Carbon cycle – Definition, Steps, Importance, Examples
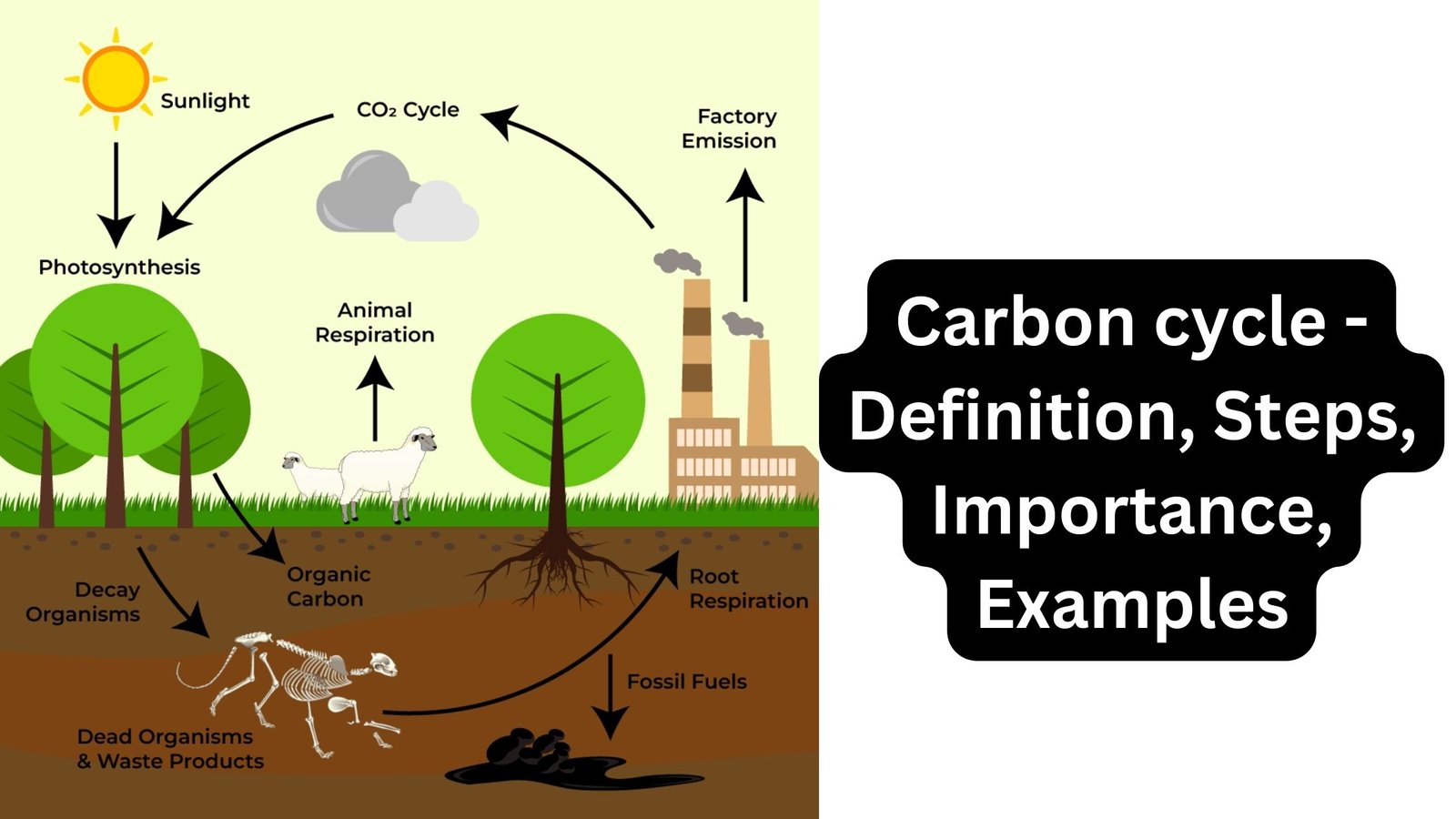
Carbon cycle Definition Carbon cycle is the process by which carbon compounds move between the earth’s atmosphere, biosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, and hydrosphere. Properties of Carbon Physical Properties of Carbon Chemical Properties of Carbon Steps of Carbon Cycle 1. Carbon in the Atmosphere 2. Producers Absorb Carbon 3. Producers are Eaten 4. Decomposers Release Carbon 5. … Read more