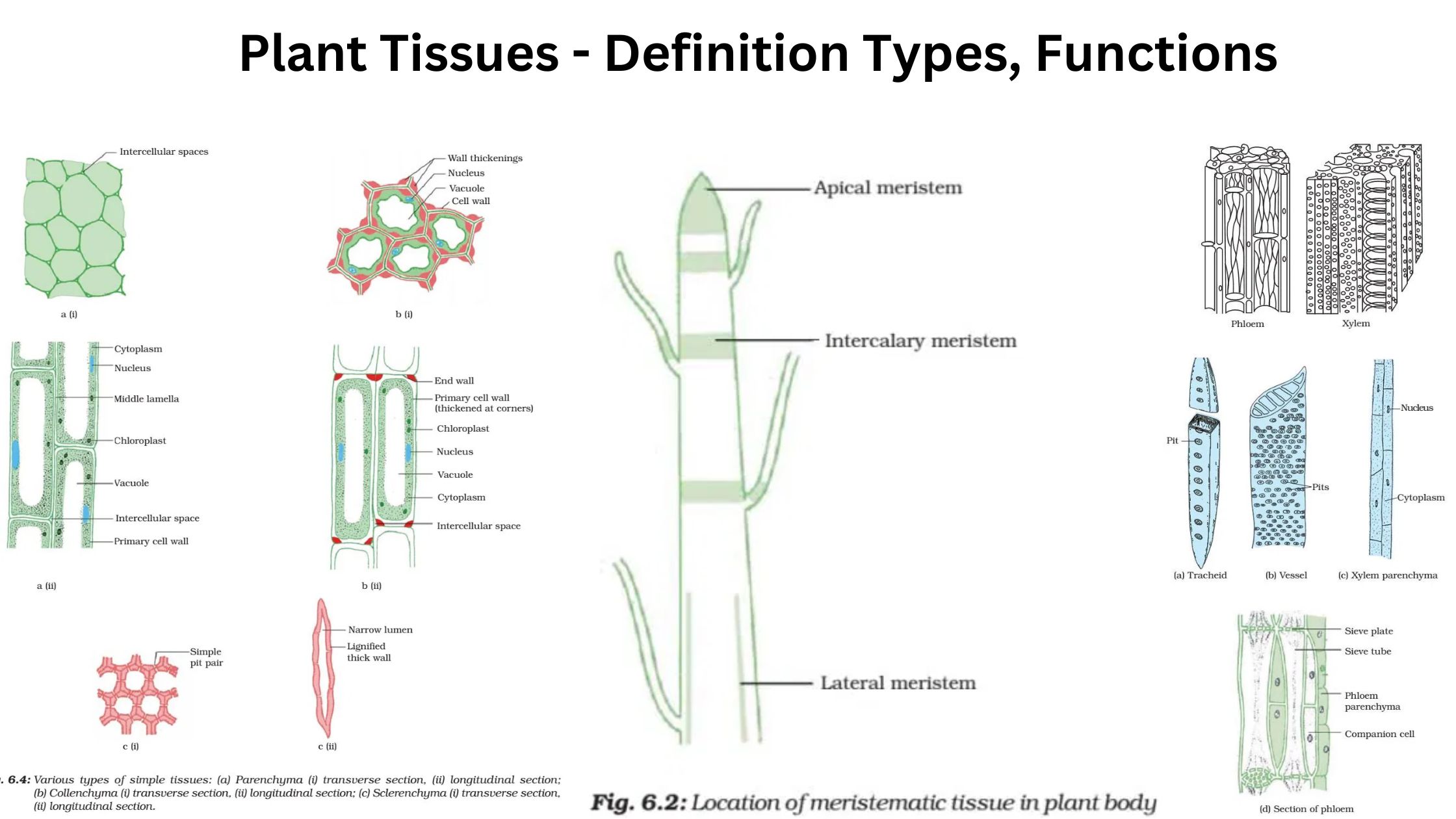
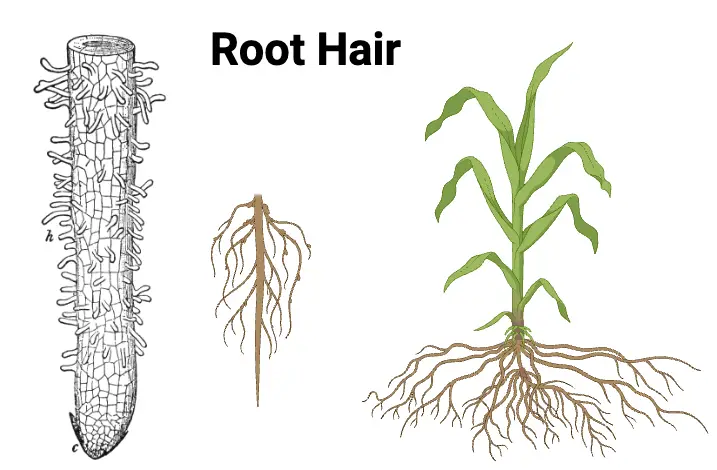
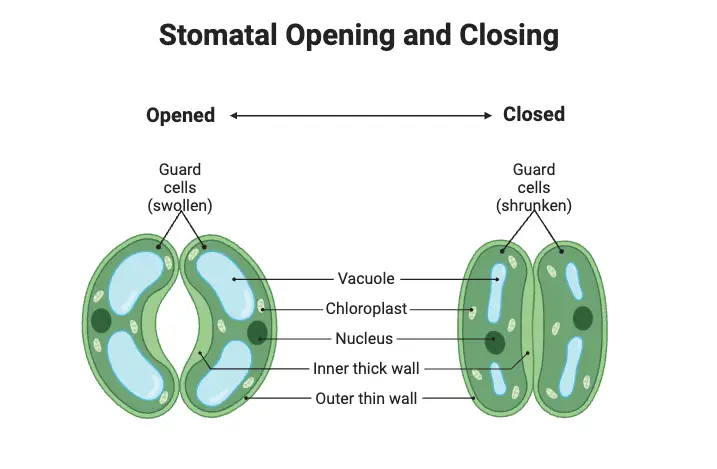
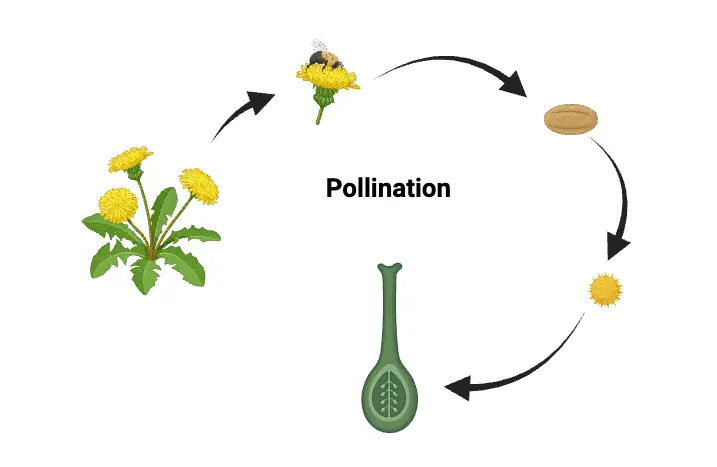
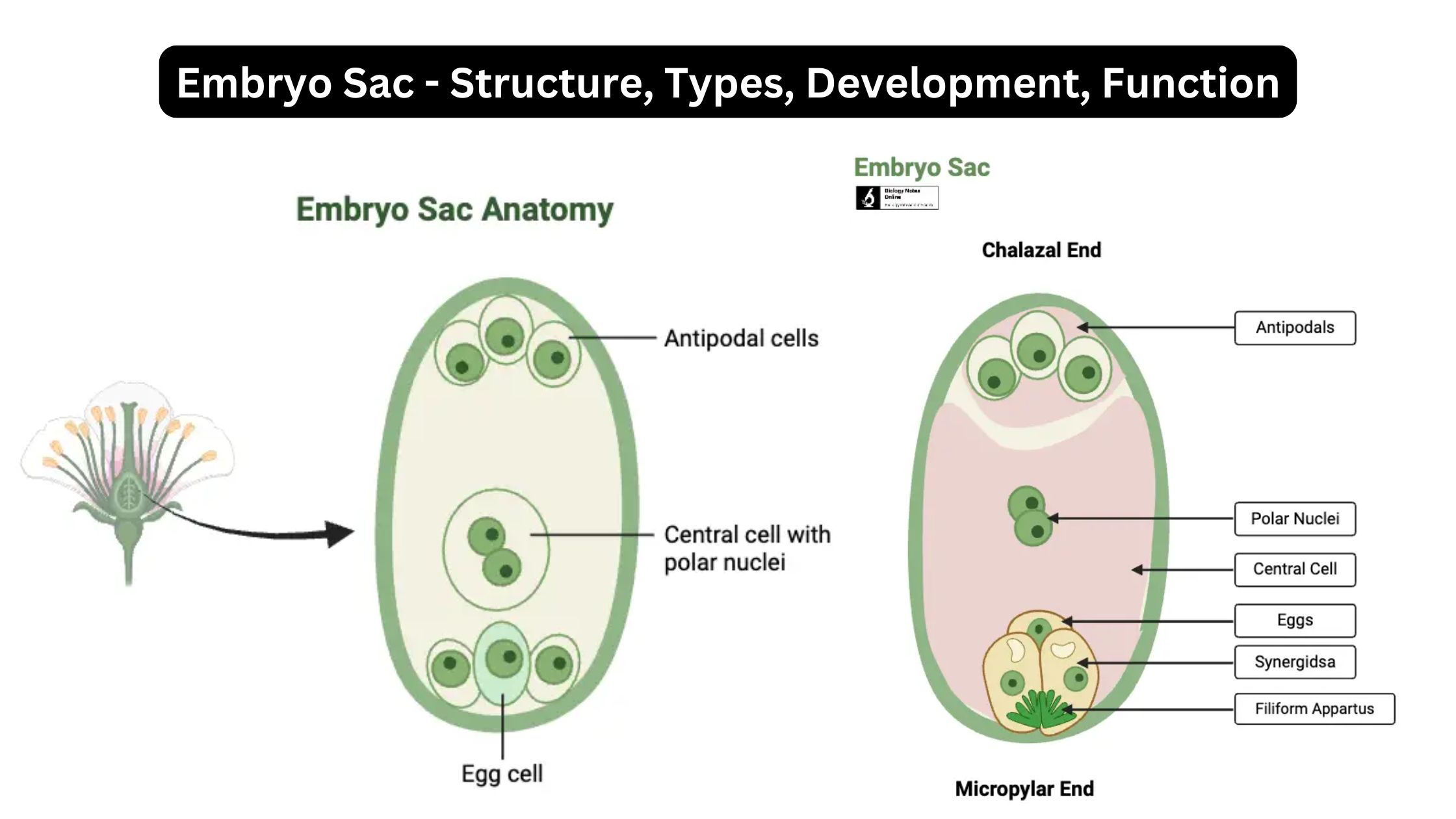
Plant Tissues – Definition Types, Functions
What are Plant Tissues? Plant tissues are organized cell groups within a plant that collectively enable essential life functions, like growth, protection, and nutrient transport. There are two main categories of plant tissues: meristematic and permanent. Meristematic tissues contain actively dividing cells that promote growth. Found in regions like root and shoot tips, these cells … Read more