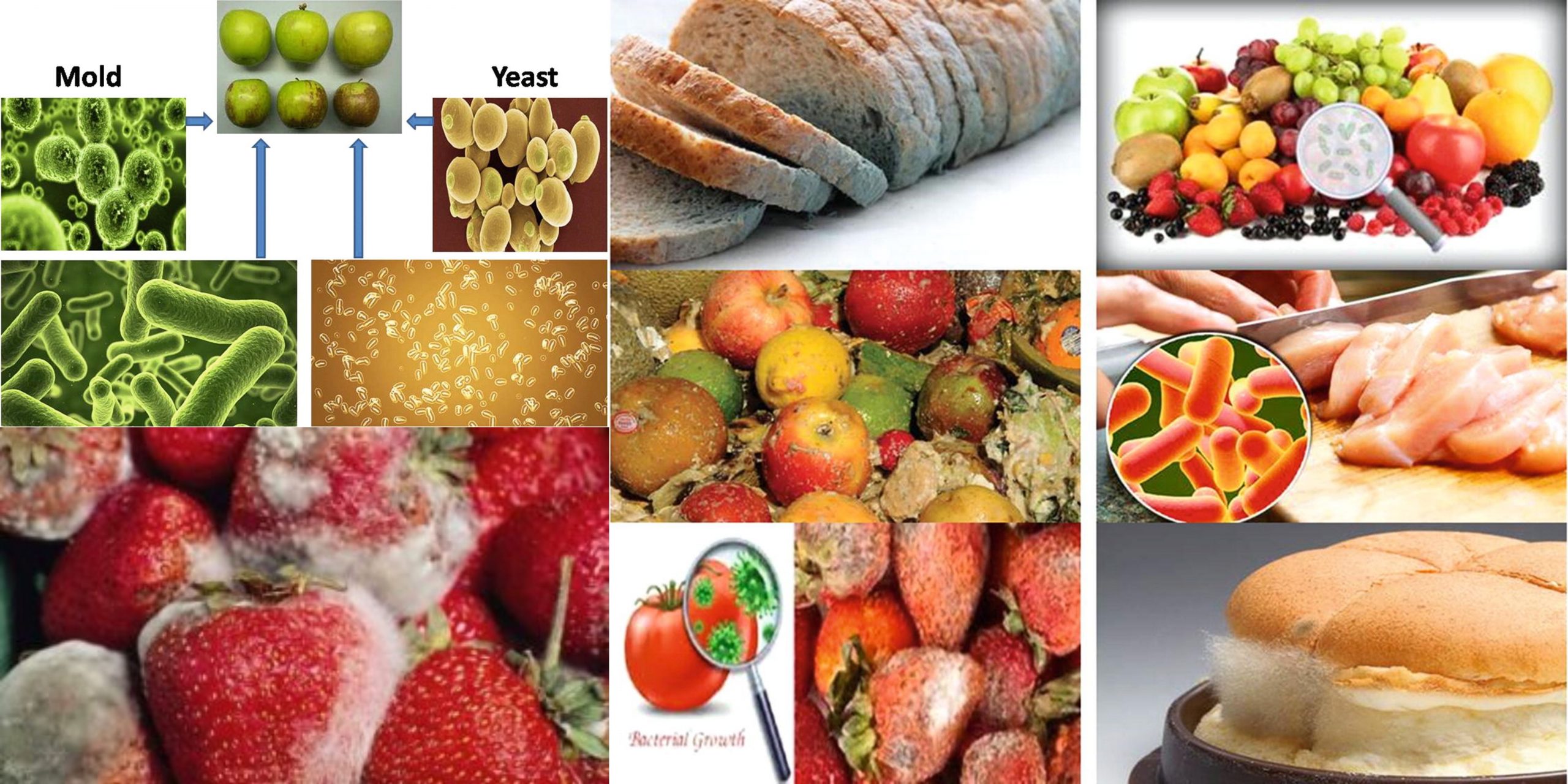
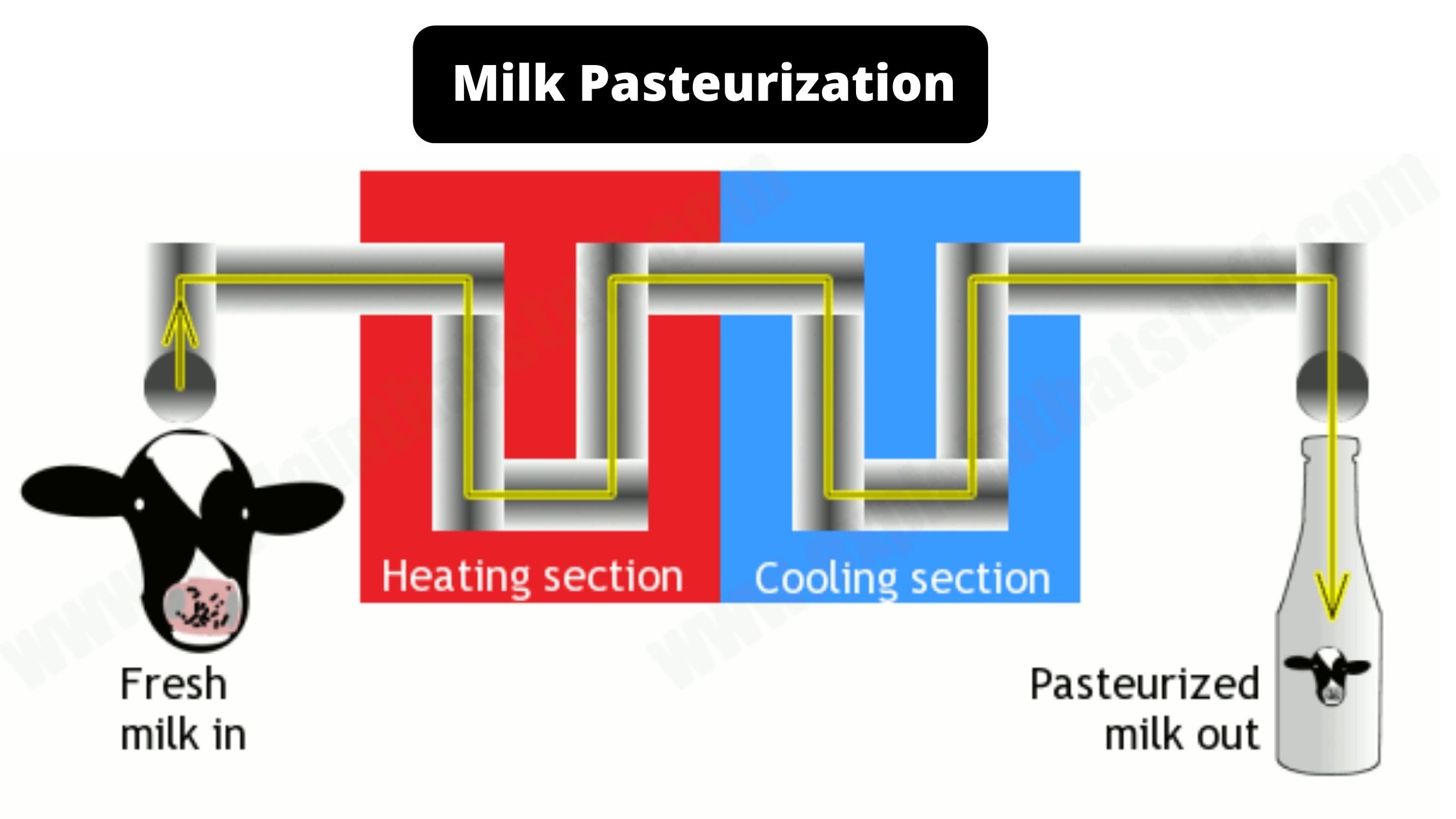
Factors affecting the