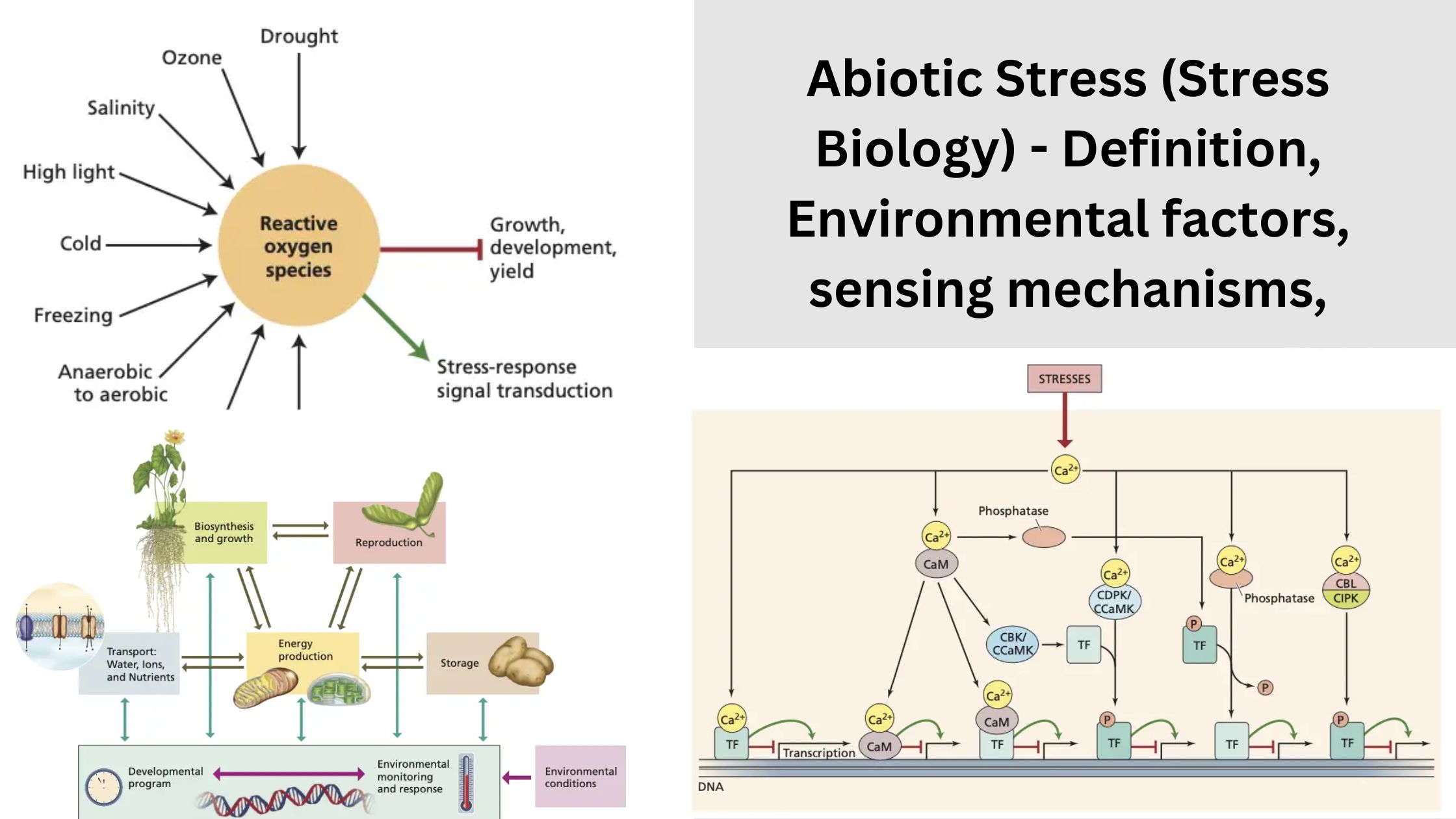
Landscaping and Garden Design
What is Landscape Gardening? Landscape gardening is a specialized field that integrates art and science to enhance the aesthetic and functional aspects of outdoor spaces. It involves the systematic planning and design of gardens while considering various environmental factors, plant selections, and local conditions. The goal is to create a harmonious landscape that reflects the … Read more