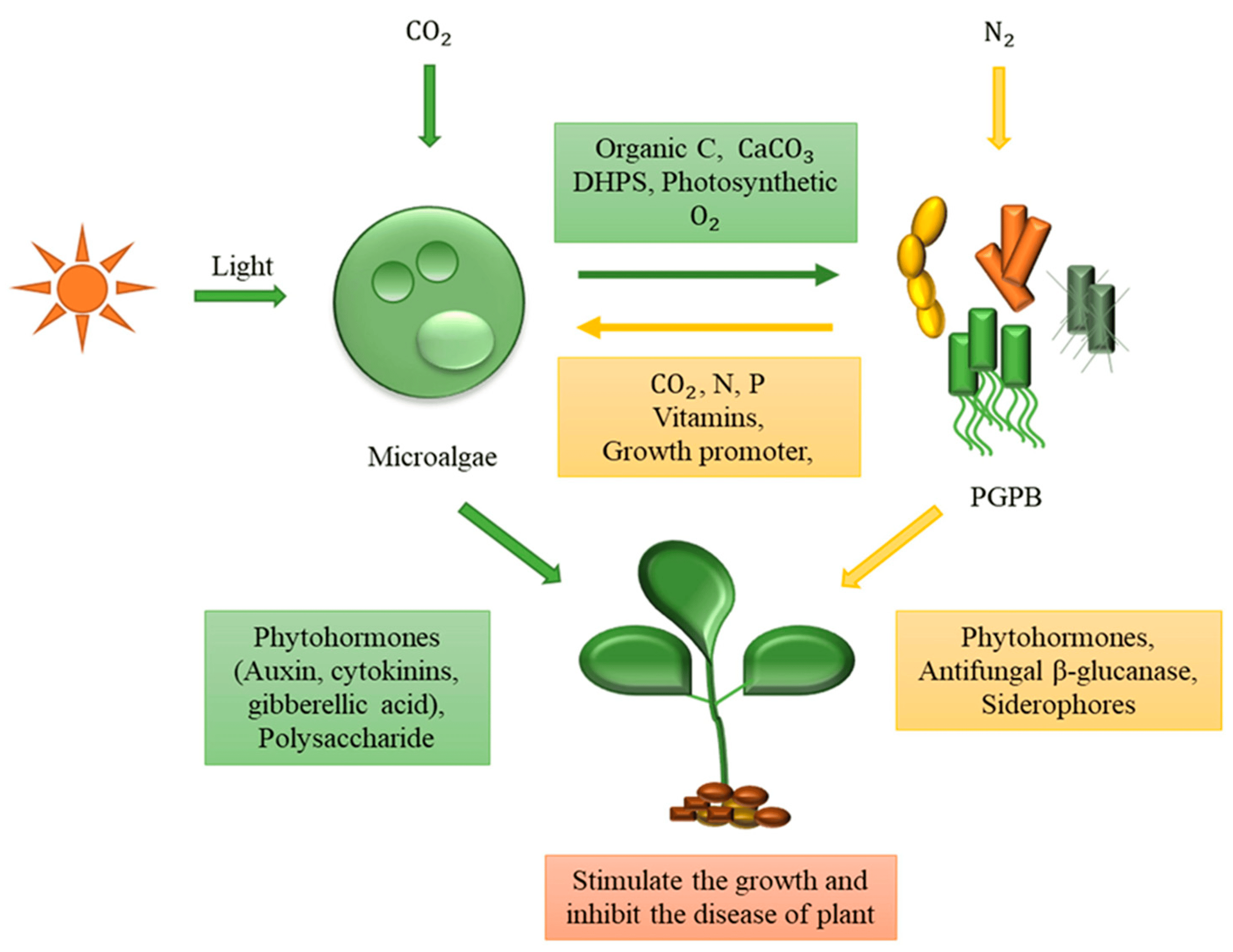
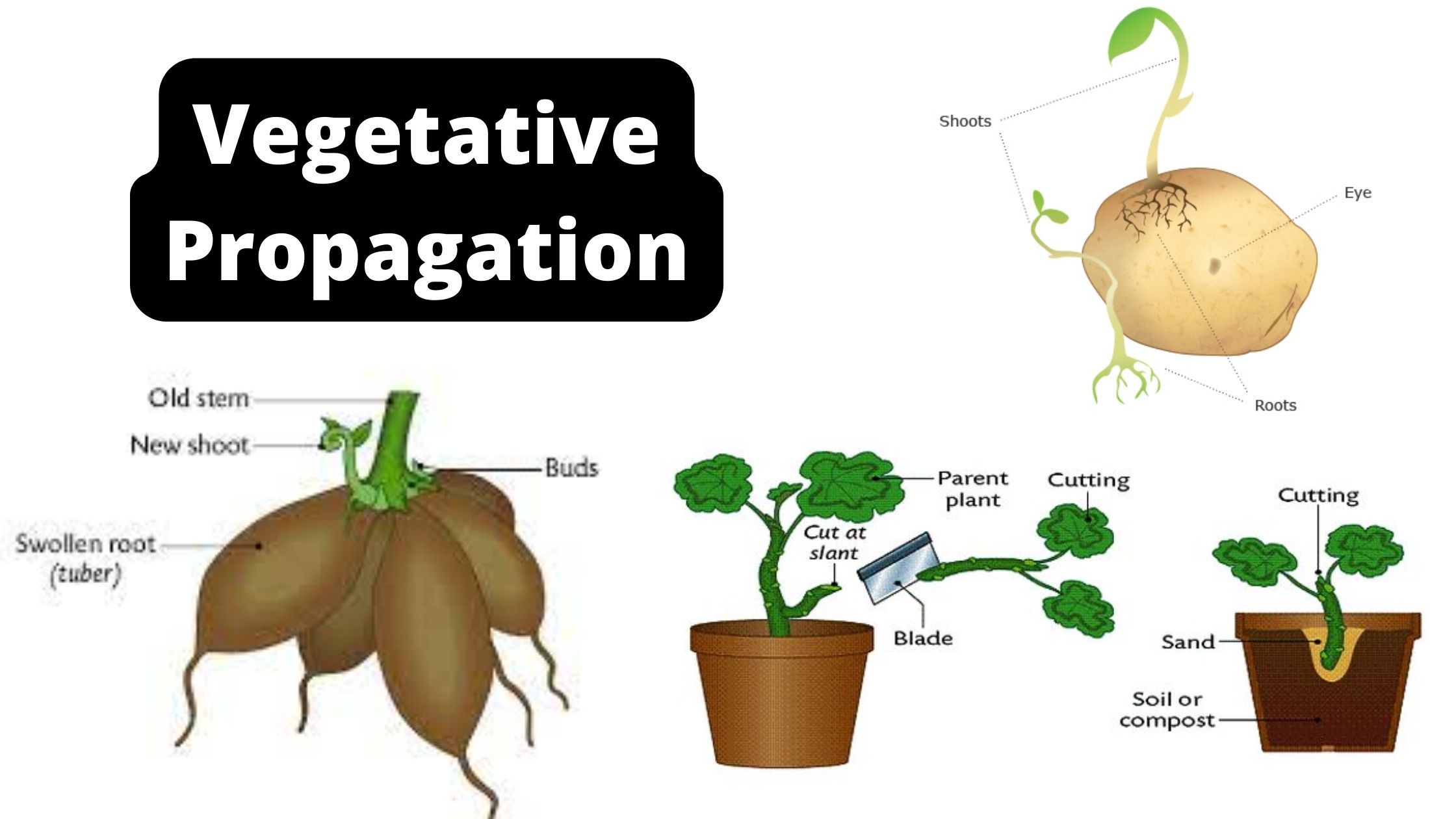
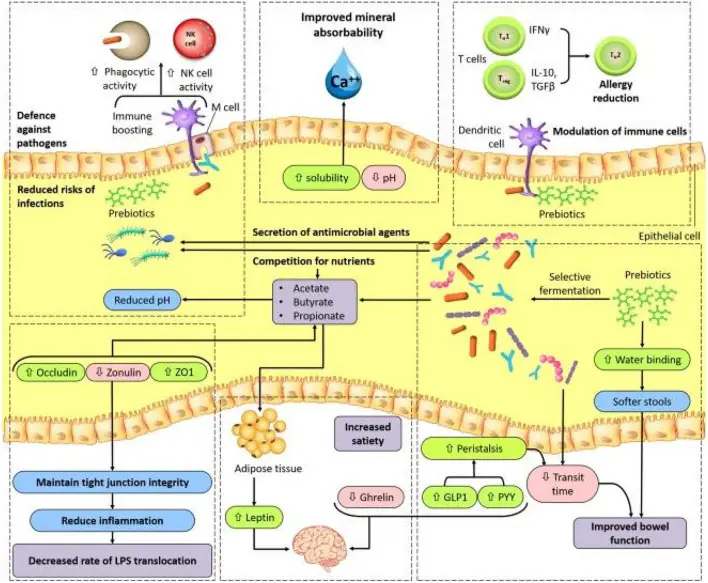
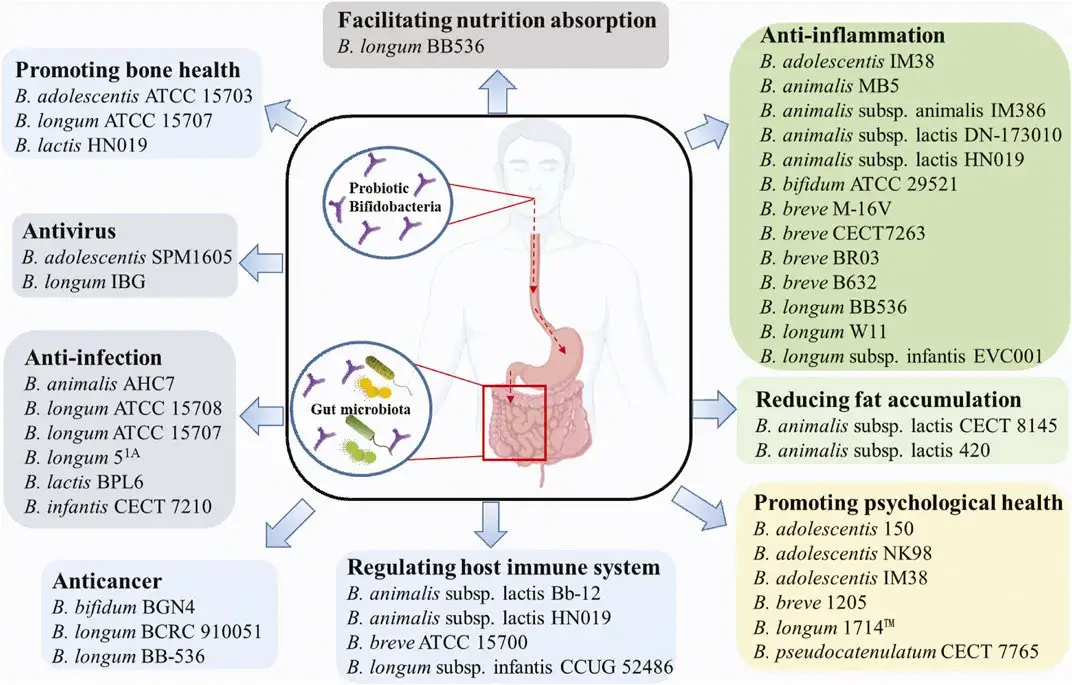
