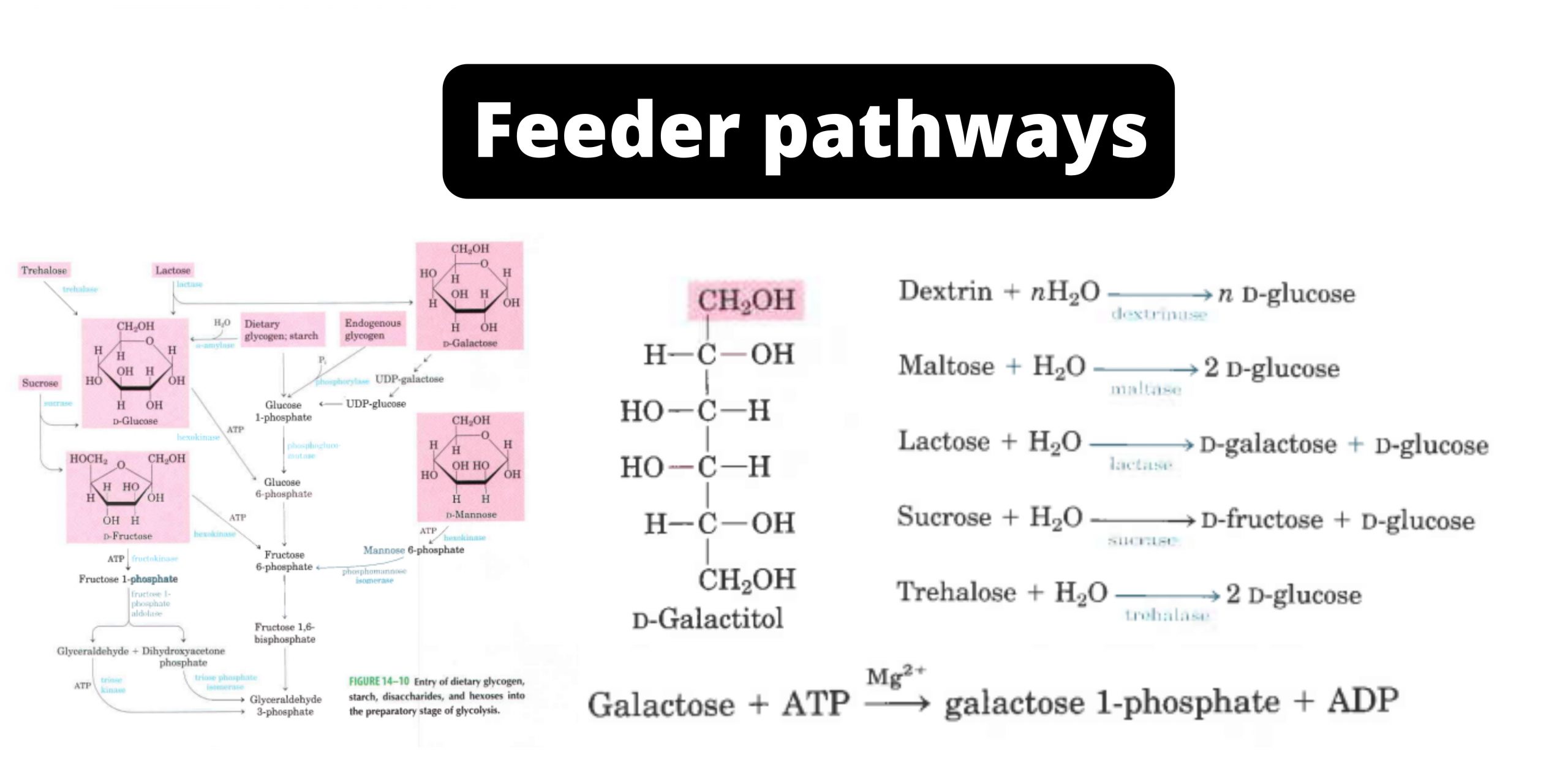
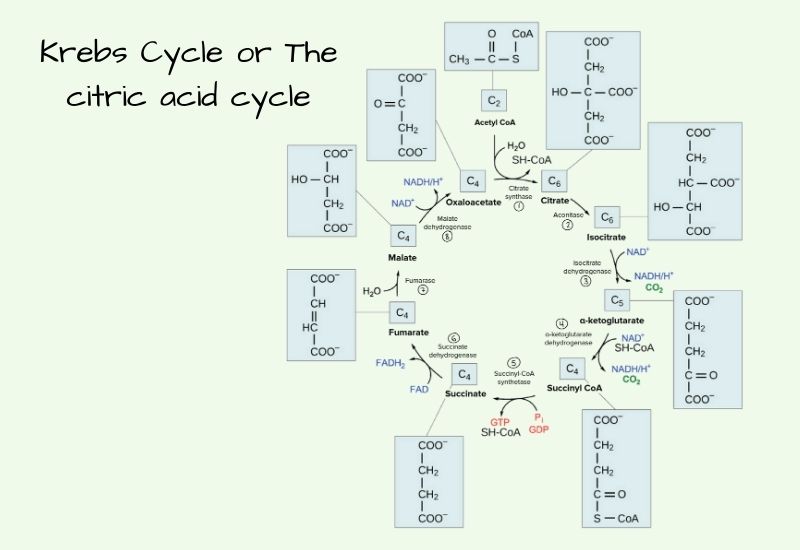
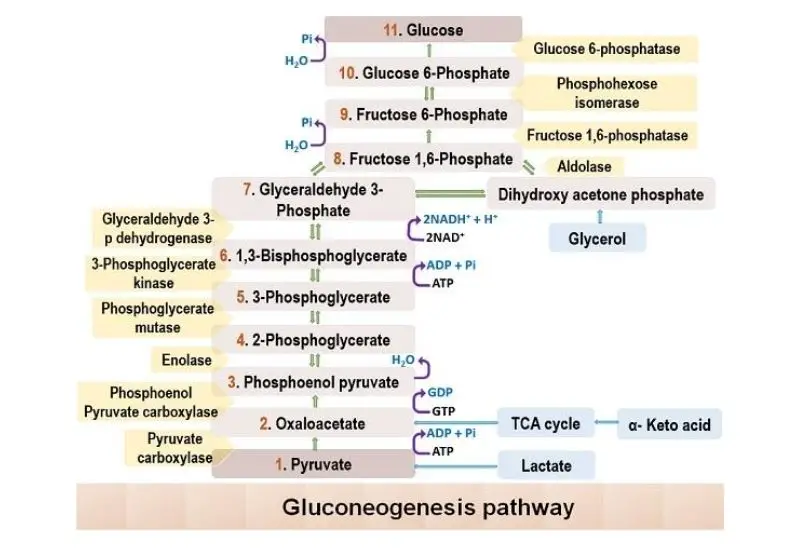
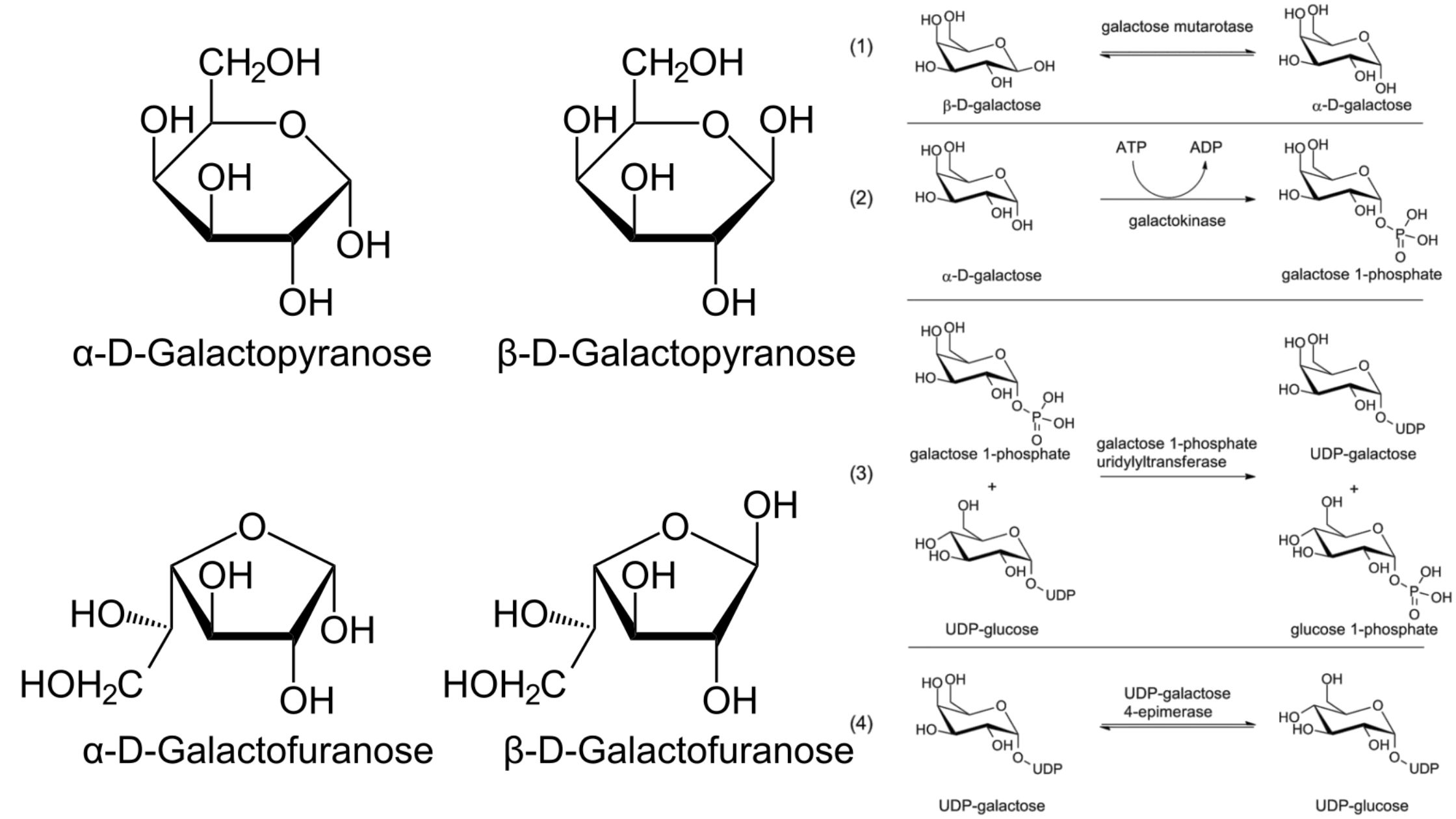
