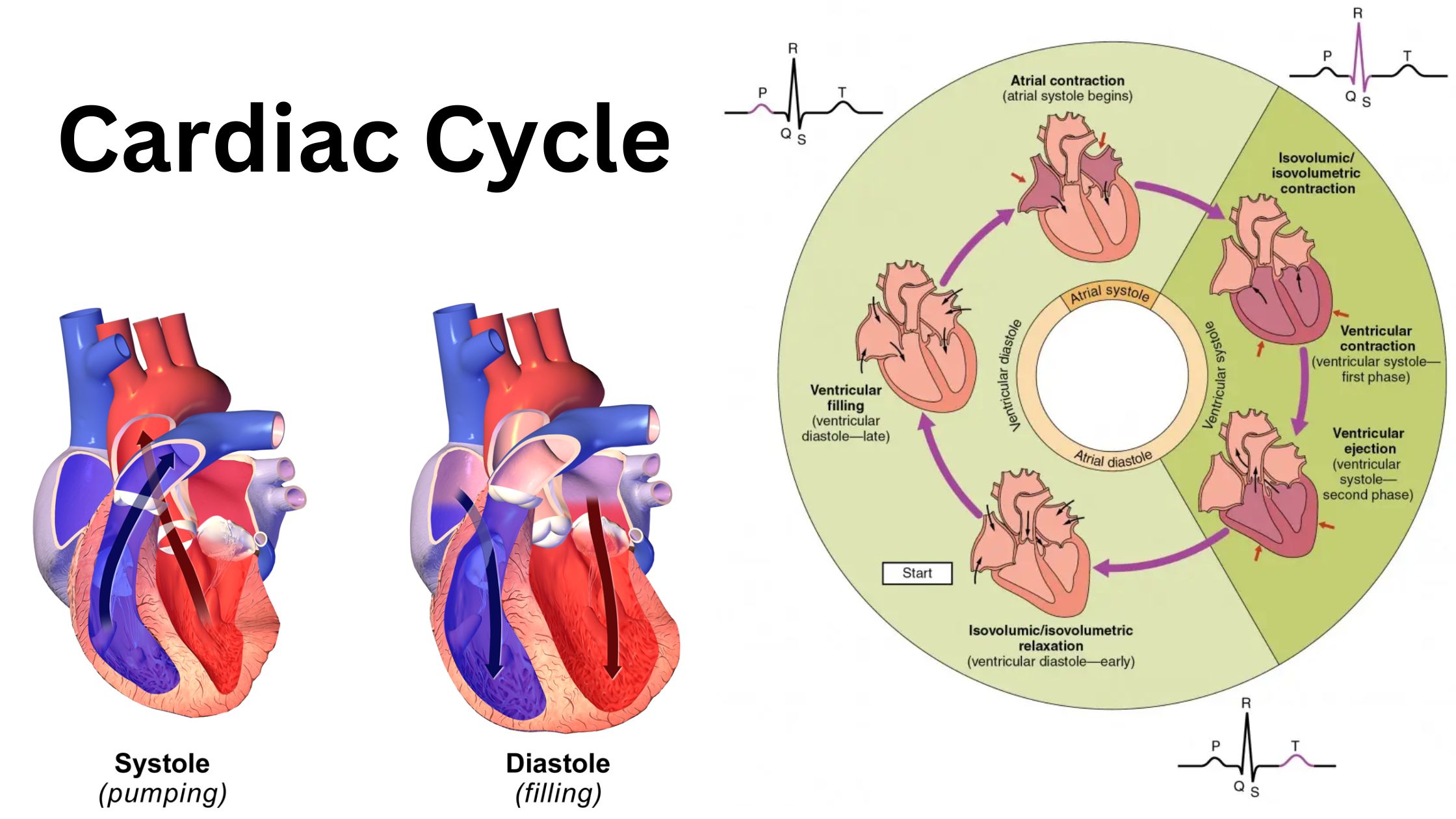
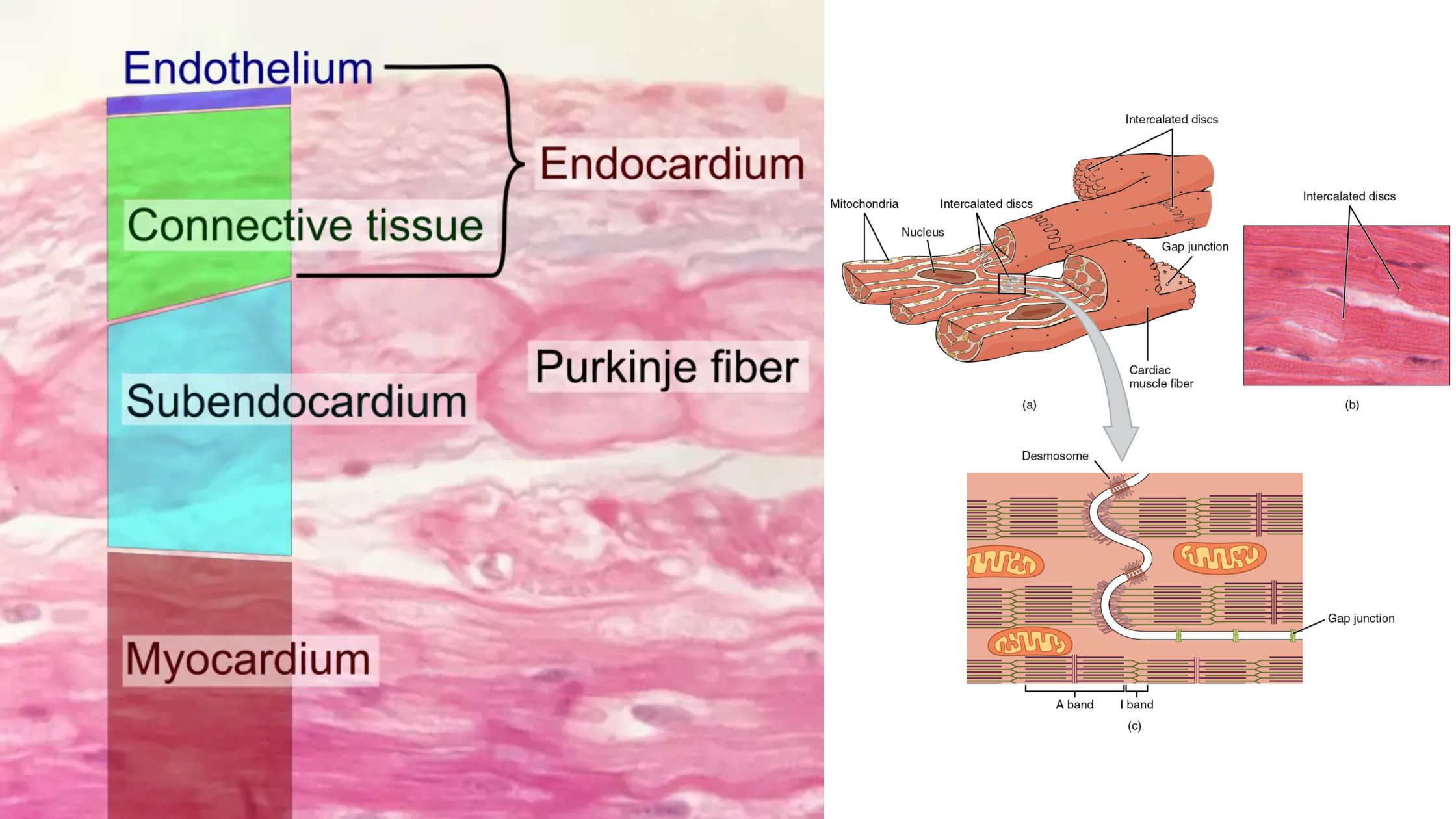
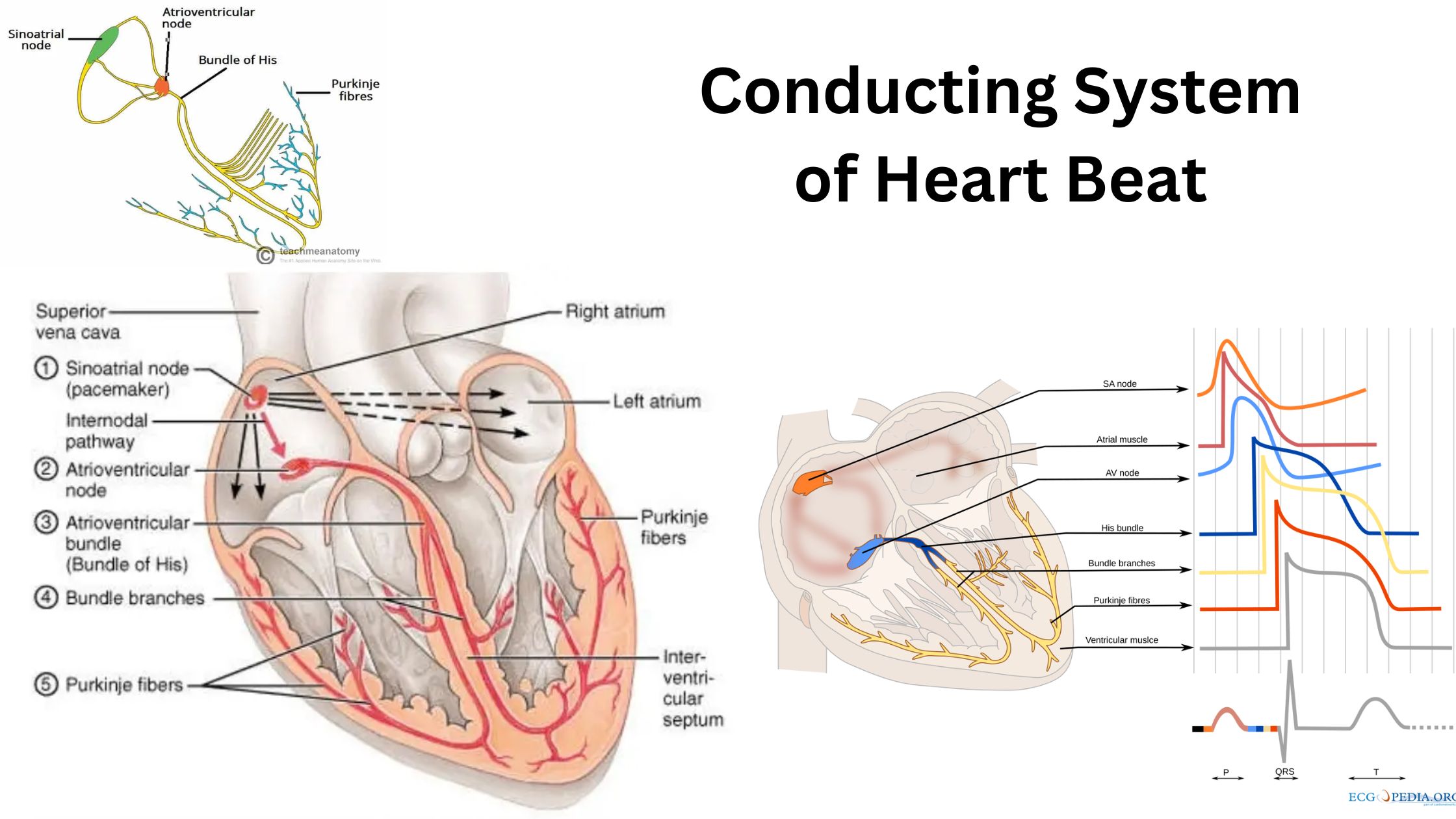
