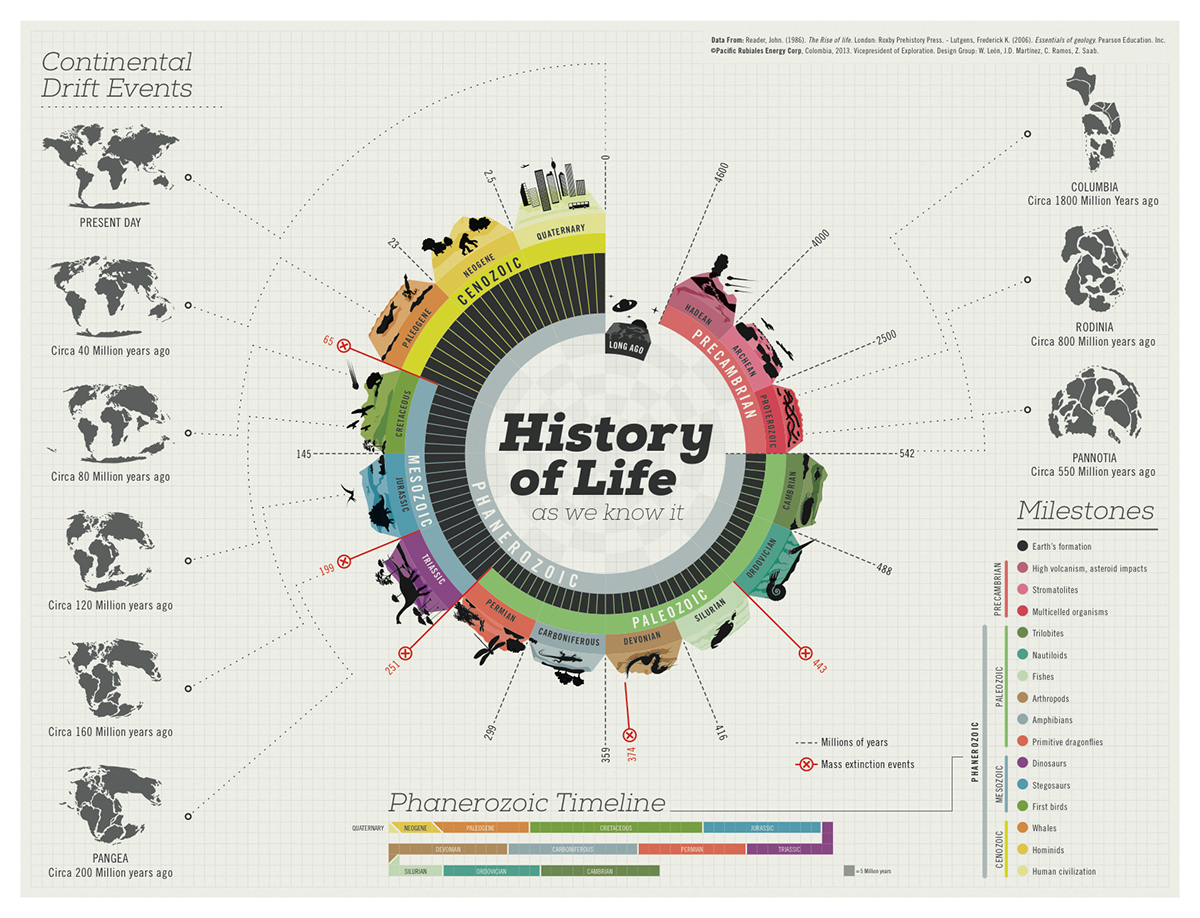
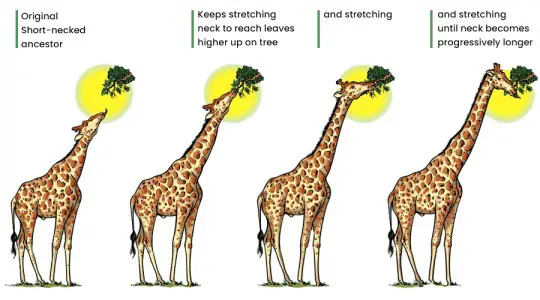
Processes of Evolutionary Change
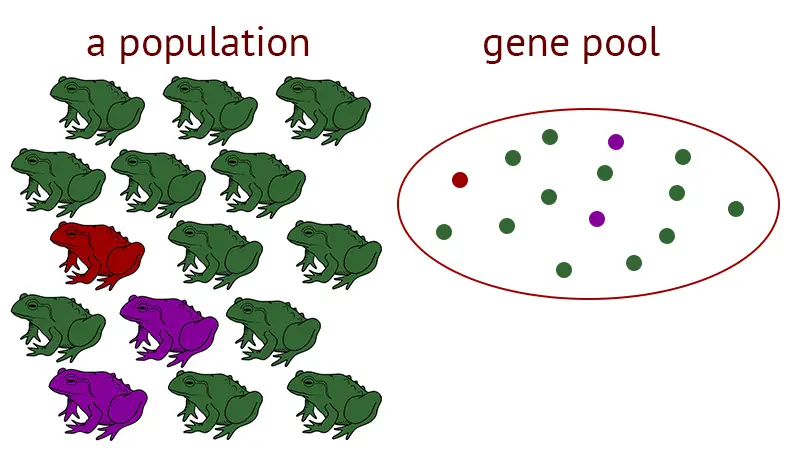
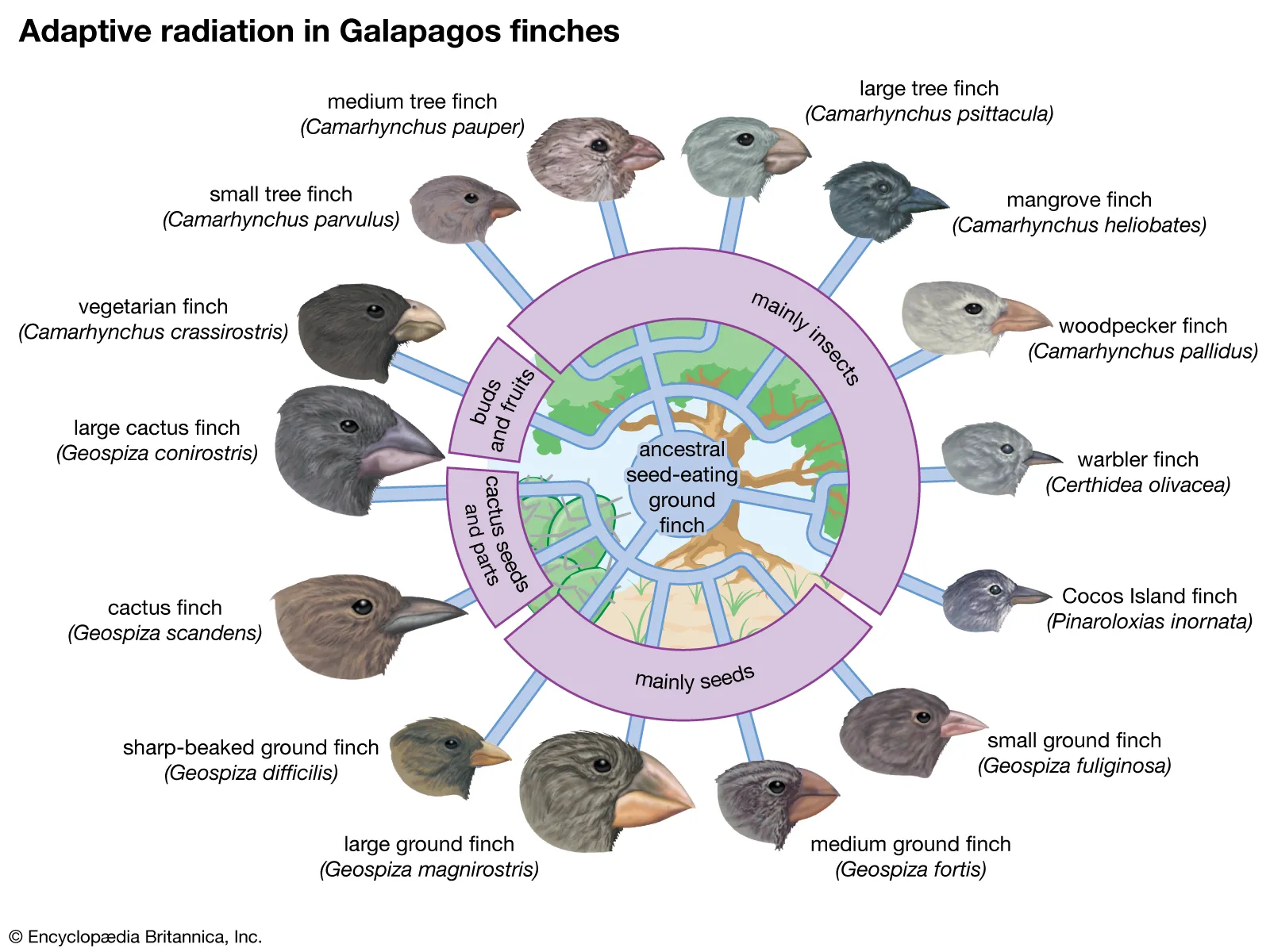