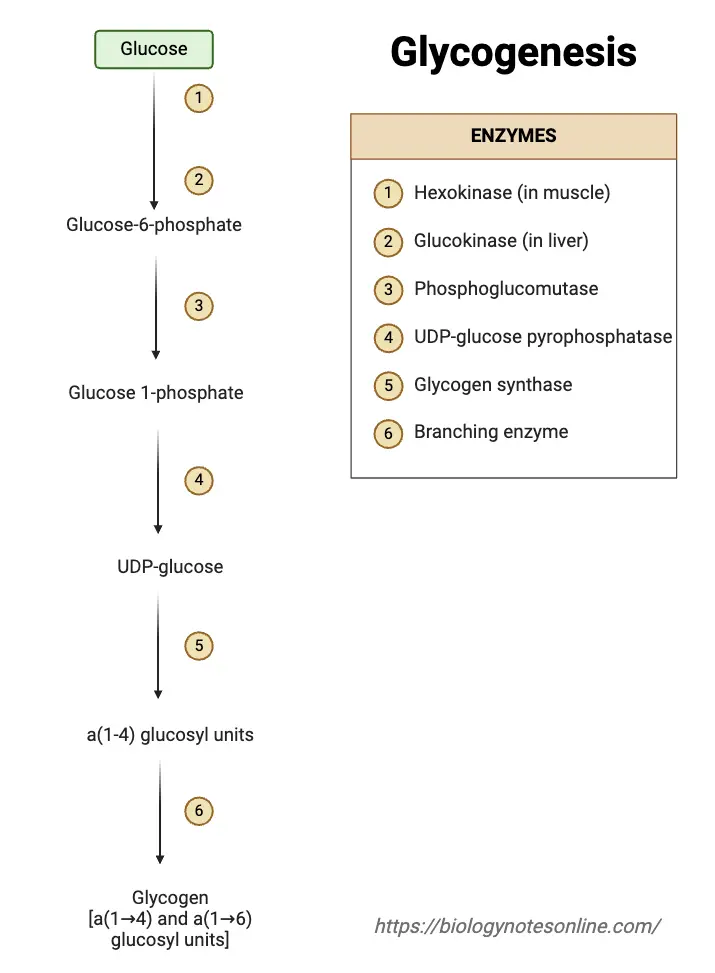
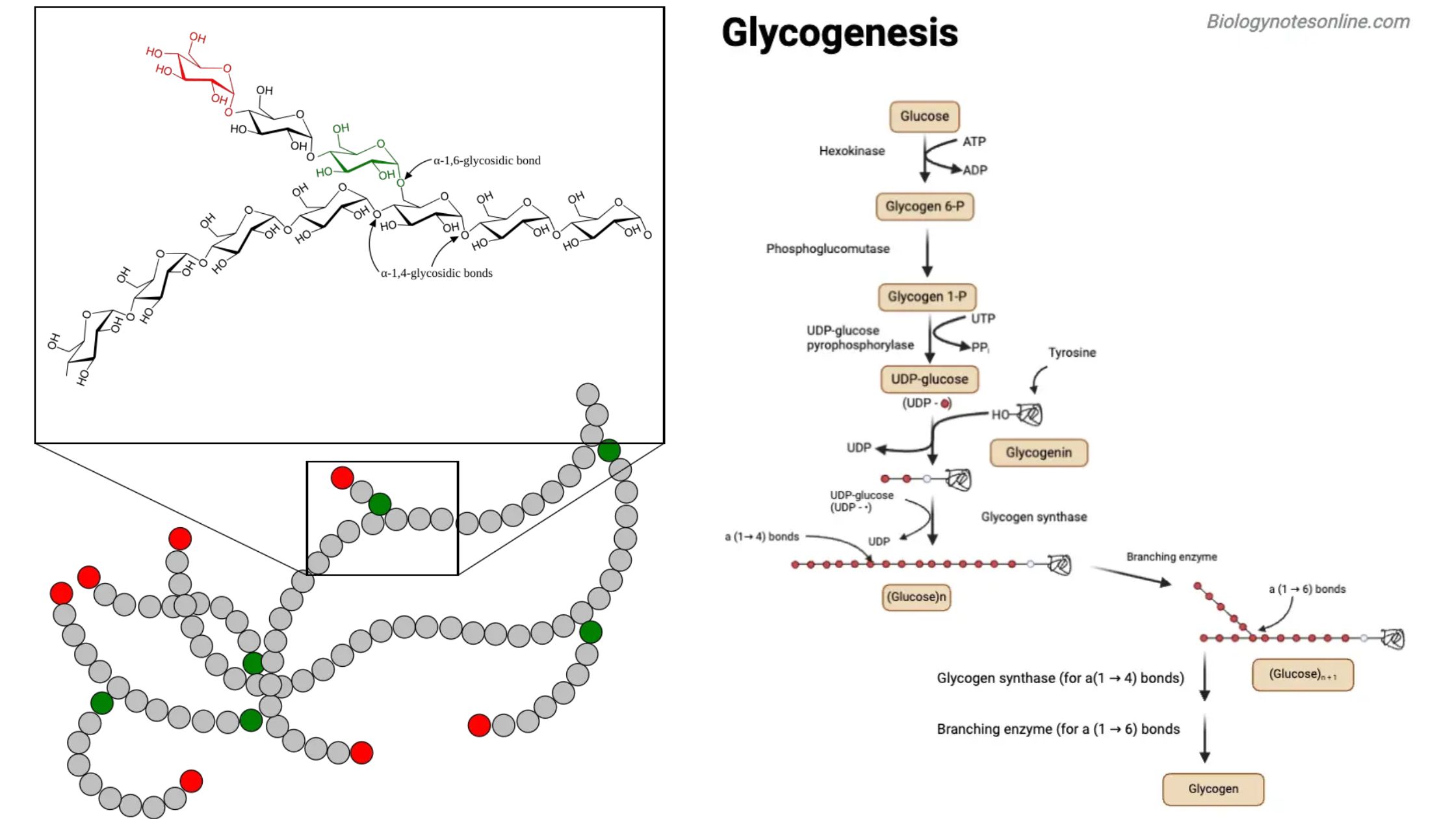
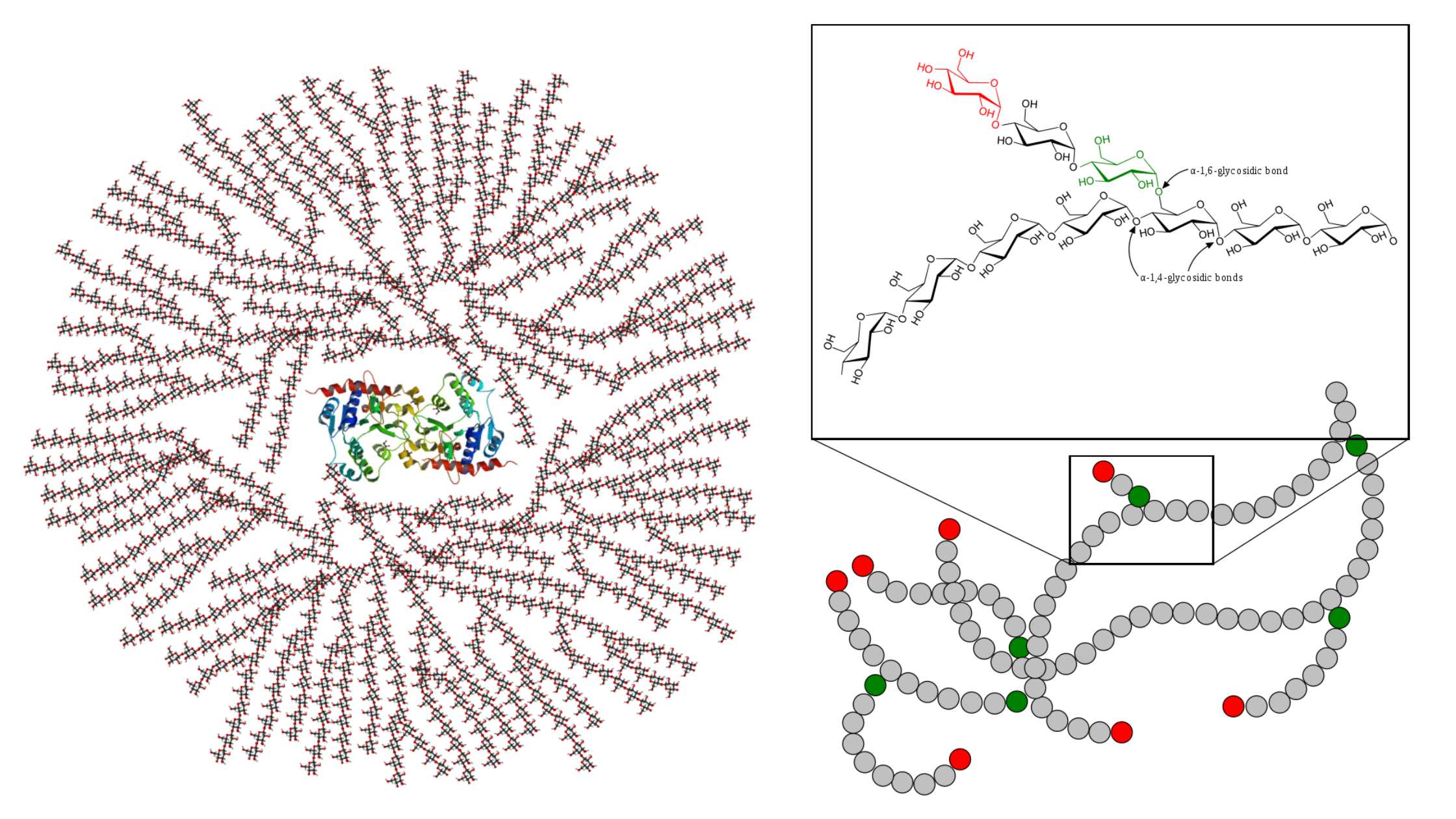
Feeder Pathway – Pathways, Mechanism, Importance
Feeder pathway is the metabolic process in which different non-glucose carbohydrates are changed into intermediates that can enter glycolysis. It is the process that allows fructose, galactose, mannose and stored polysaccharides like glycogen to be converted into common glycolytic compounds. These intermediates then move into the normal glycolytic steps for further breakdown. In this pathway … Read more