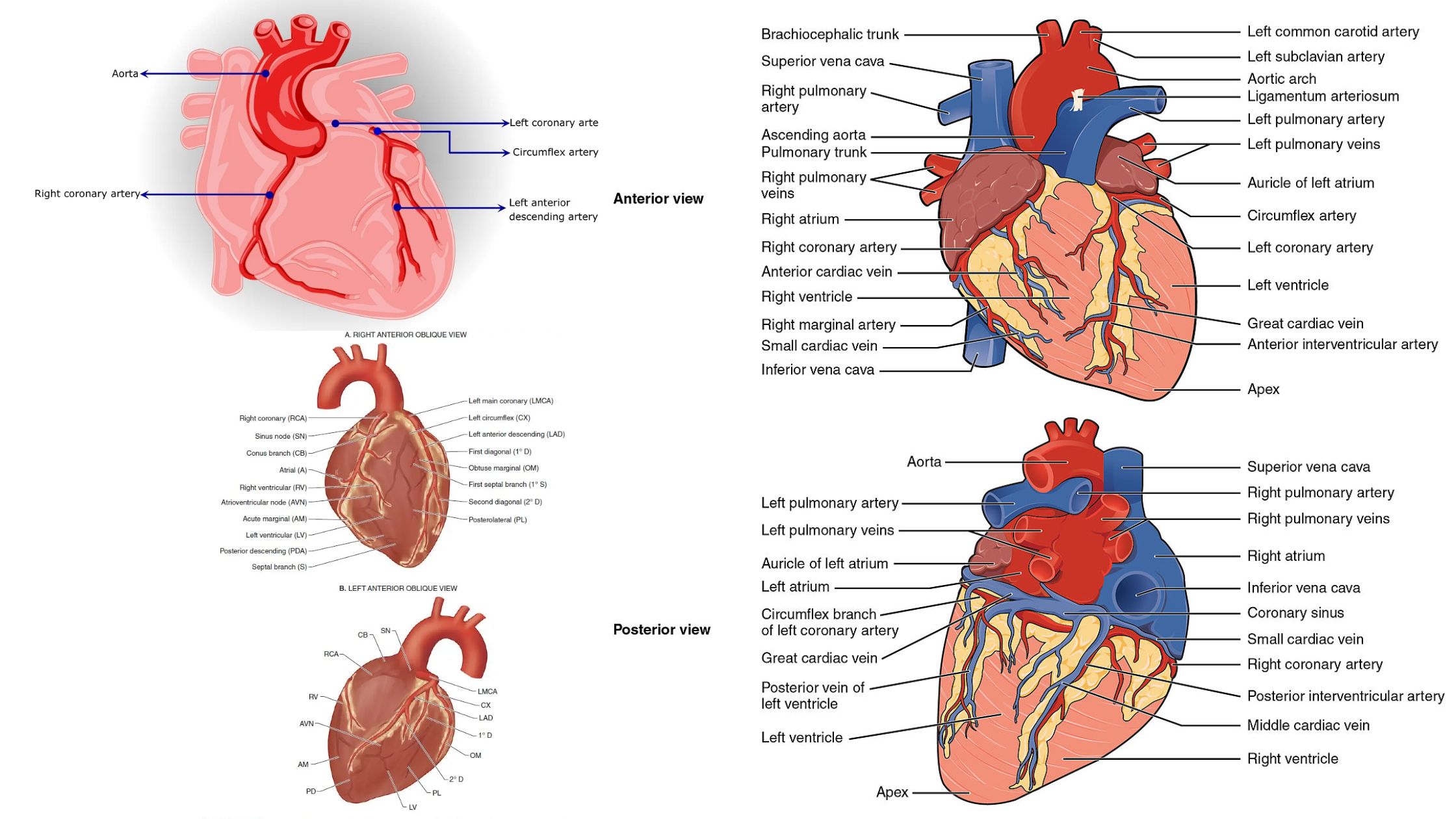
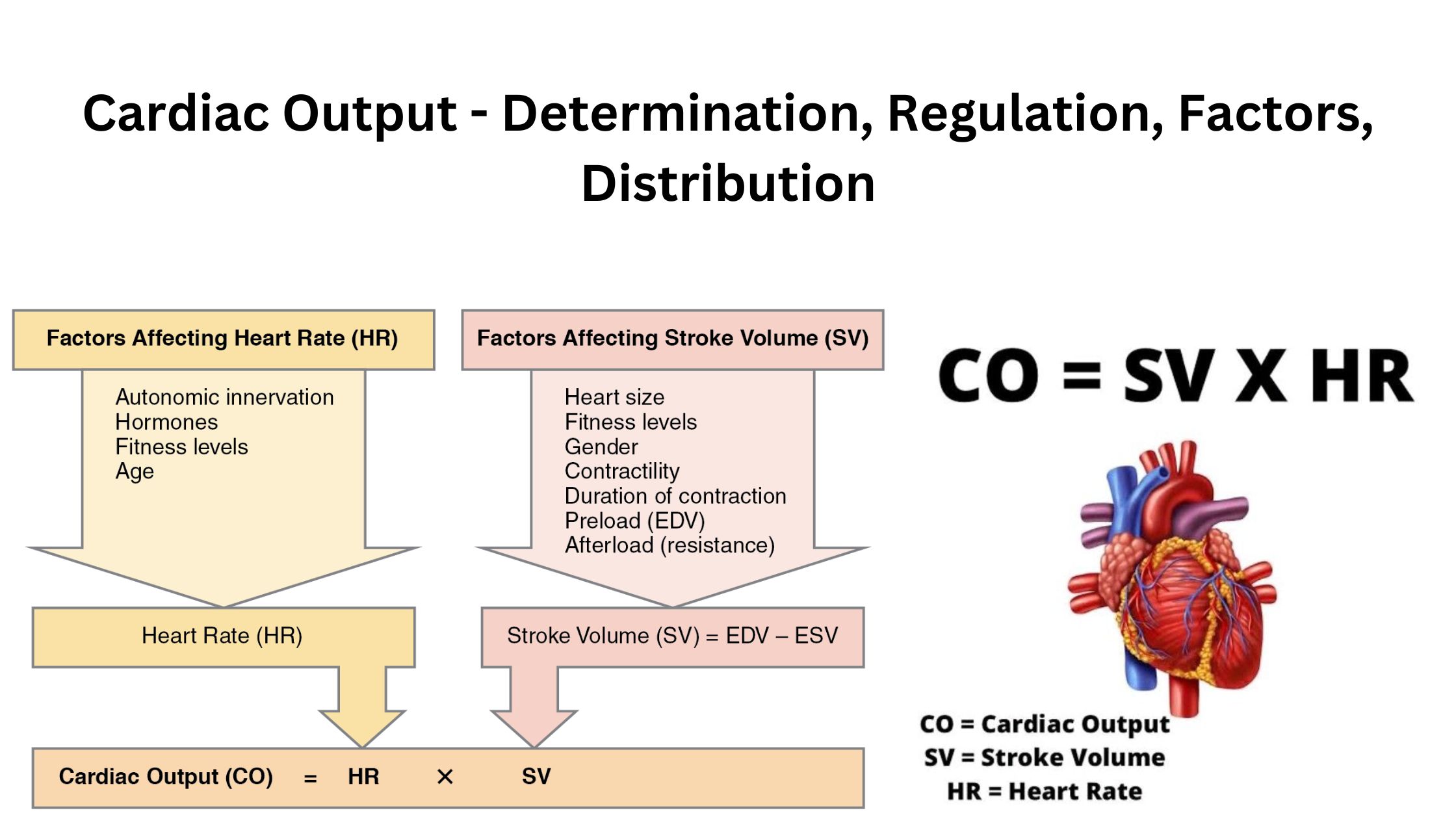
Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Purpose