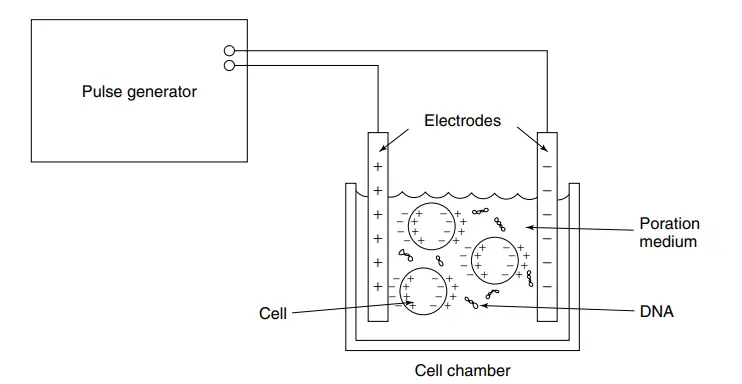
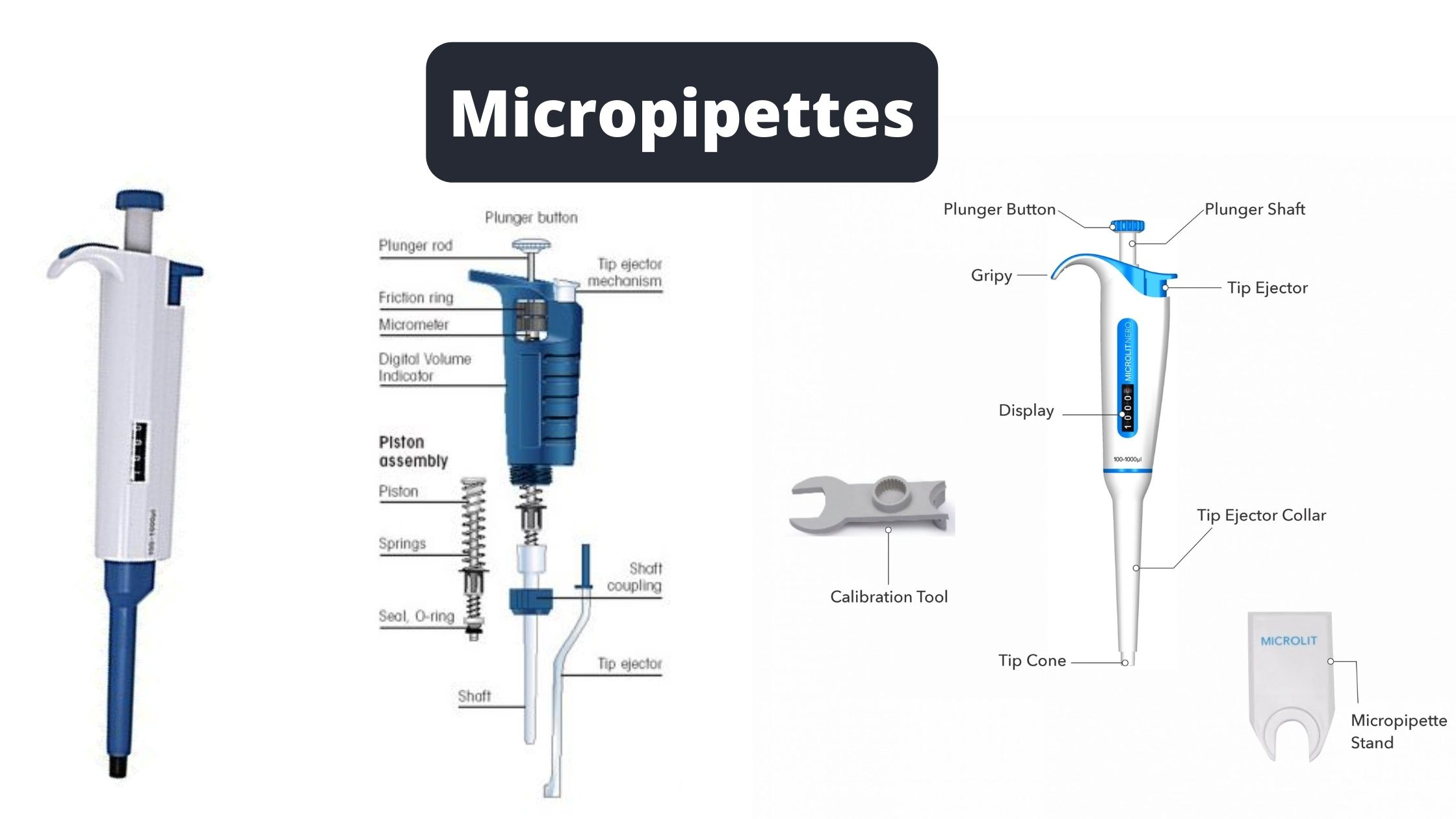
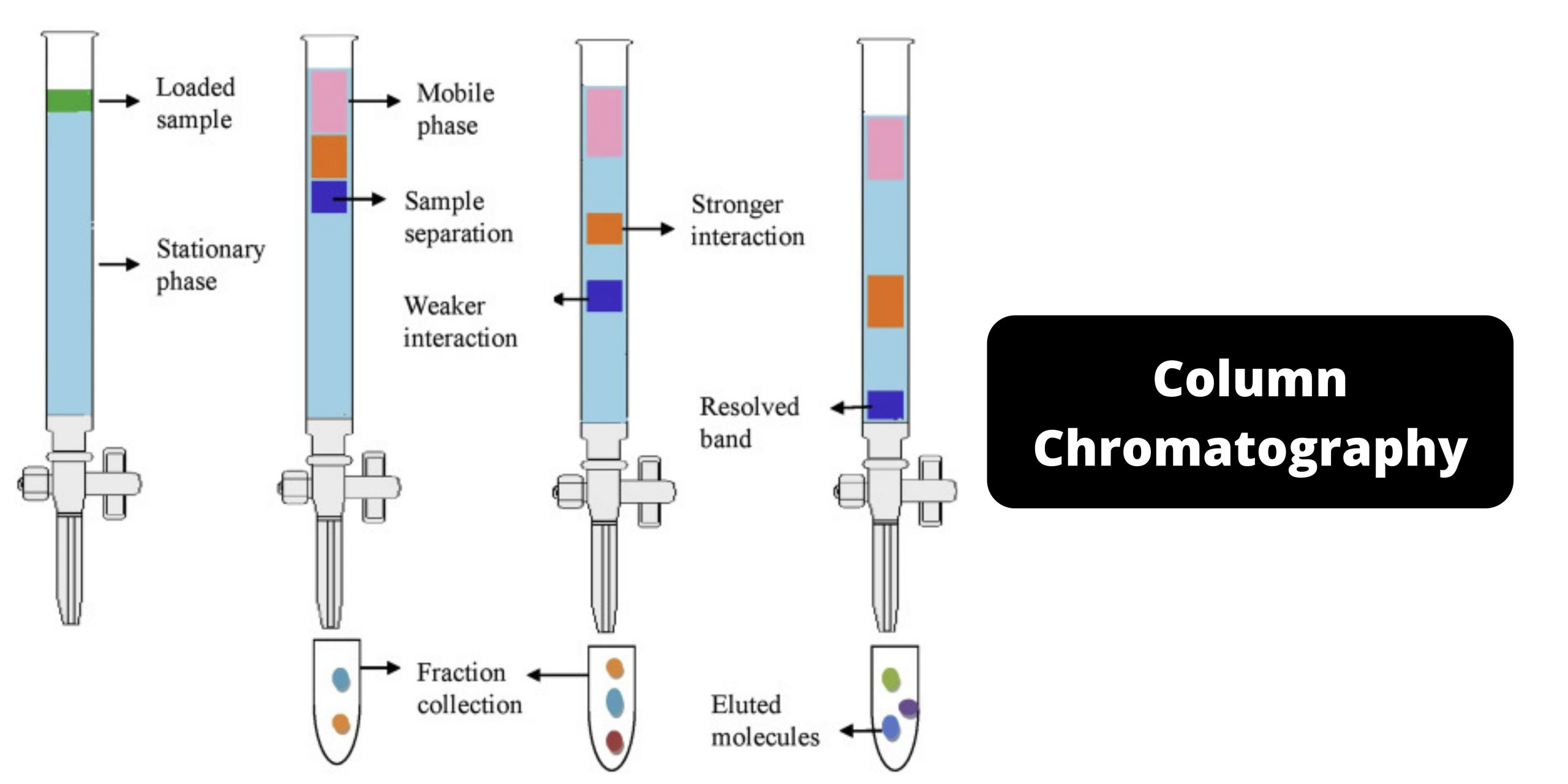
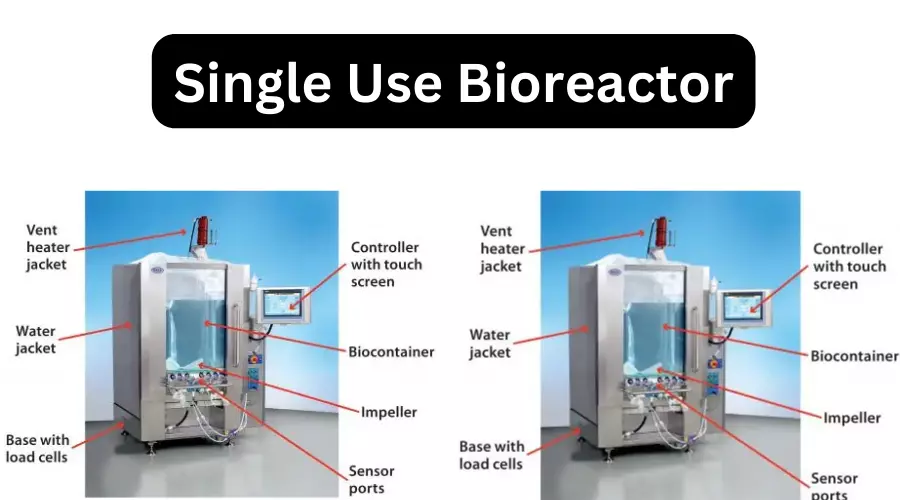
Electroporator – Definition, Principle, Types, Protocol, Applications
What is Electroporator (Electroporation machine)? An electroporator, often called an electroporation machine, is a lab instrument used to temporarily make cell membranes more permeable. Think of it as a precision tool that helps scientists sneak substances like DNA, drugs, or proteins into cells—something that’s tricky to do manually because cell membranes are naturally protective. The … Read more