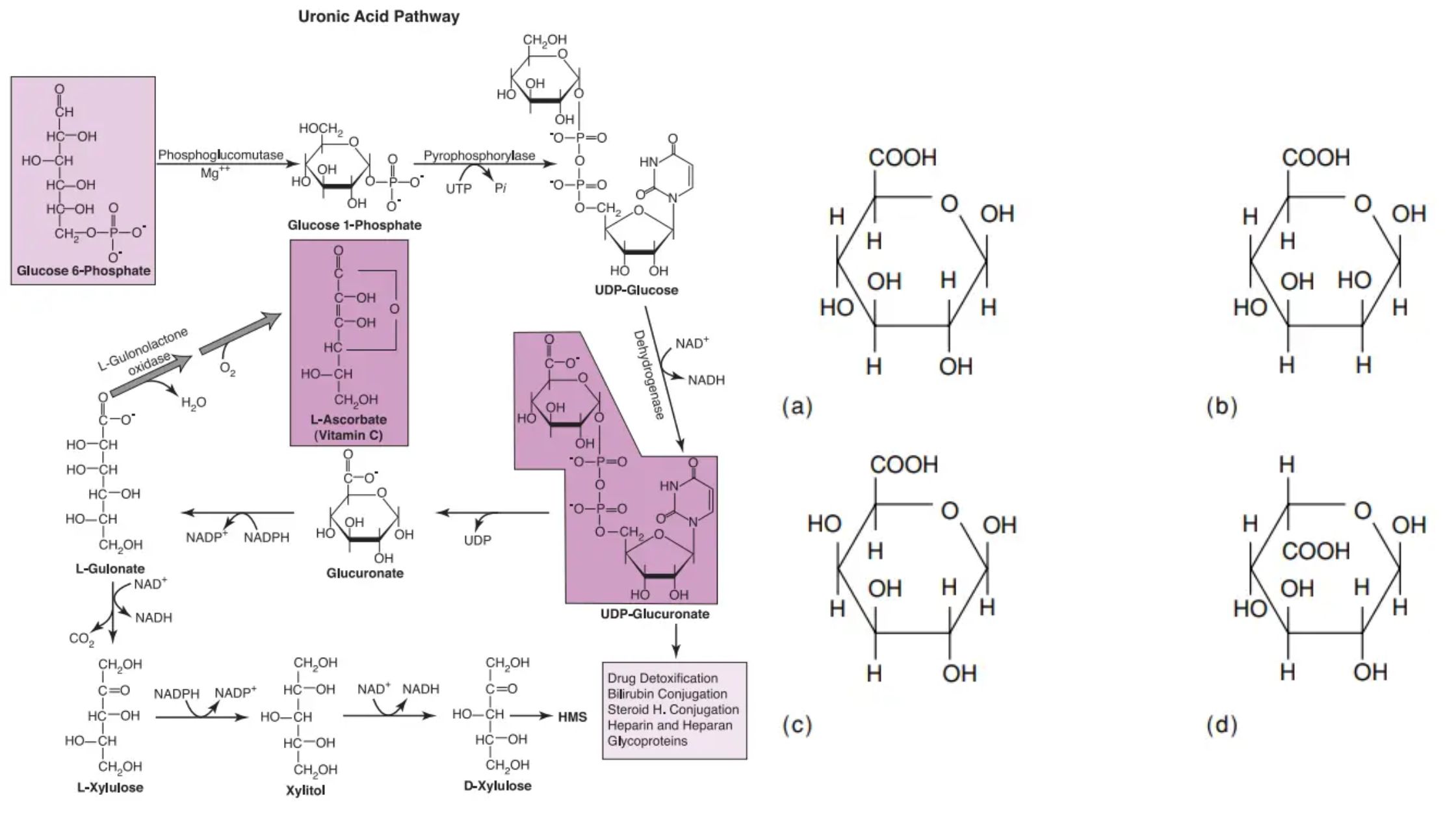
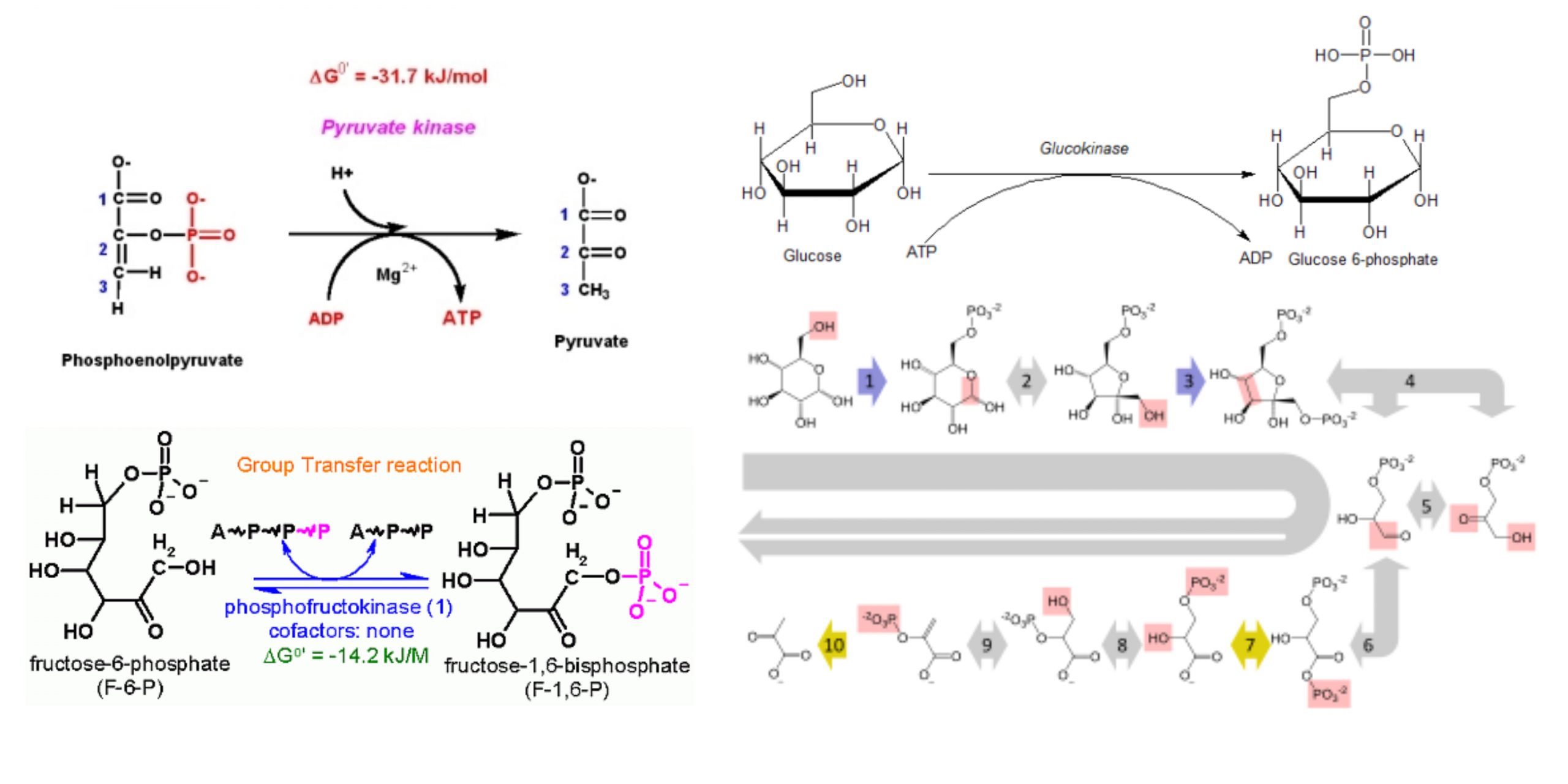
Uronic Acid Pathway – Definition, Enzymes, Steps, Importance
What is Uronic Acid Pathway or Glucuronic pathway? Overview The uronic acid pathway stands as a distinctive cytoplasmic thoroughfare within cellular metabolism, orchestrating intricate transformations that hold pivotal significance for various physiological processes. As we embark on an exploration of this biochemical route, we uncover its multifaceted roles and far-reaching implications for cellular health and … Read more