, Principle, Parts, Types, Procedure, Application
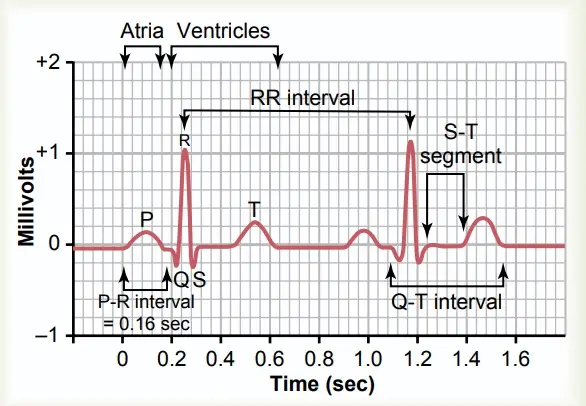
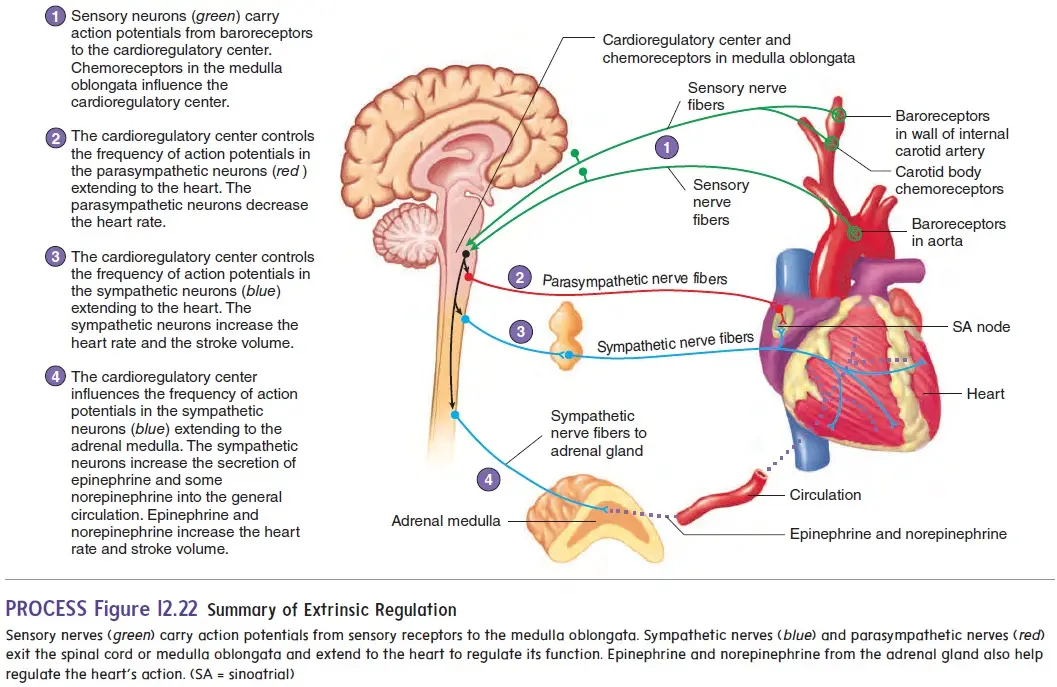
