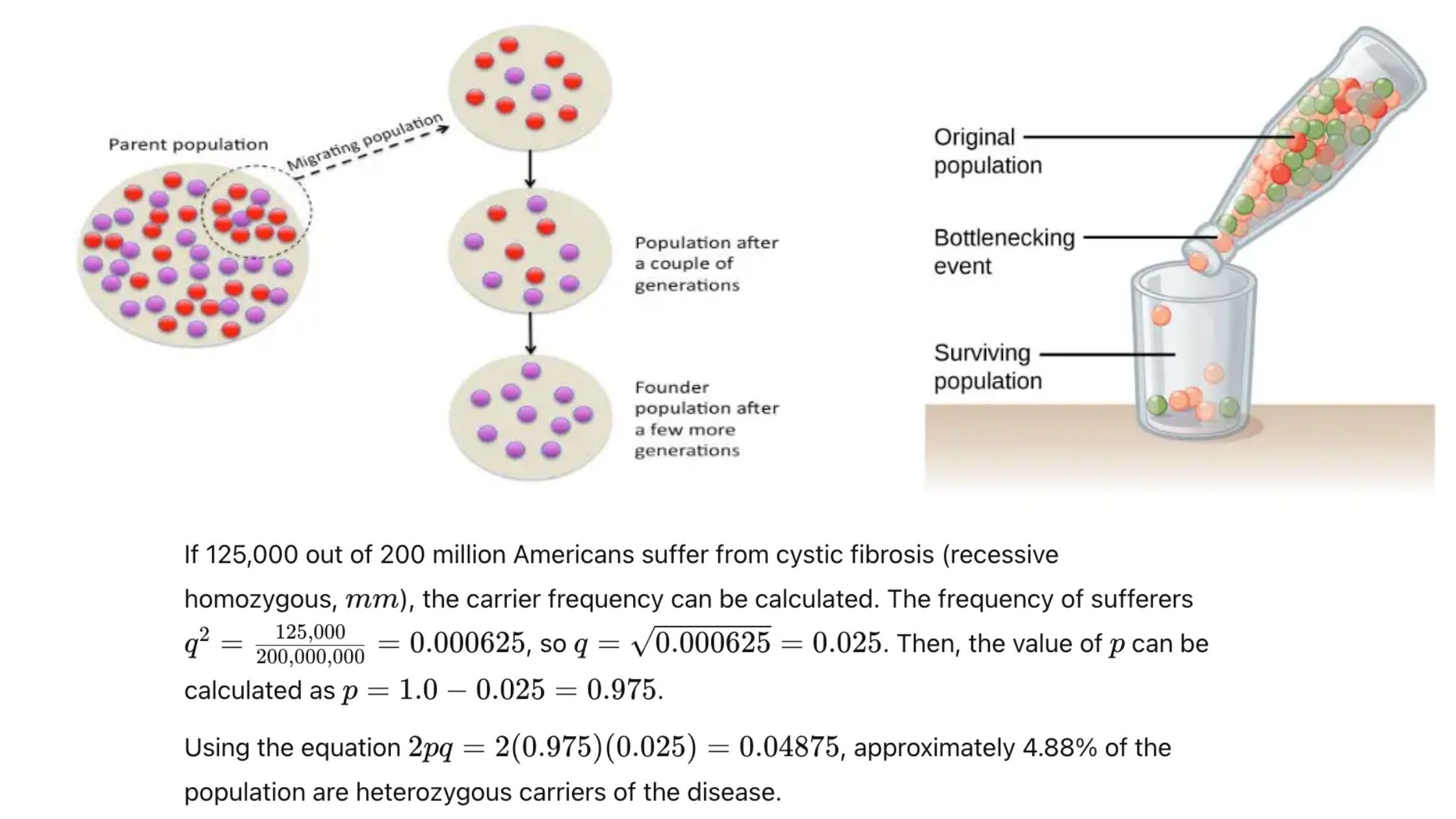
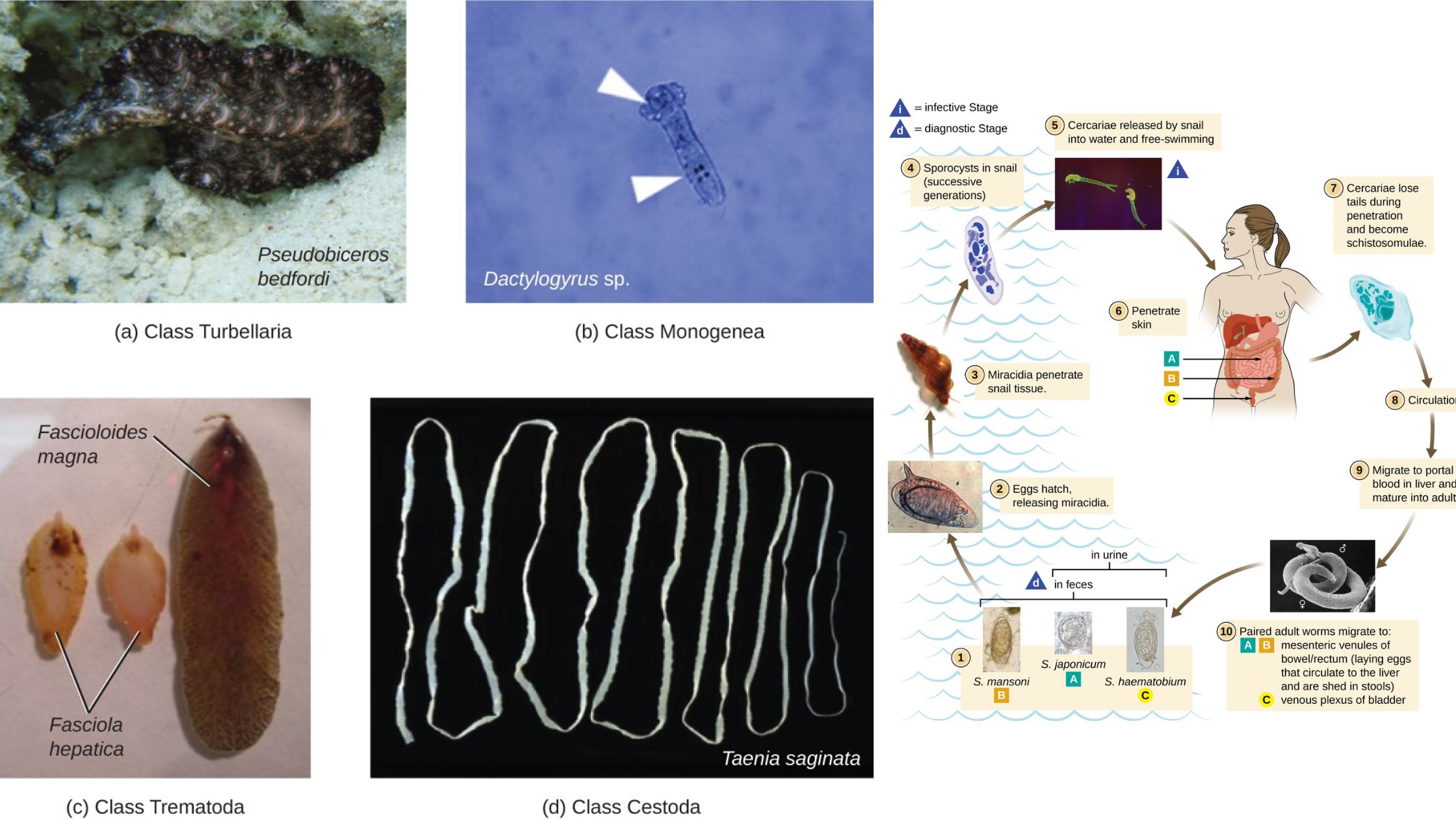
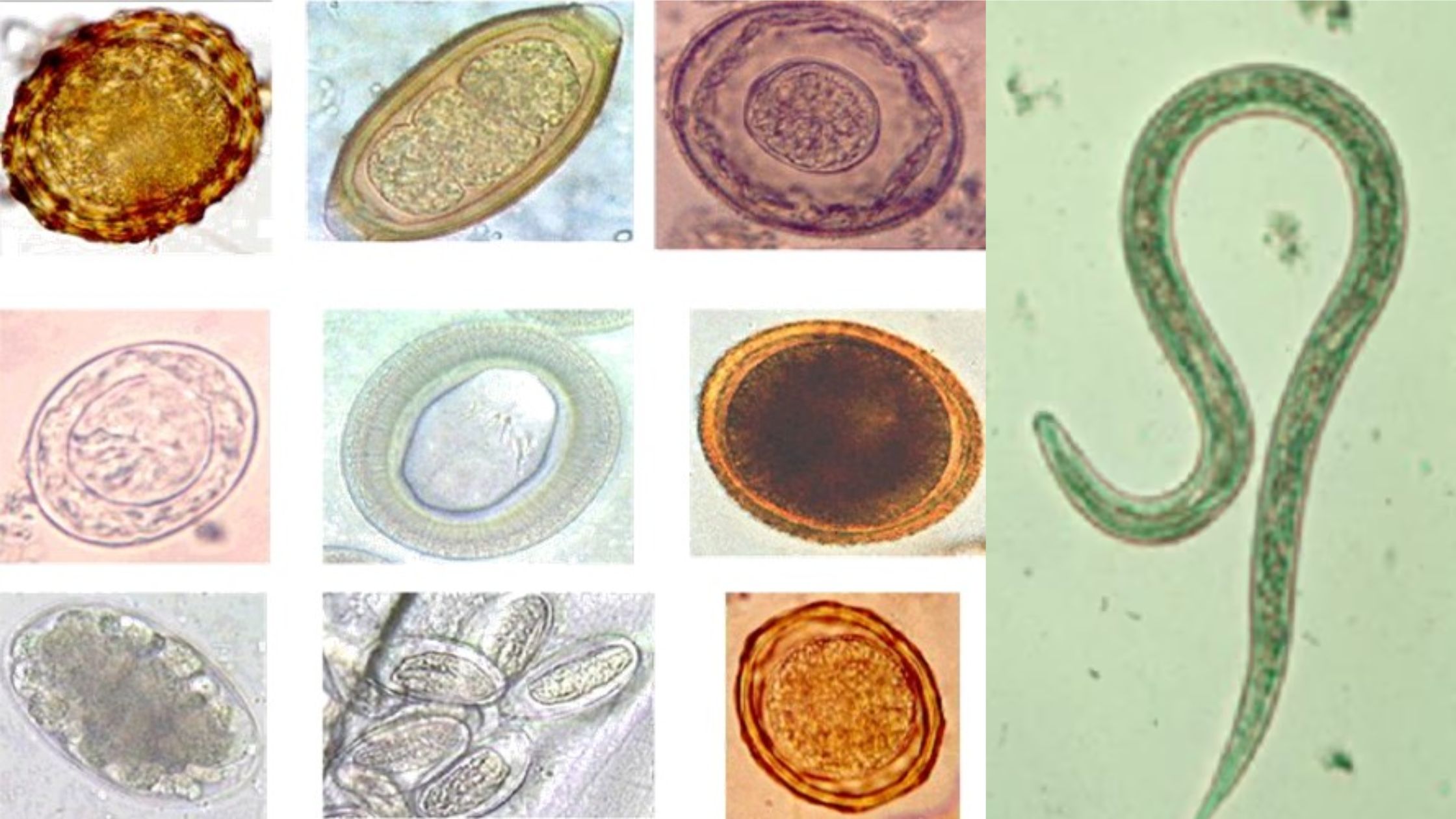
Ecology in Wildlife Conservation and Management
India boasts an exceptionally rich wildlife heritage, underpinned by a long-standing tradition of conservation. The ethical foundation of wildlife preservation in India can be traced to ancient times, where conservation principles were embedded within the cultural and spiritual practices of its people. These values were cultivated by sages, emphasizing the connection between humans and nature. … Read more