Scientific Method – Dfinition, Steps, Examples, Importance
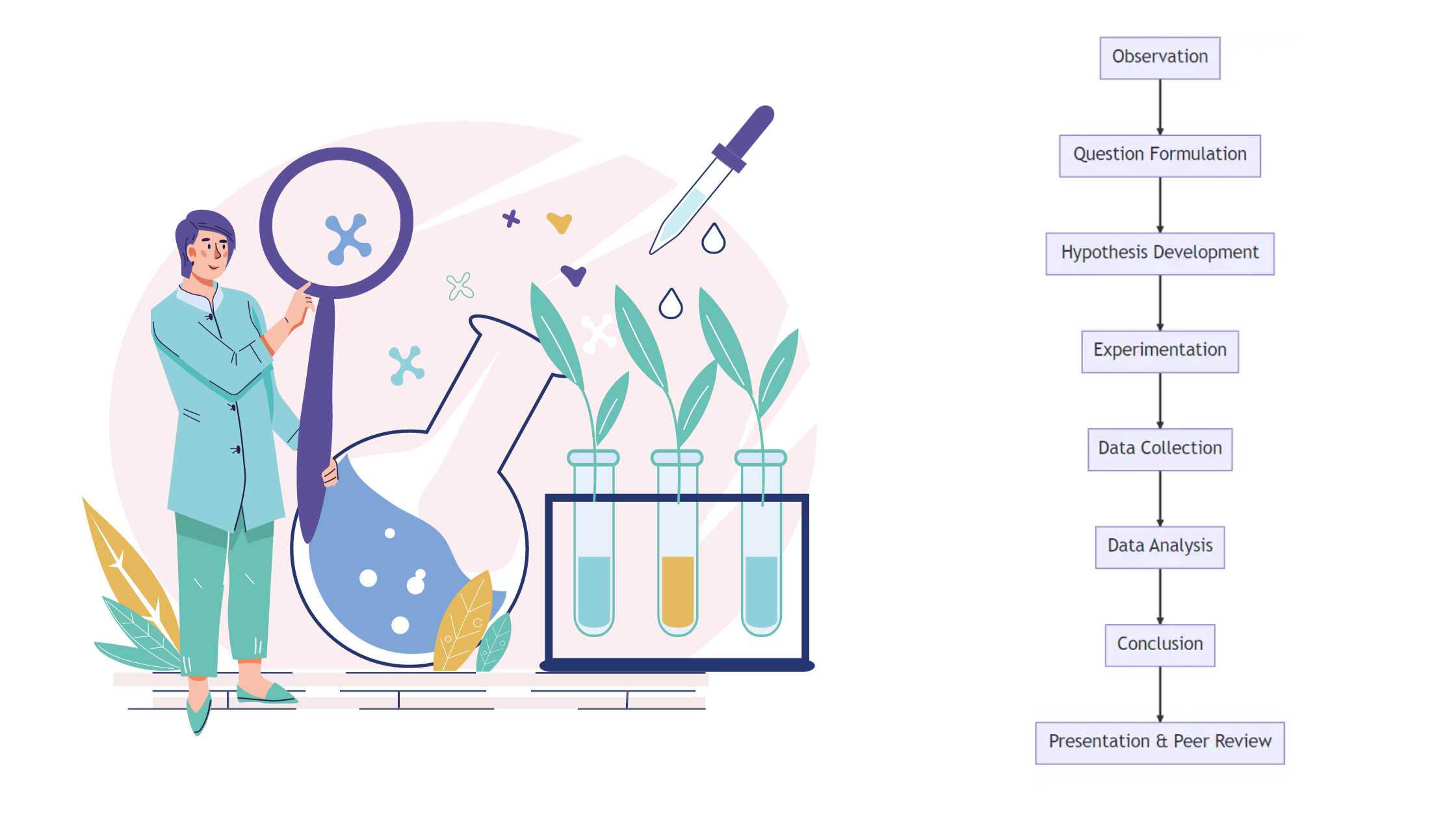
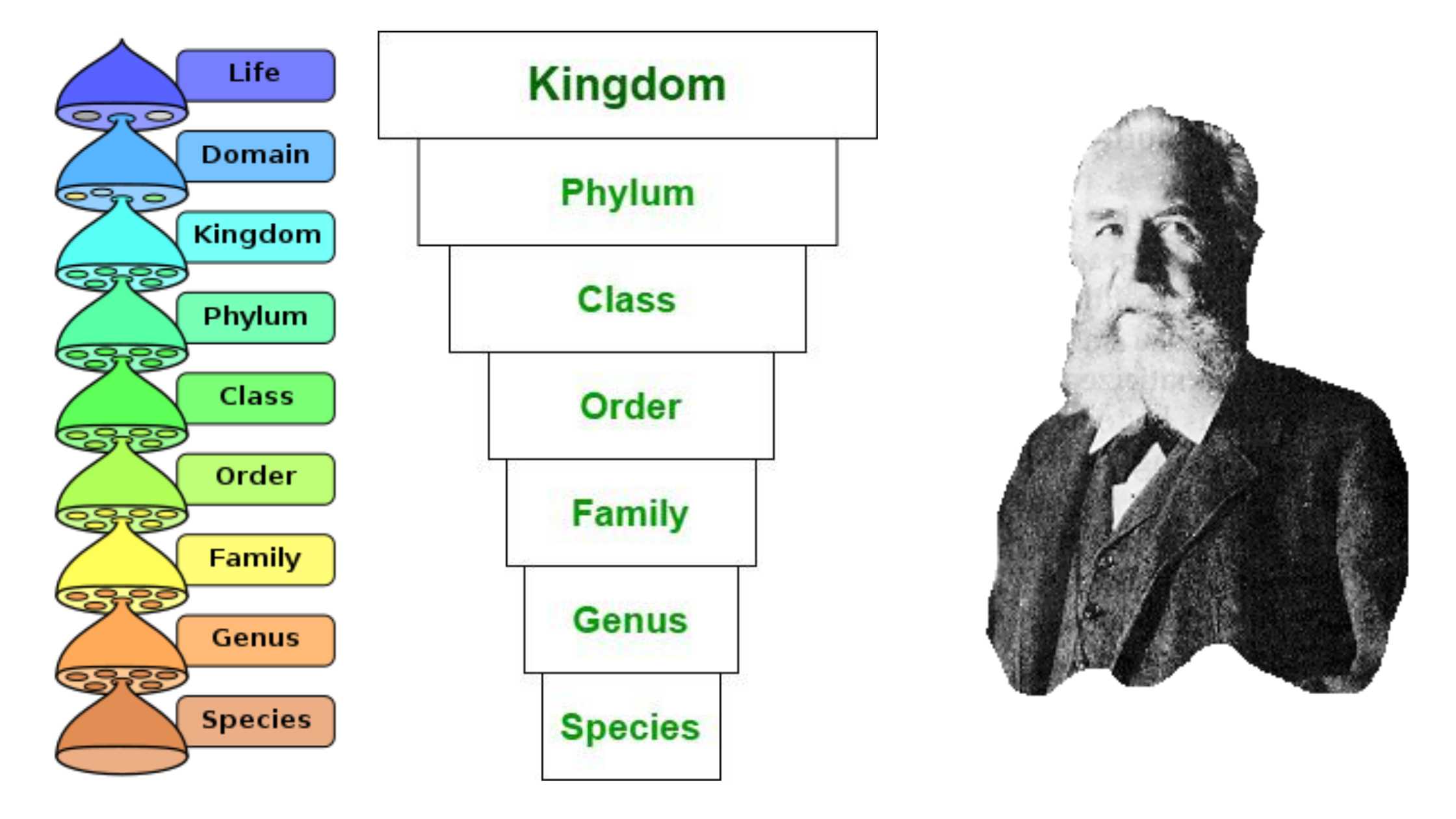
What is Scientific Method? Definition of Scientific Method The scientific method is a systematic procedure used in scientific research to formulate hypotheses, gather data through observation and experimentation, and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. It emphasizes objectivity, repeatability, and falsifiability in the pursuit of knowledge. Scientific Method Steps The scientific method is a systematic … Read more