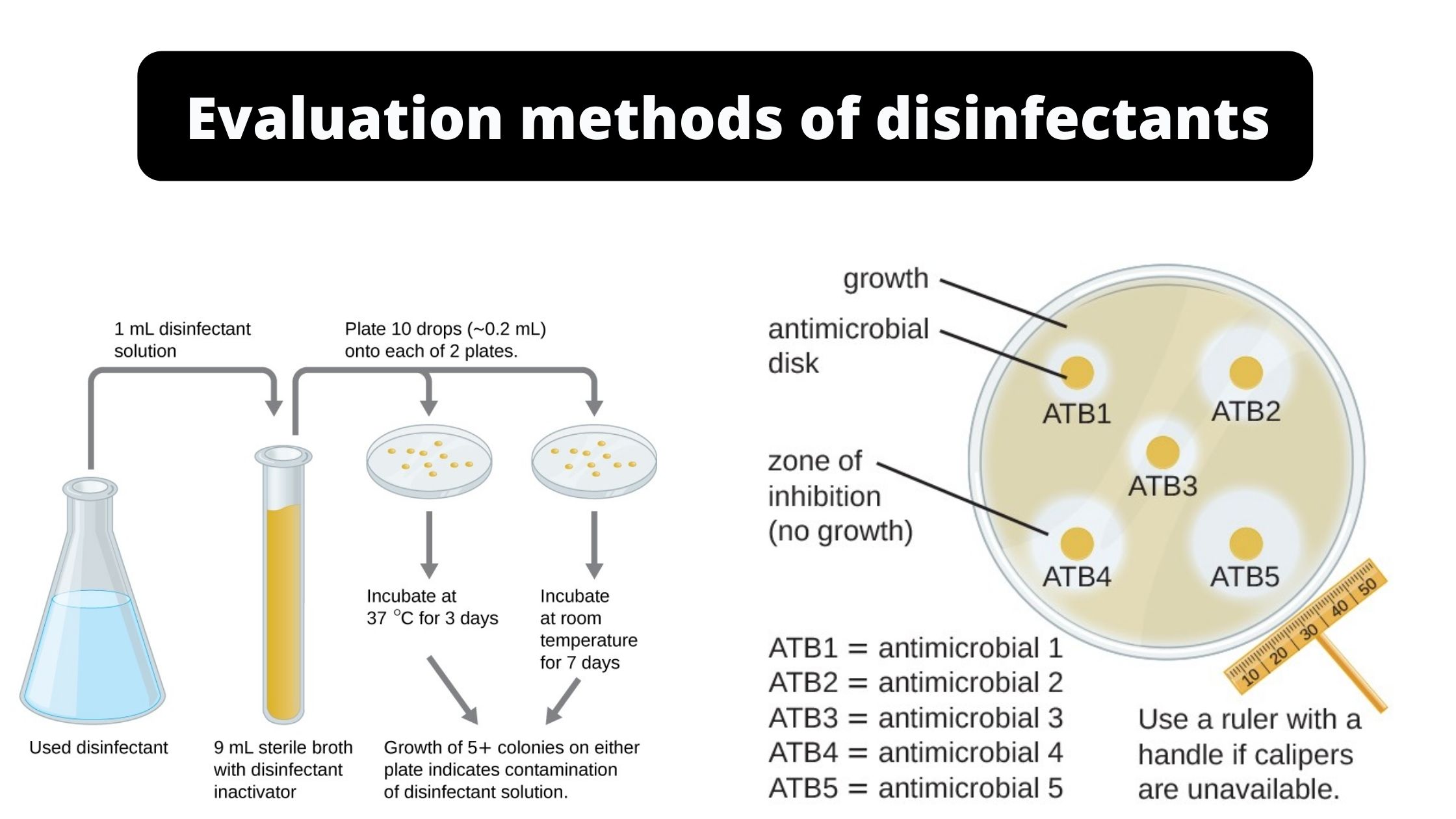
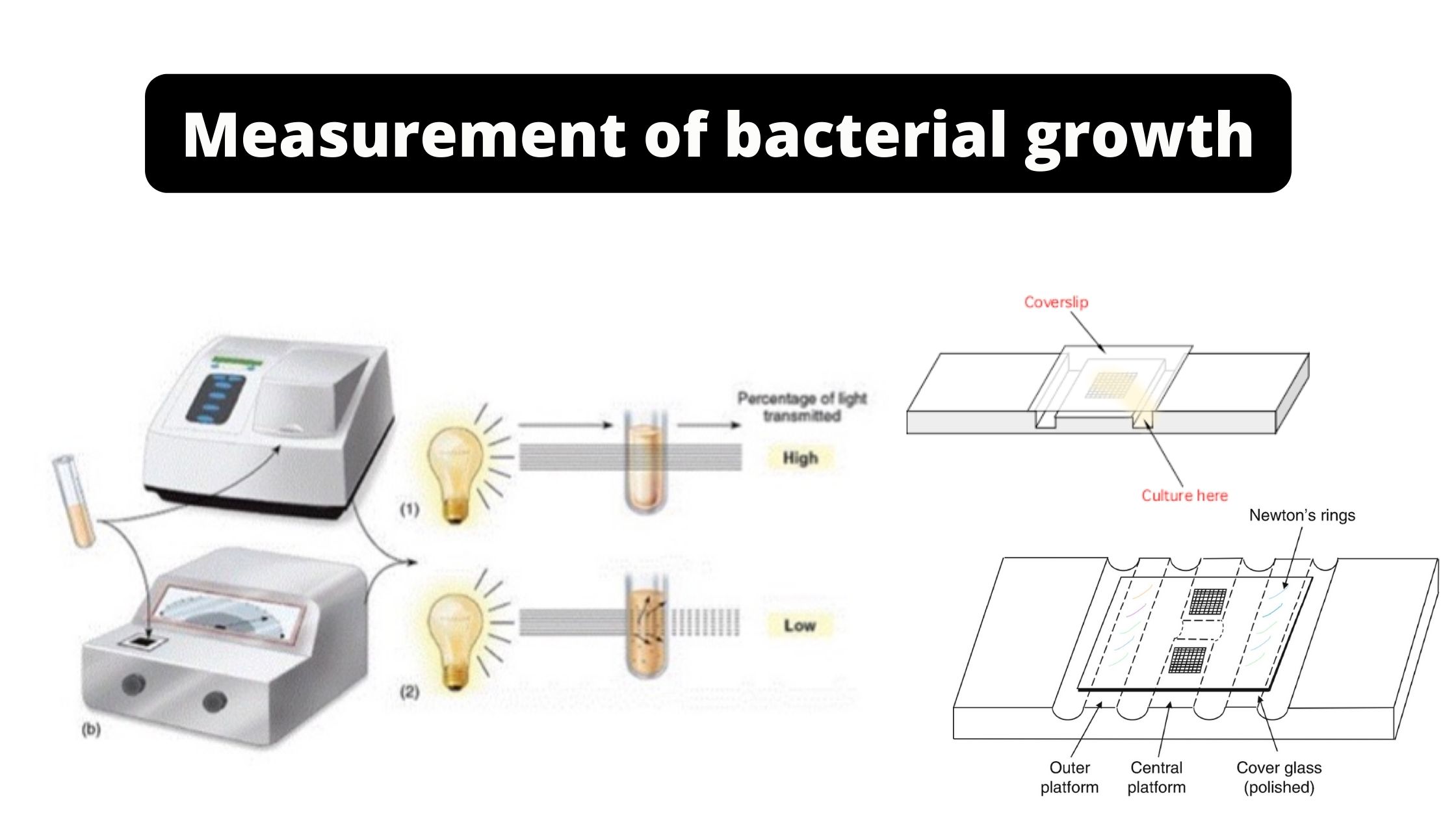
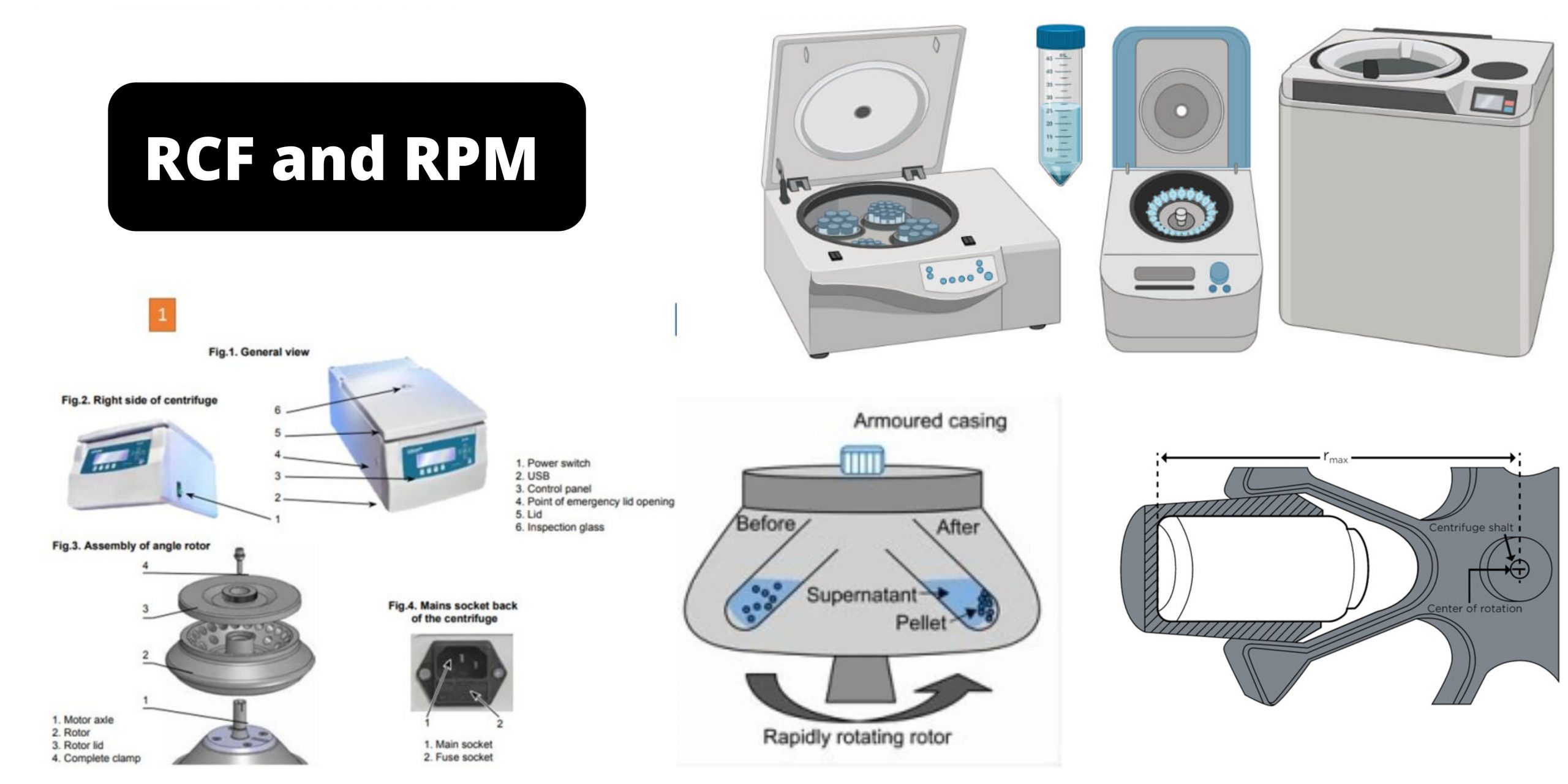
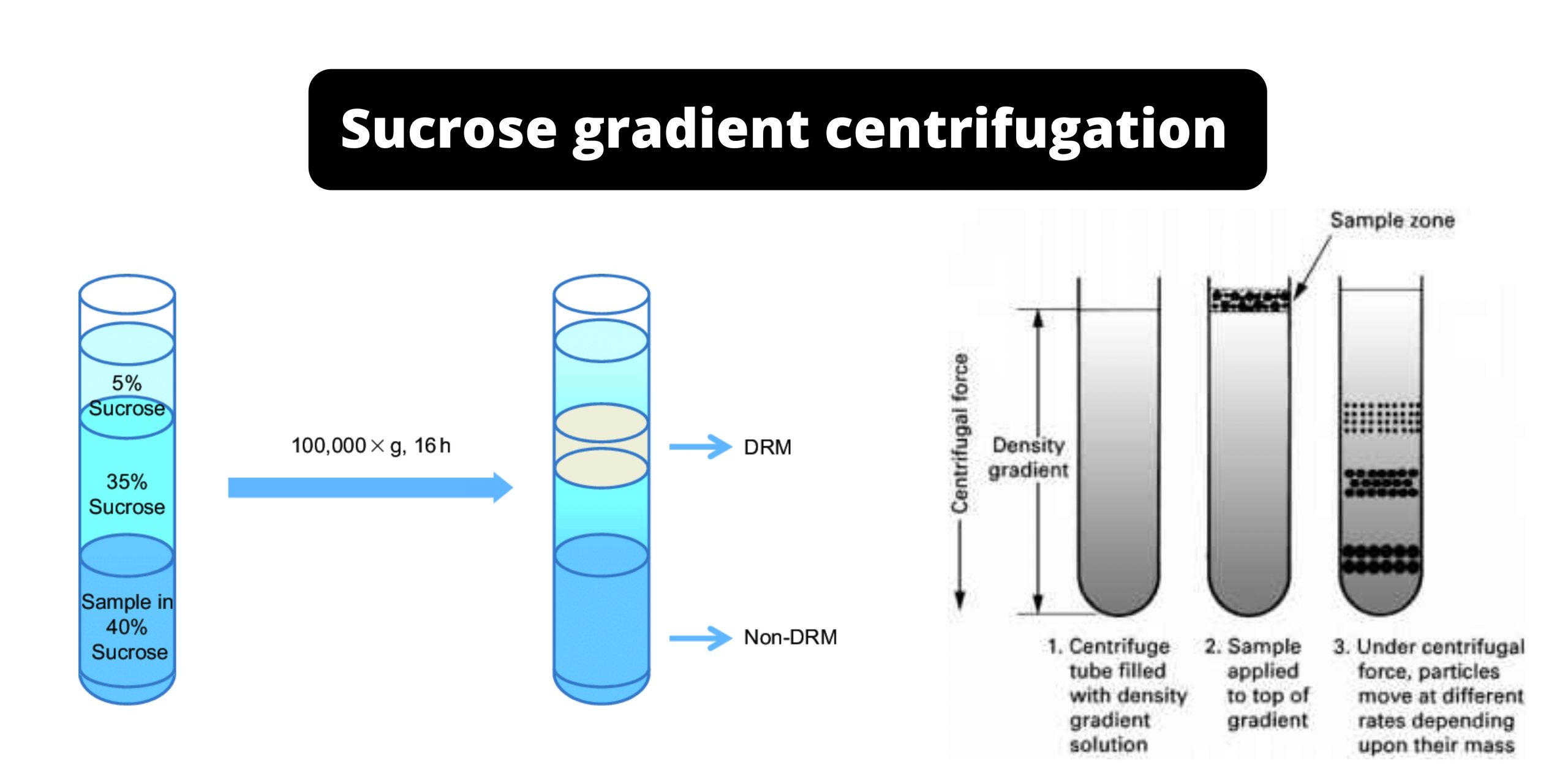
Scope of Microbiology in Nursing
As their name suggests, microorganisms are minute organisms with the potential to adapt to their environment; for instance, commensals can become pathogenic in certain altered environments. The adaptability of microbes to certain treatments or medications remains a challenge for nurses and other medical professionals. Microbiology influences the lives of a nurse working in a medical … Read more