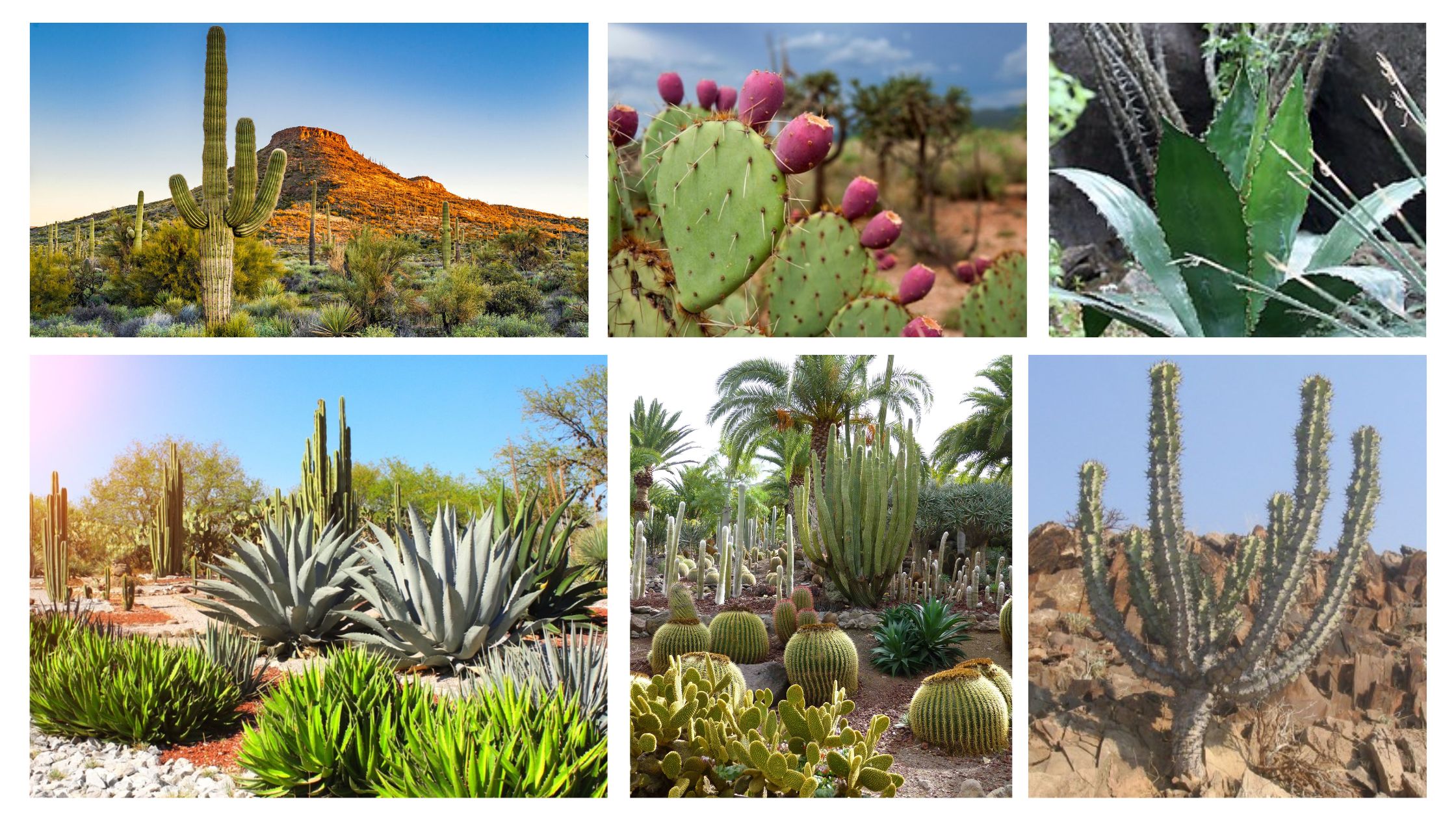
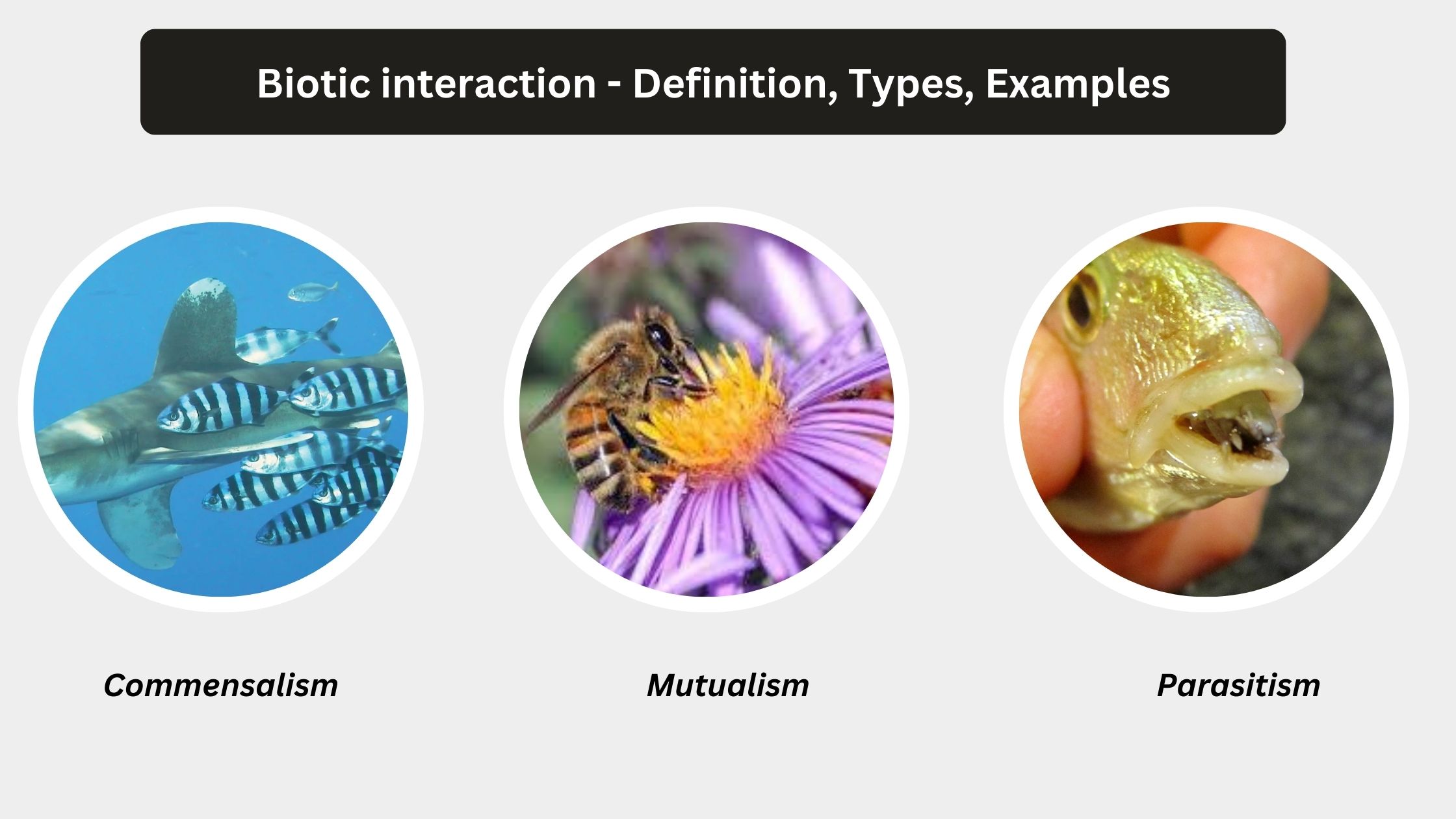
Biotic interaction – Definition, Types, Examples
What is Biotic interaction? Types of Biotic Interactions Based on the nature of these effects, biotic interactions can be categorized into three main types: positive, neutral, and negative. Below are the types of interactions, along with detailed descriptions: A. Positive Interactions 1. Mutualism Mutualism is a type of biotic interaction where two species engage in … Read more