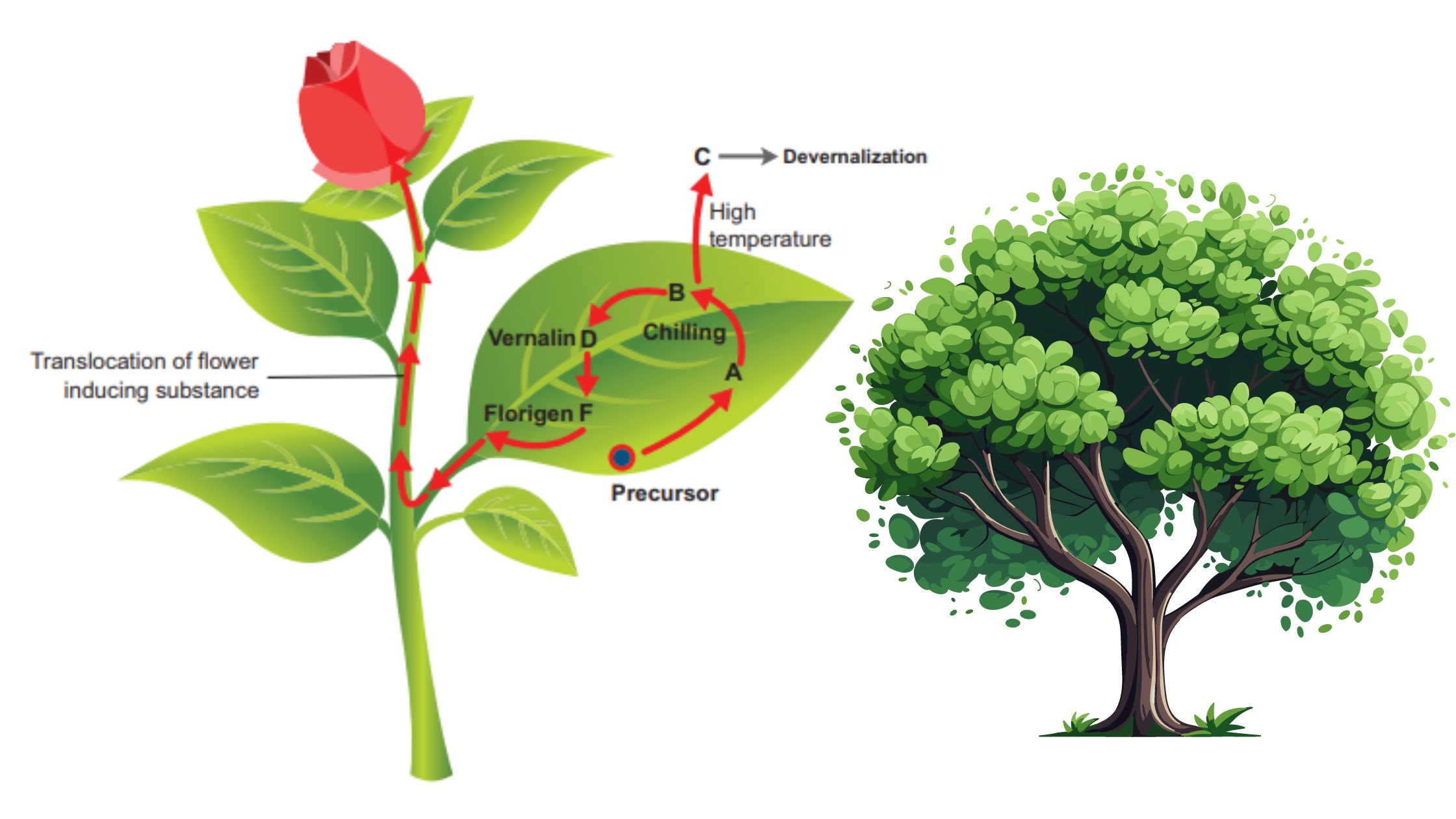
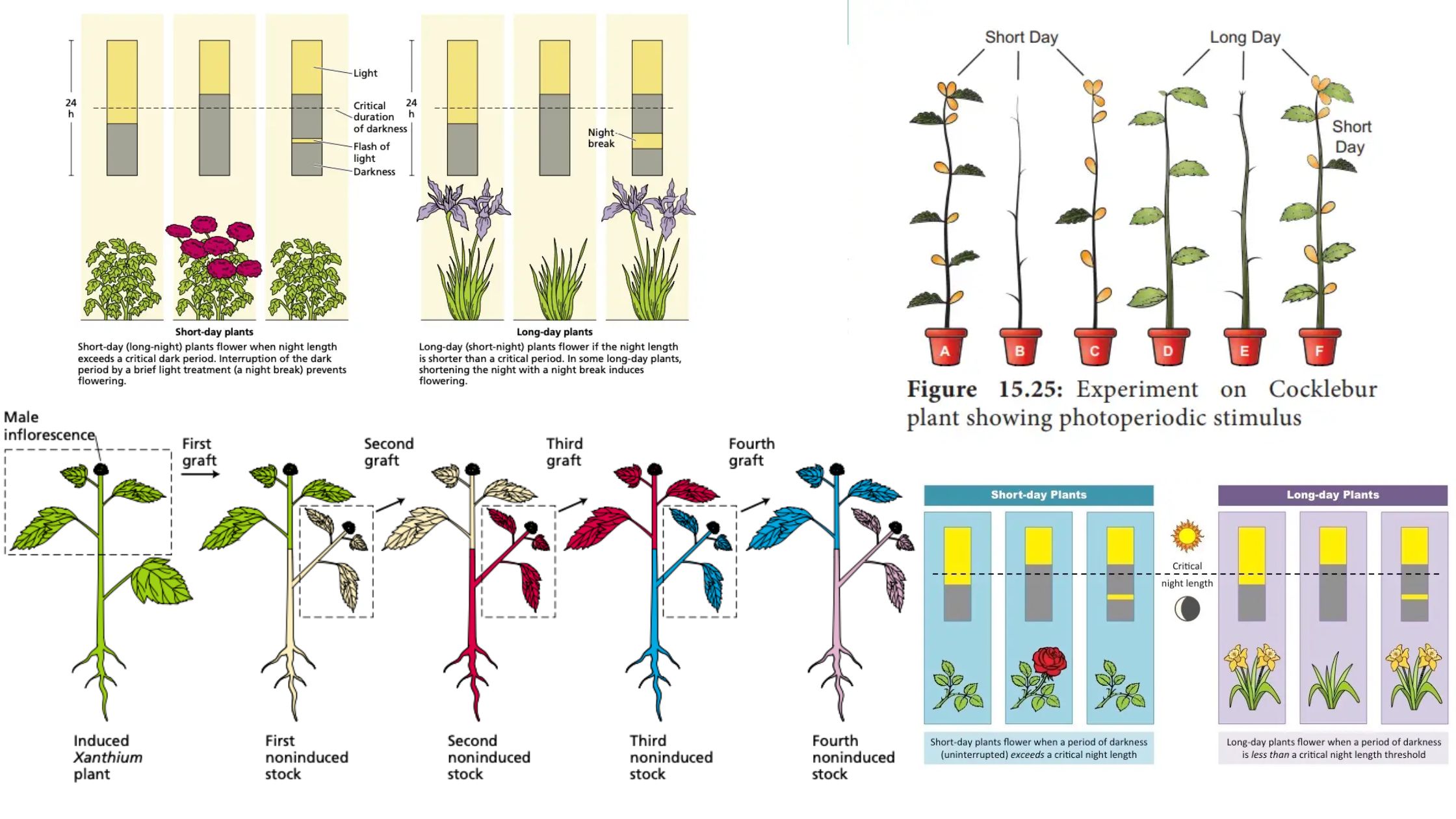
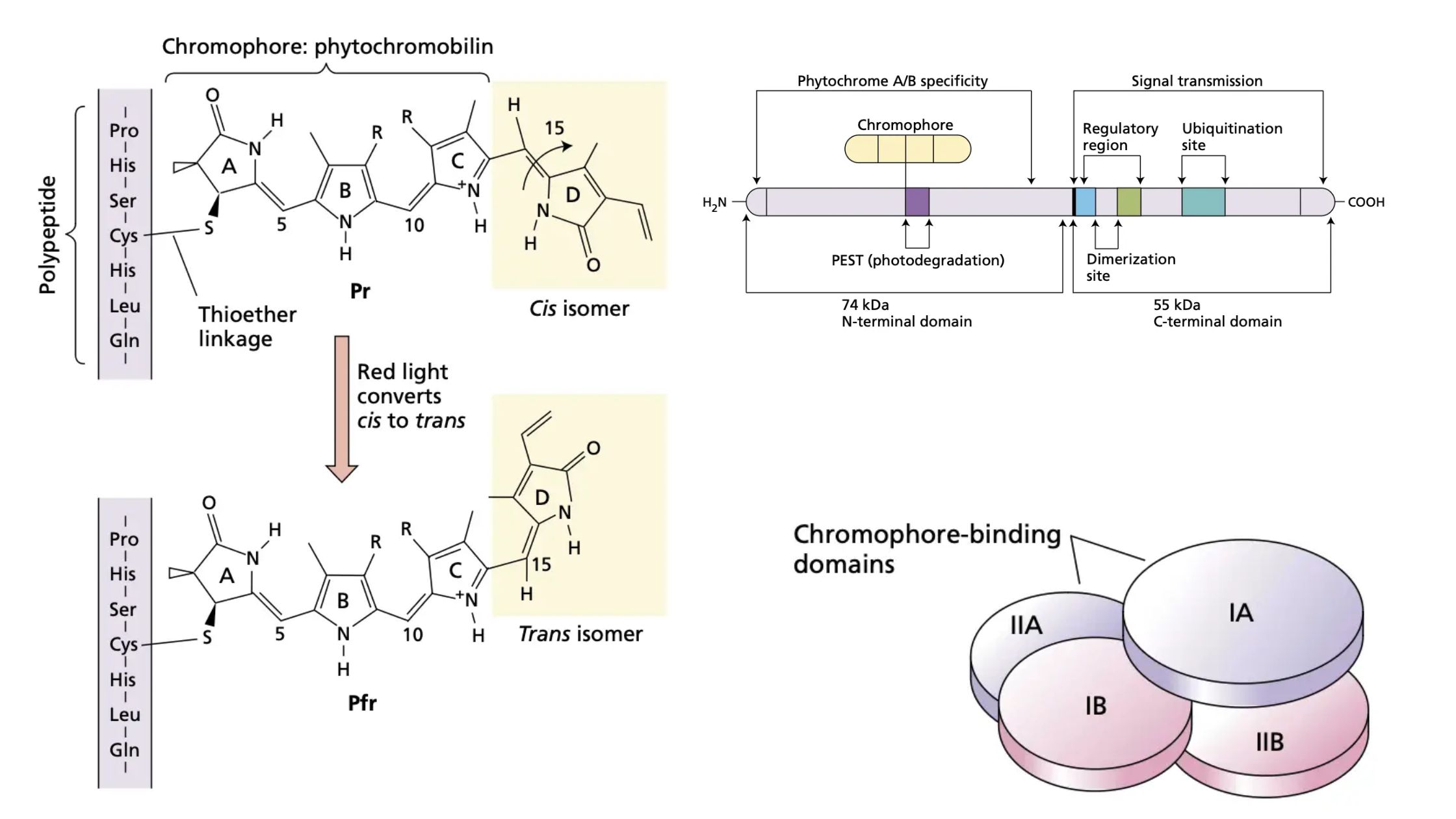
Plant Growth Regulators – Types, Characteristics, Functions, Examples
What is Plant growth regulator? Types of Plant Growth There are several distinct types of plant growth, each characterized by specific processes and outcomes. These growth types define how plants develop in size, form, and function throughout their life cycle. Below is a detailed breakdown of the main types of plant growth: Factors Affecting Plant … Read more