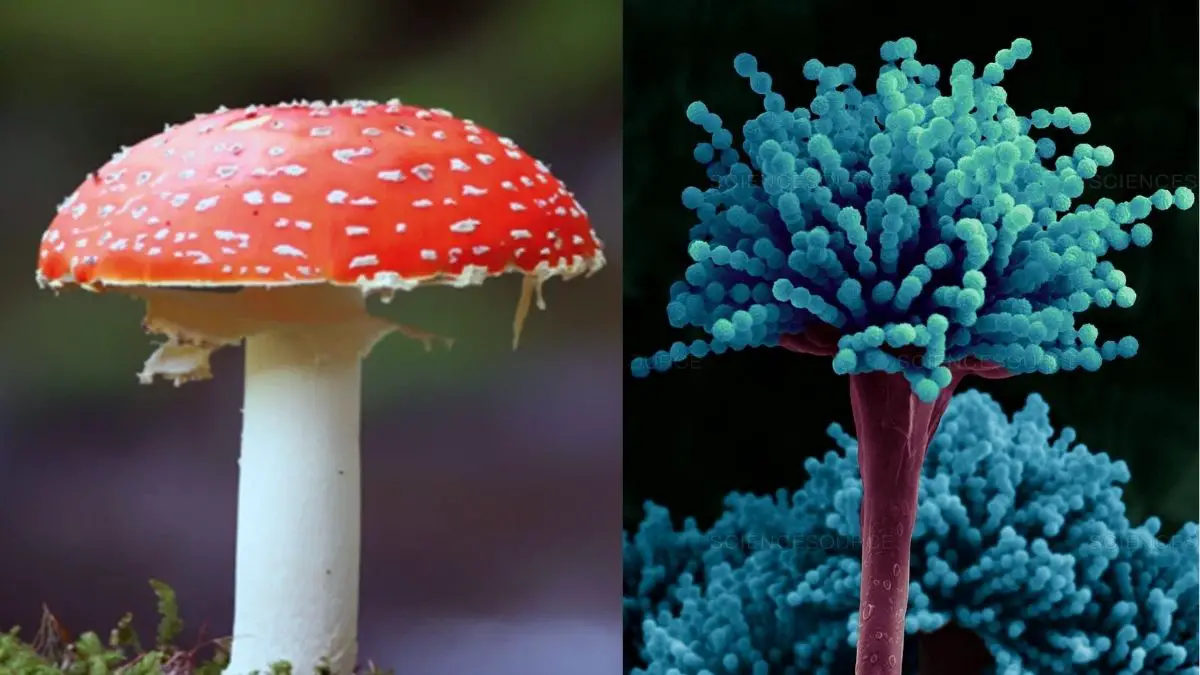
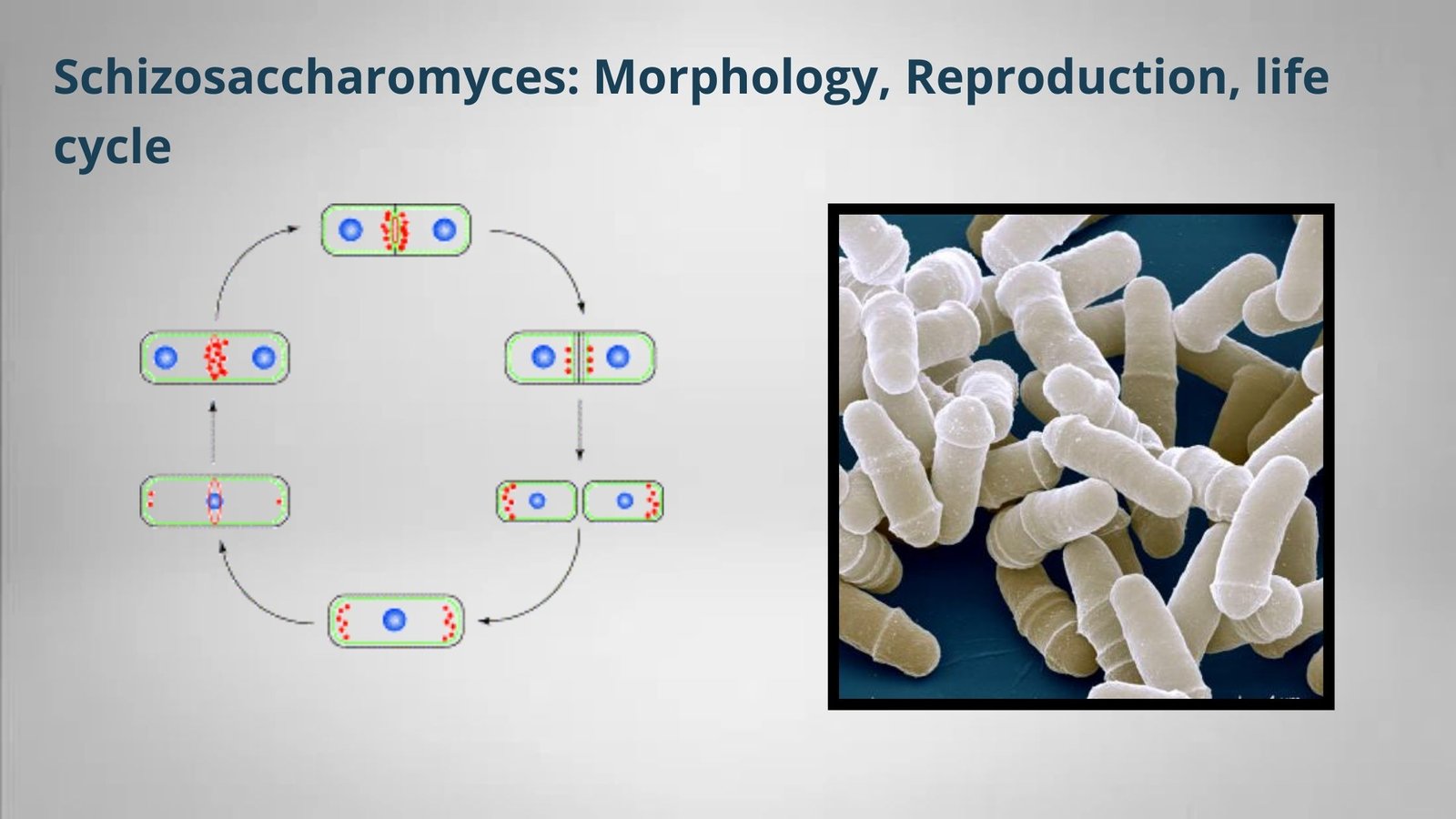
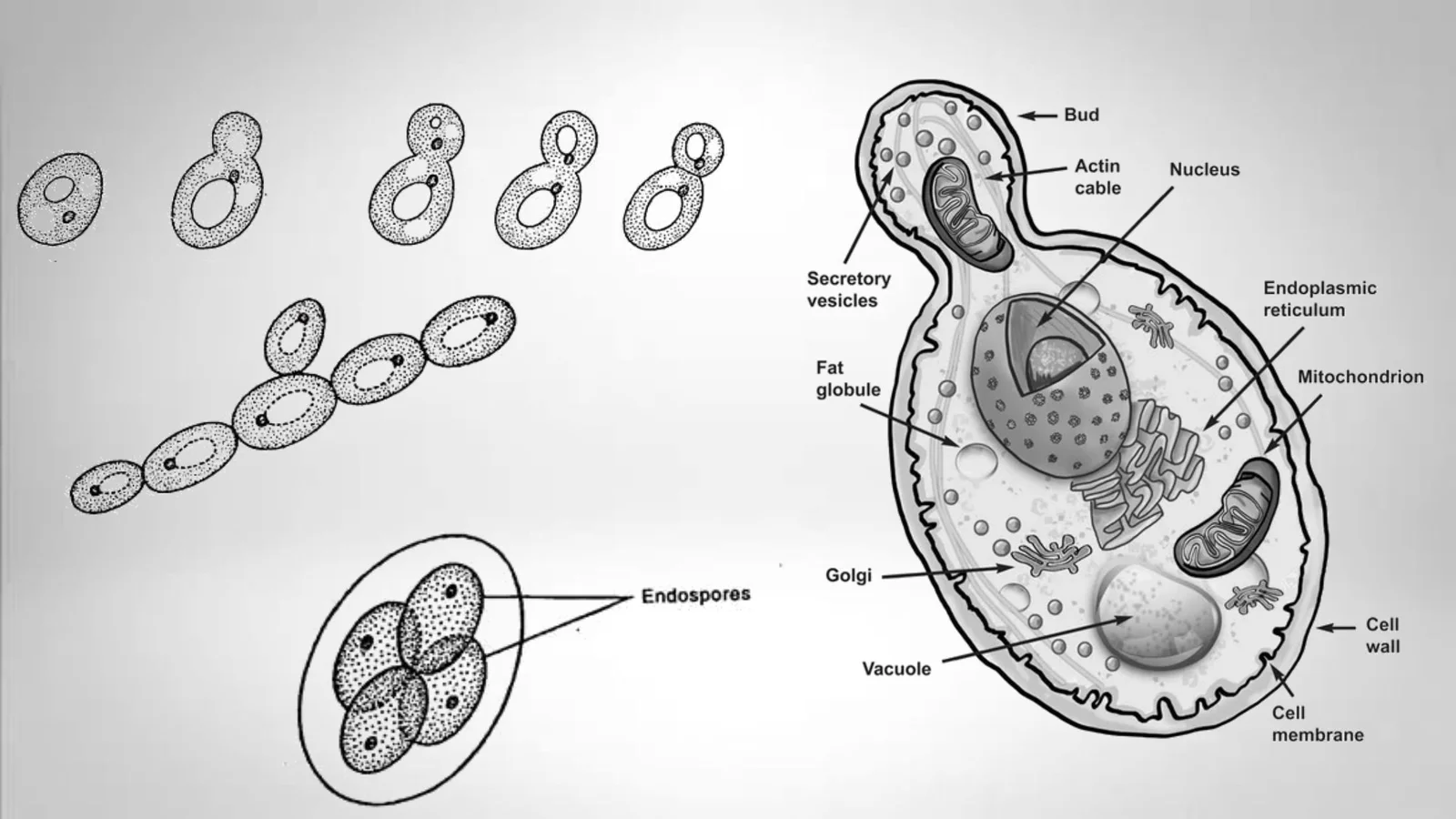
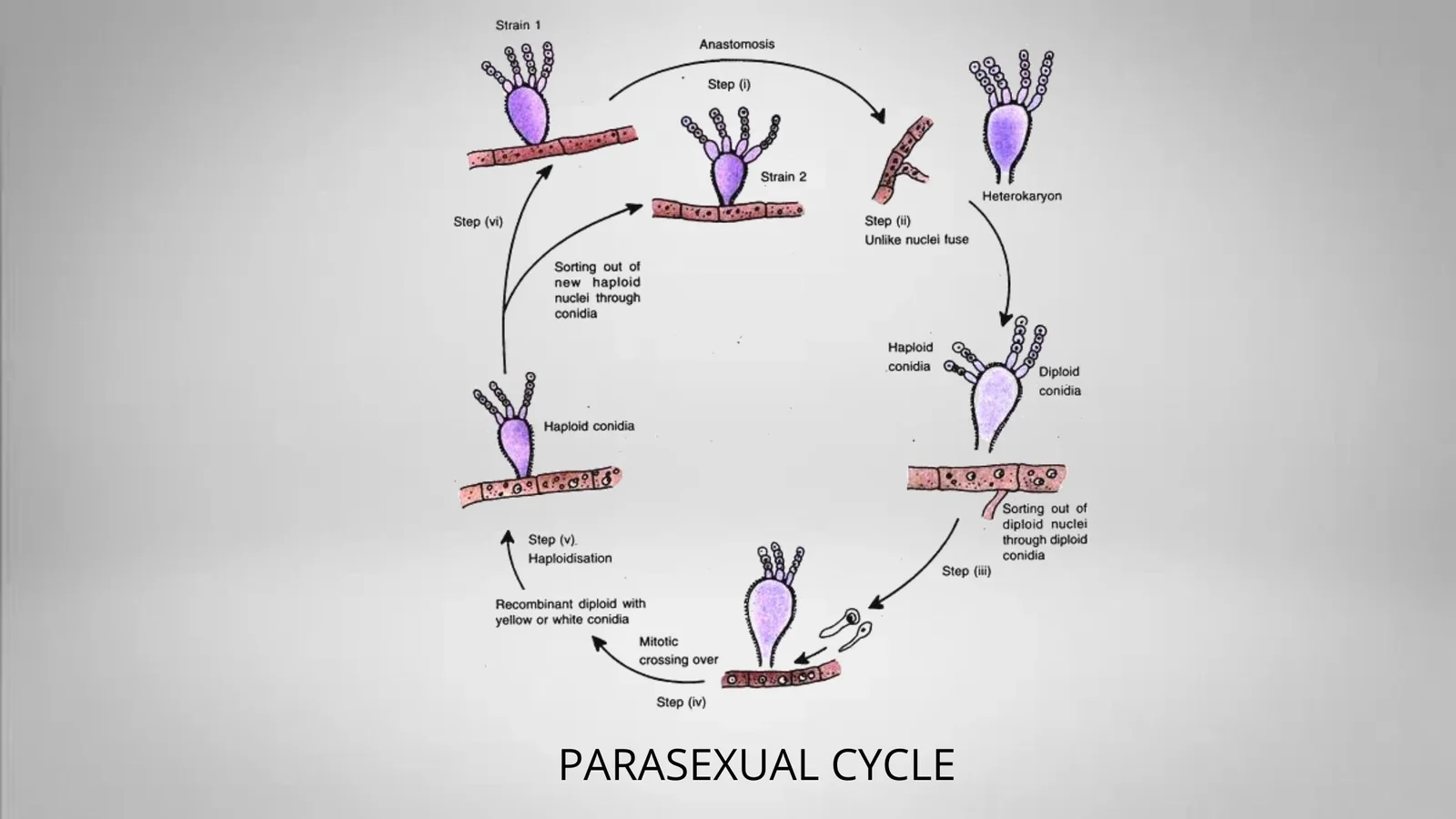