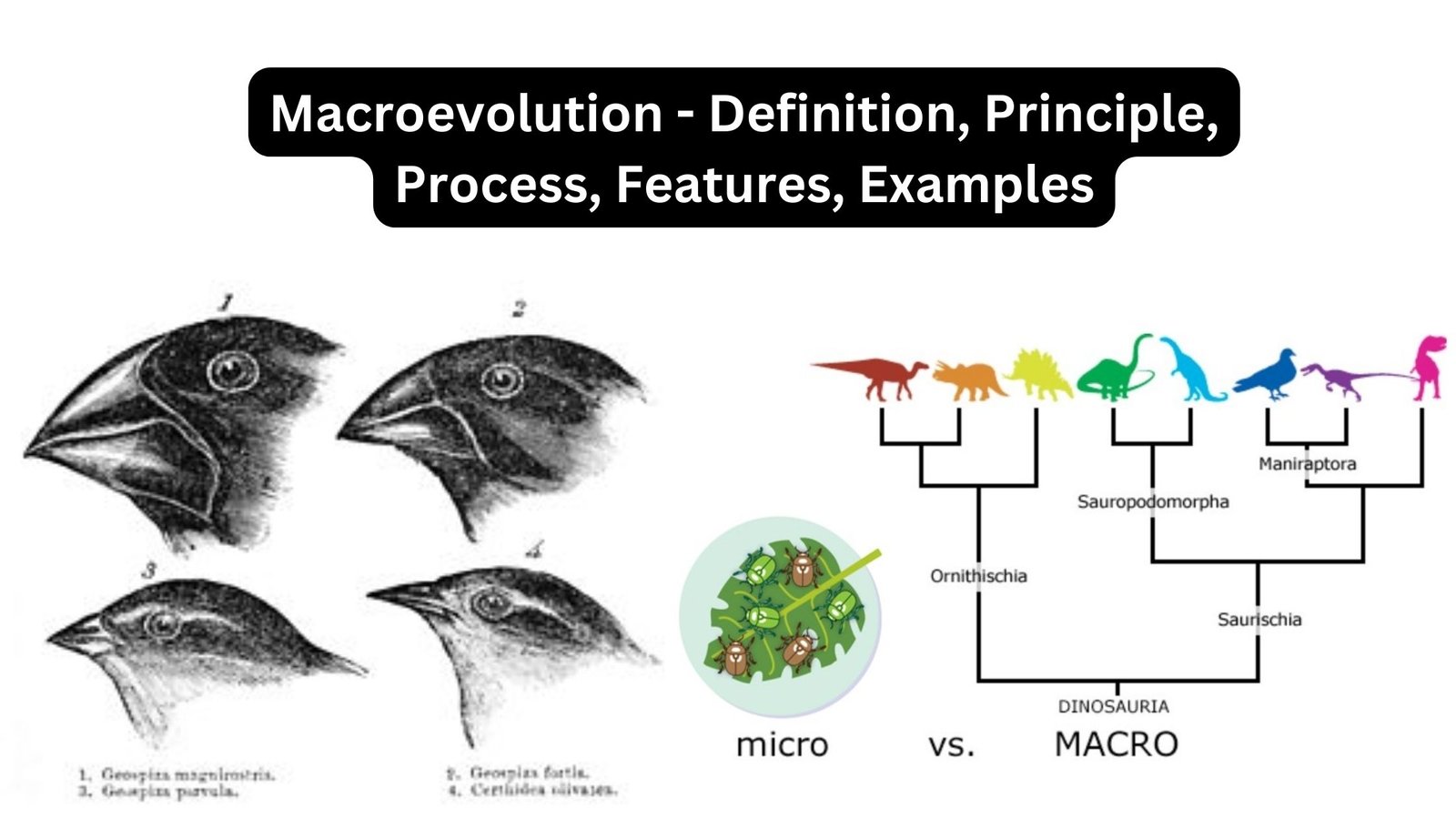
What is Evolution? Evolution refers to the process of change and development that occurs in living organisms over successive generations. It is the central concept in biology that explains the diversity of life on Earth and how species have come to exist in their present forms. Evolutionary theory explains how species evolve through the gradual … Read more