Microbial degradation of Pectin – Enzymes, Steps, Mechanisms
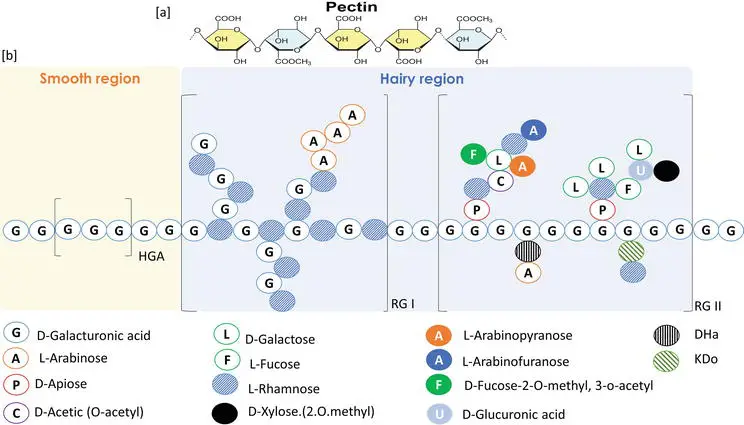
Pectin is a complicated polysaccharide that is mostly found in the cell walls of plants, notably fruits. It is a structural heteropolysaccharide made up mostly of units of galacturonic acid. Pectin is a glue that holds plant cells together, making the plant tissue strong and stable. In the culinary sector, it is often used as … Read more