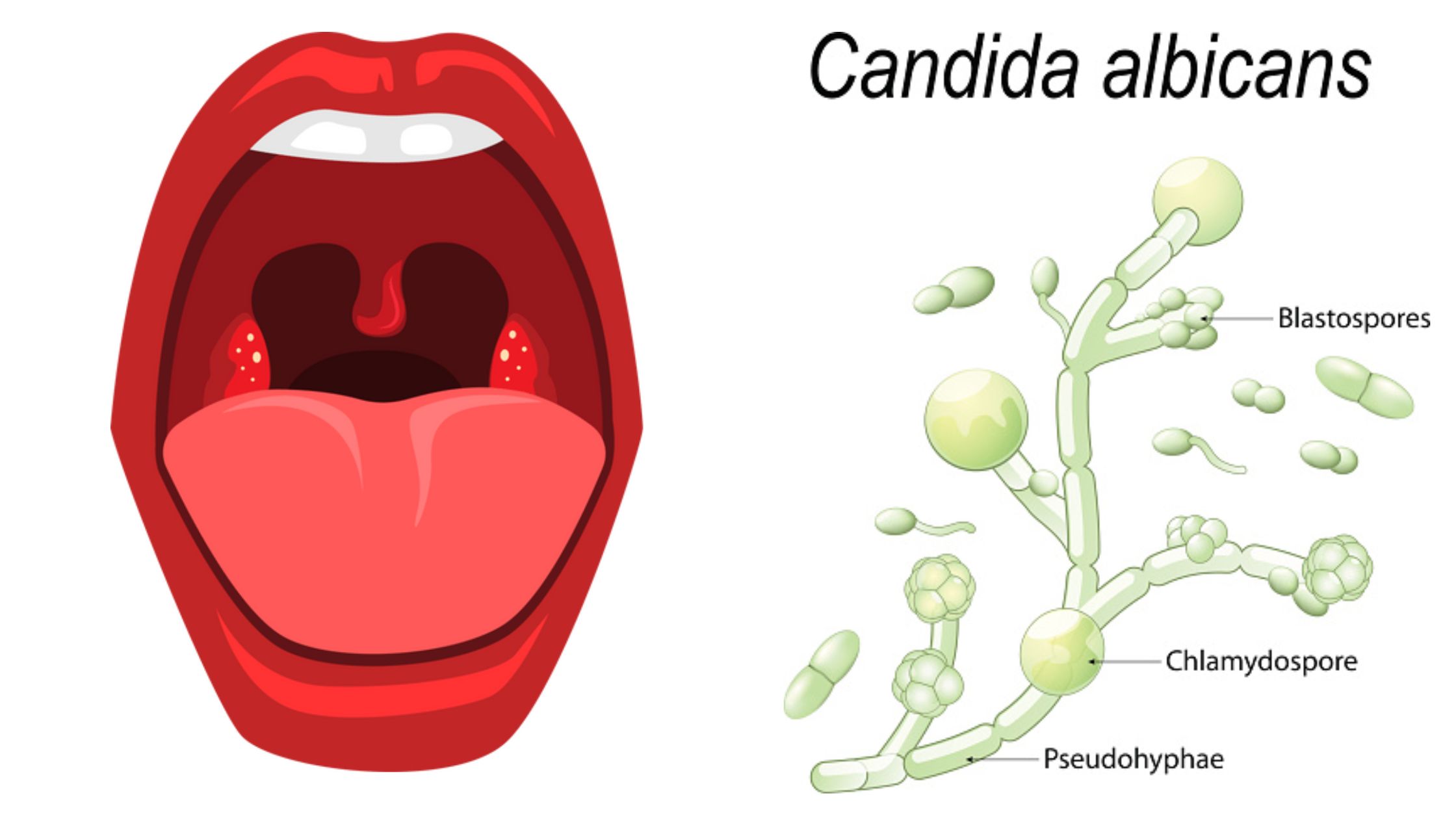
Economic Importance of Fungi In Medicine, Industry, Agriculture, and Food.
In this article, we will learn about the Economic Importance of Fungi in agriculture, industries, medicine, etc. There are present a huge number of fungi, which has tremendous economic importance to humans. Every day we benefited or were harmed directly or indirectly by those fungi. They help in yielding antibiotics, maintain the soil fertility, cause … Read more