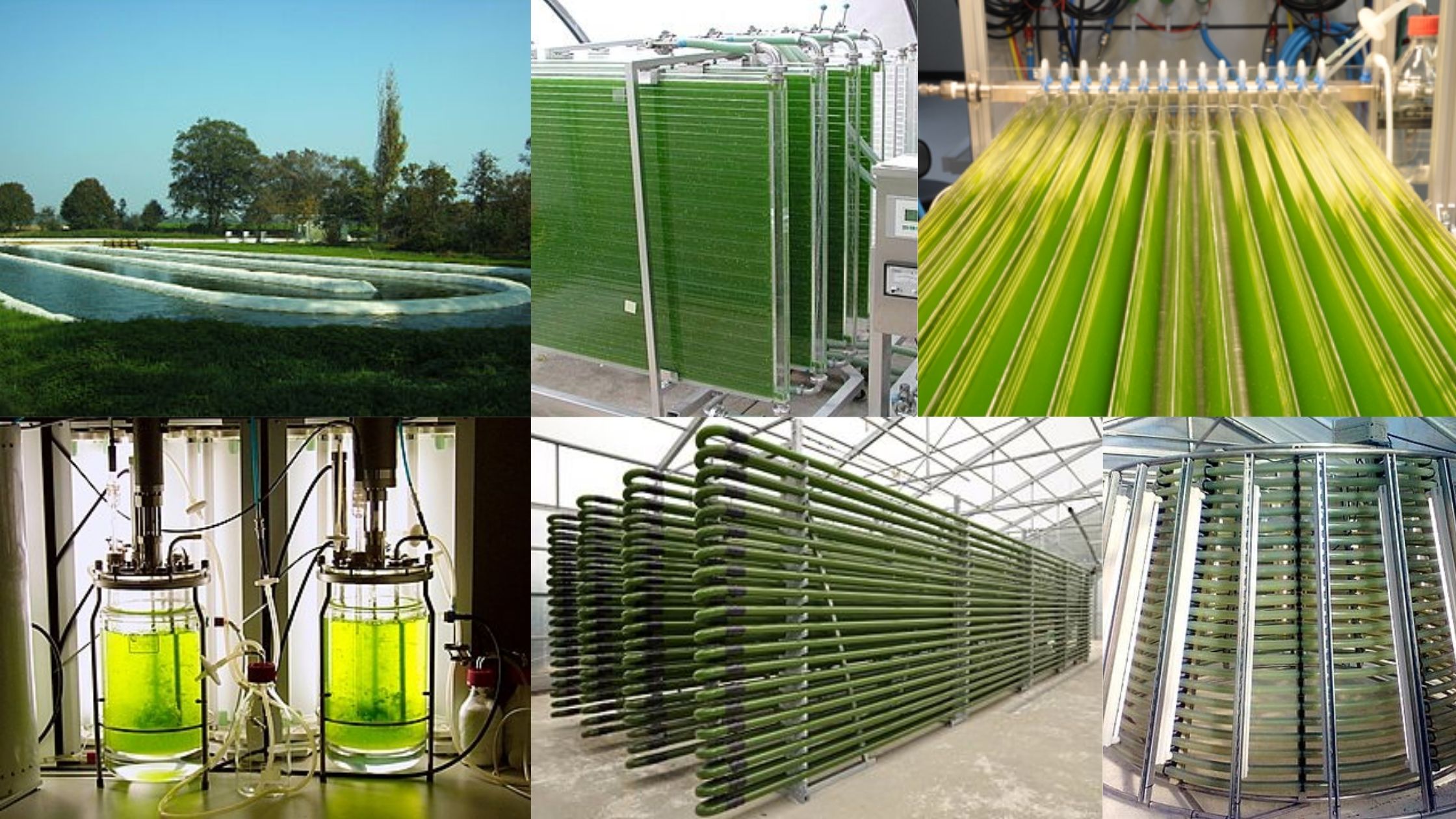
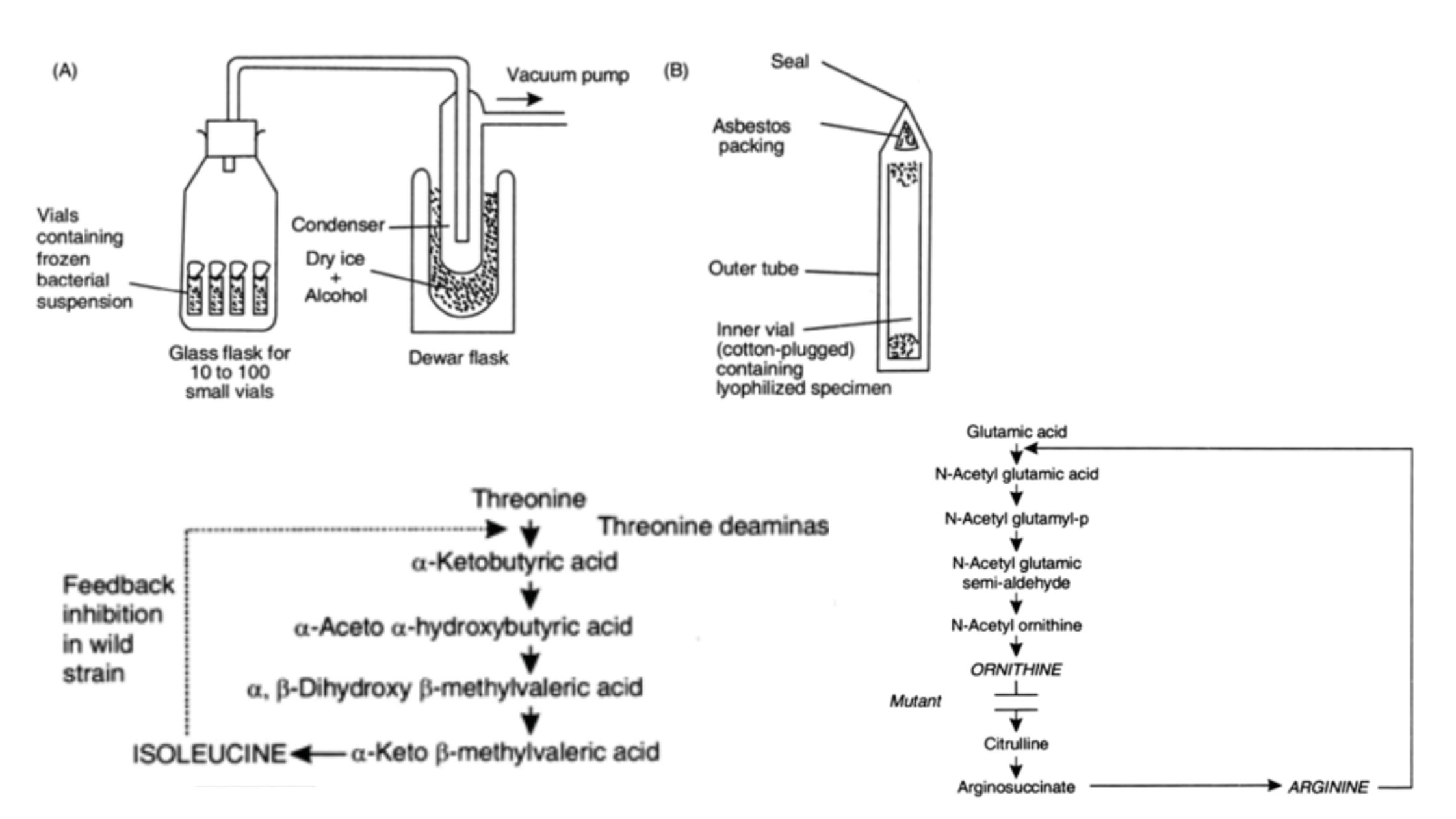
Photo bioreactor – Definition, Types, Application, Advantages
Photo bioreactor is an innovative type of reactor that has the advantages of biofilm reactors and photobioreactors that can be utilized to cultivate microalgae in wastewater treatment facilities (WWTPs). The major benefit of this type of system is its capacity to use sunlight as a source of energy for photosynthesis, which reduces the requirement for carbon from external sources.