growth of microorganisms in food
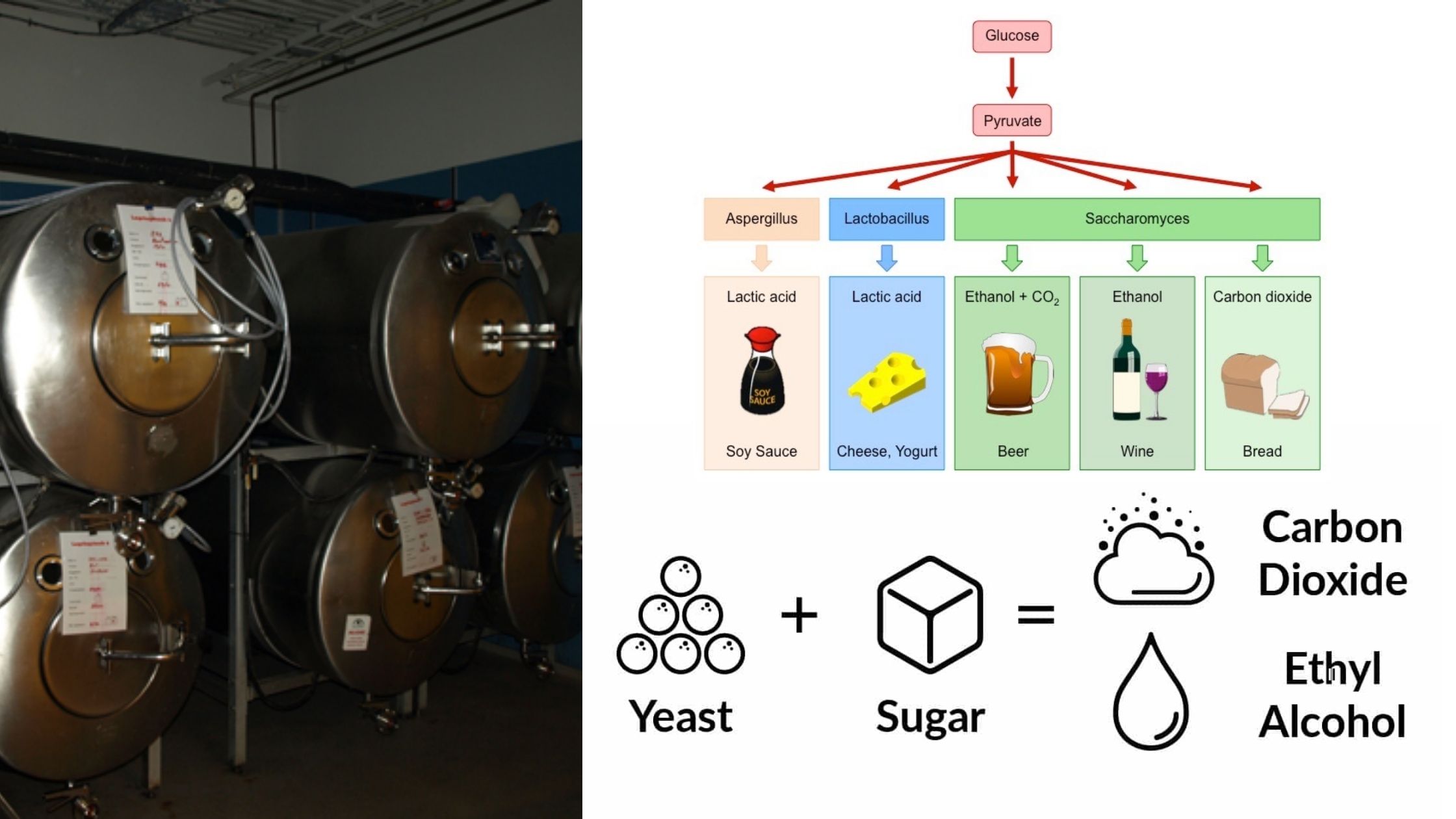
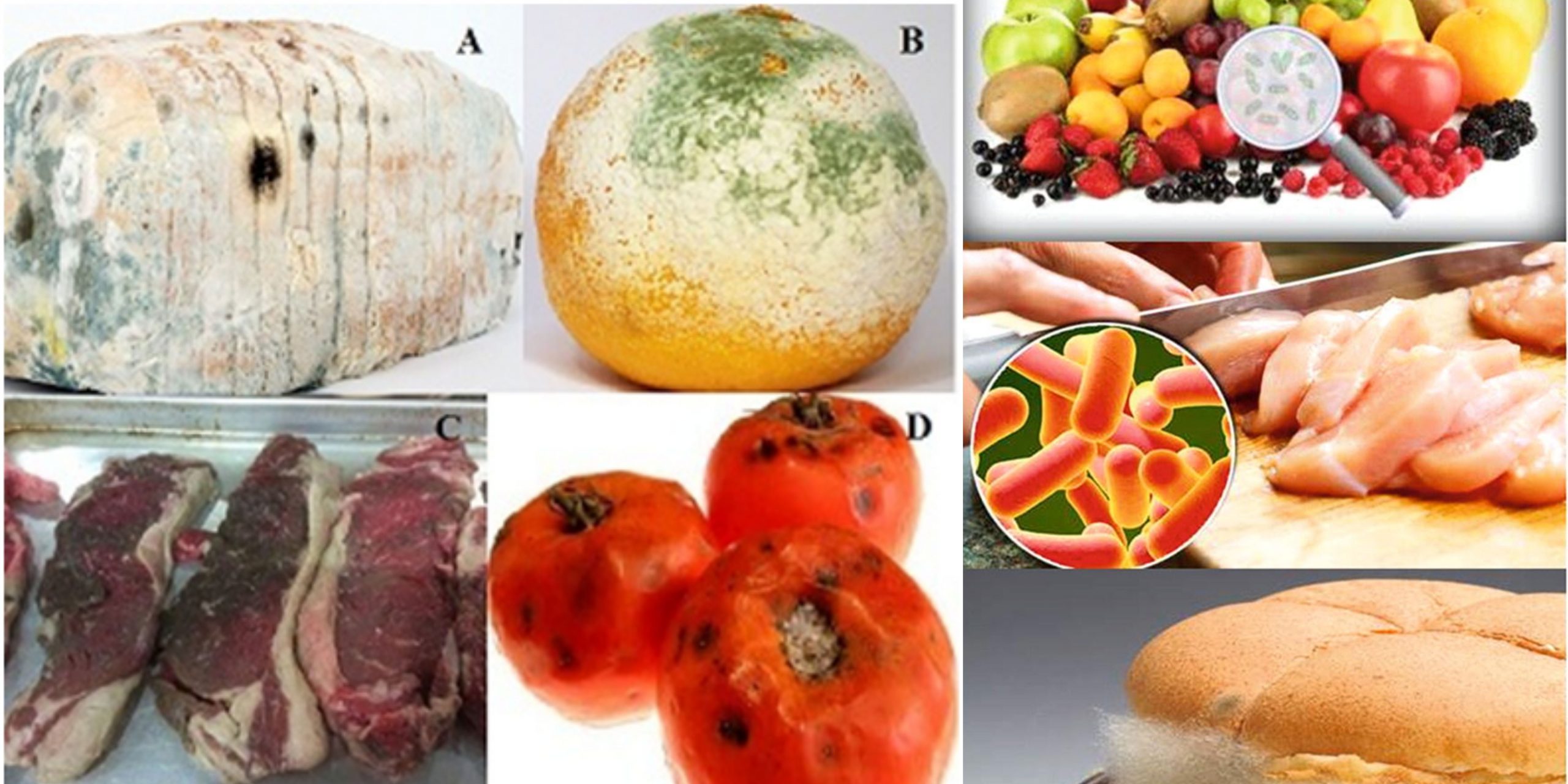
Foods that are both animal and plant source play a significant role in the development of microbial communities. The ability of microorganisms develop or multiply in such food is contingent on the environment.