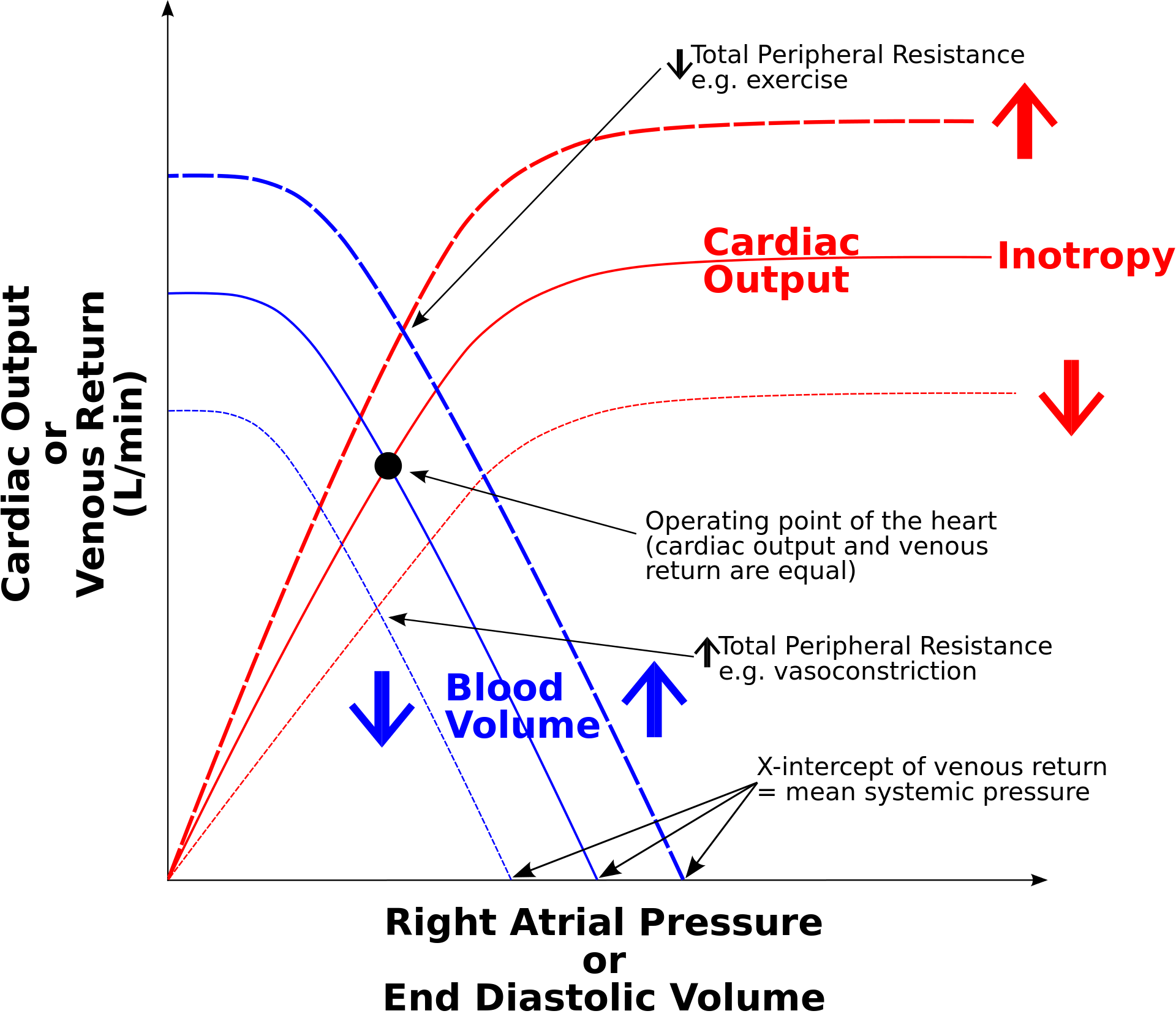
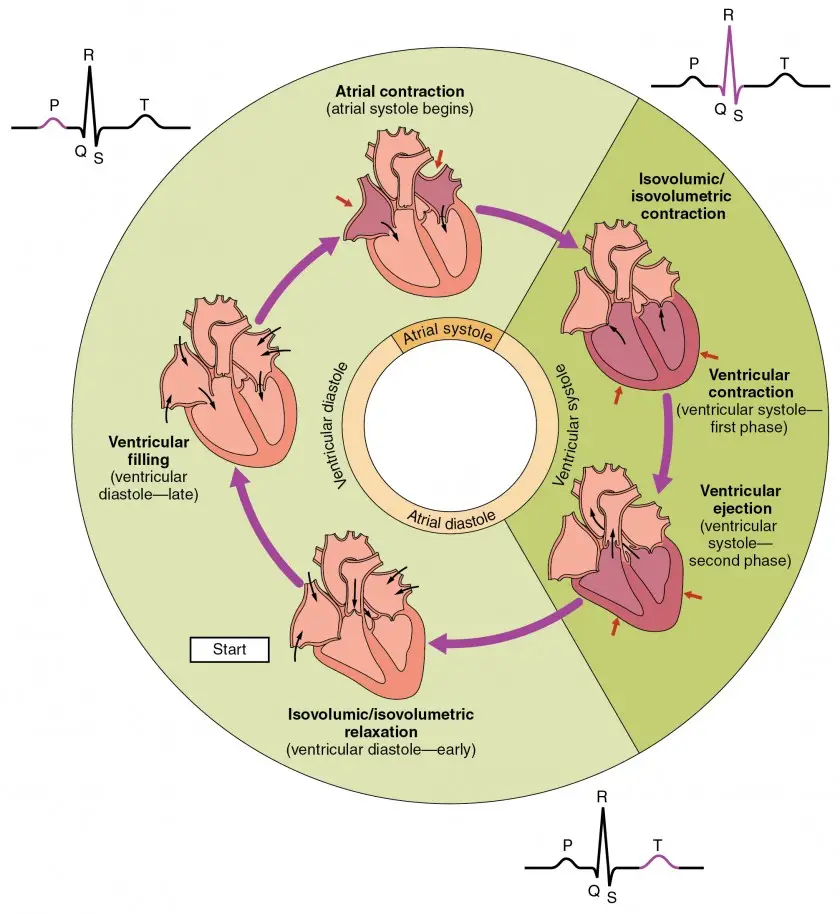
What is Electrocardiogram (ECG)? Purpose of ECG Test The electrocardiogram (ECG) test is a fundamental diagnostic tool utilized in cardiology to assess the heart’s electrical activity and rhythm. Its purposes are multifaceted, enabling healthcare providers to detect, diagnose, and monitor various cardiac conditions effectively. Working principle of electrocardiograph/Electrocardiogram Waves of Normal ECG A normal electrocardiogram … Read more