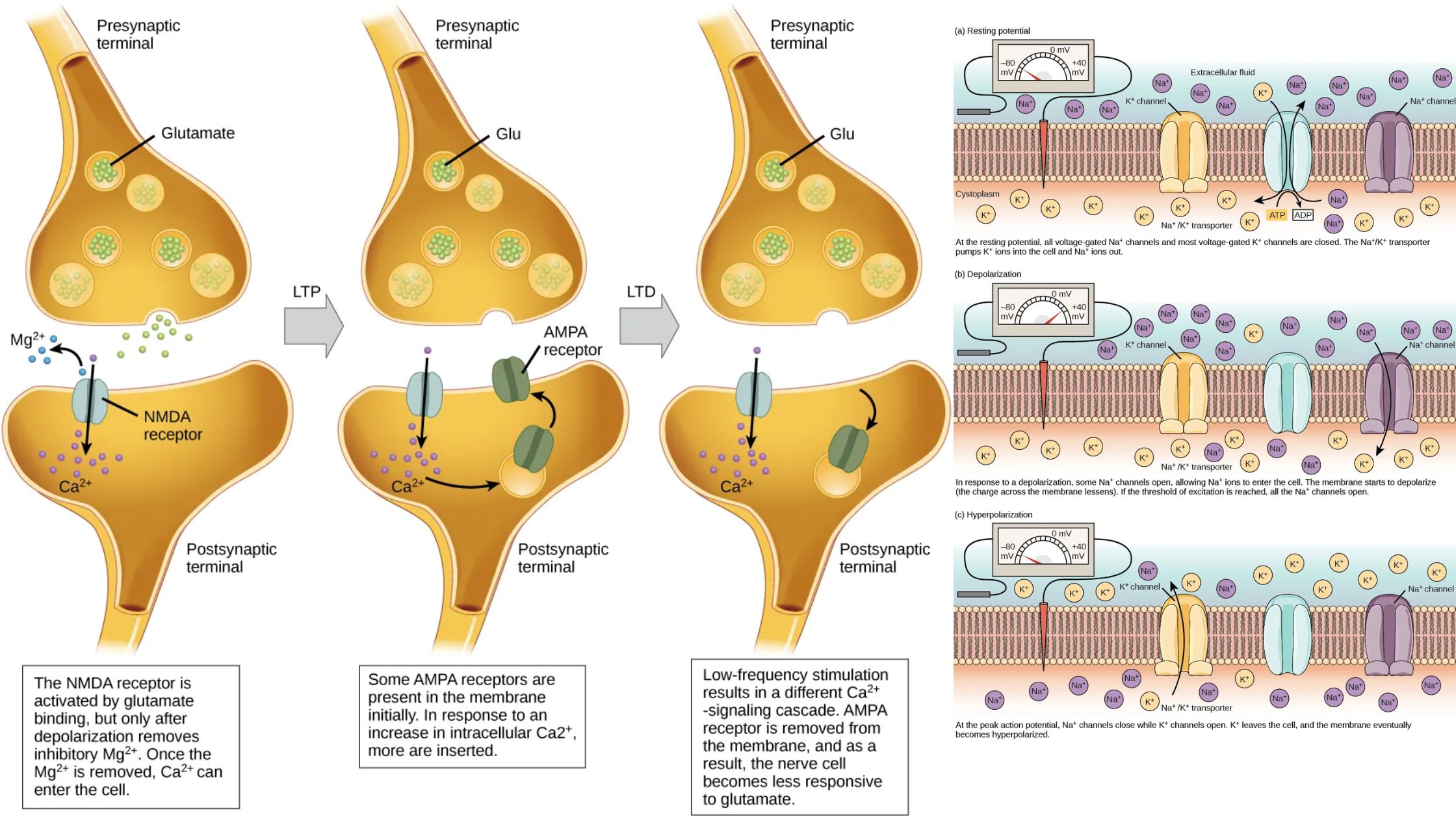
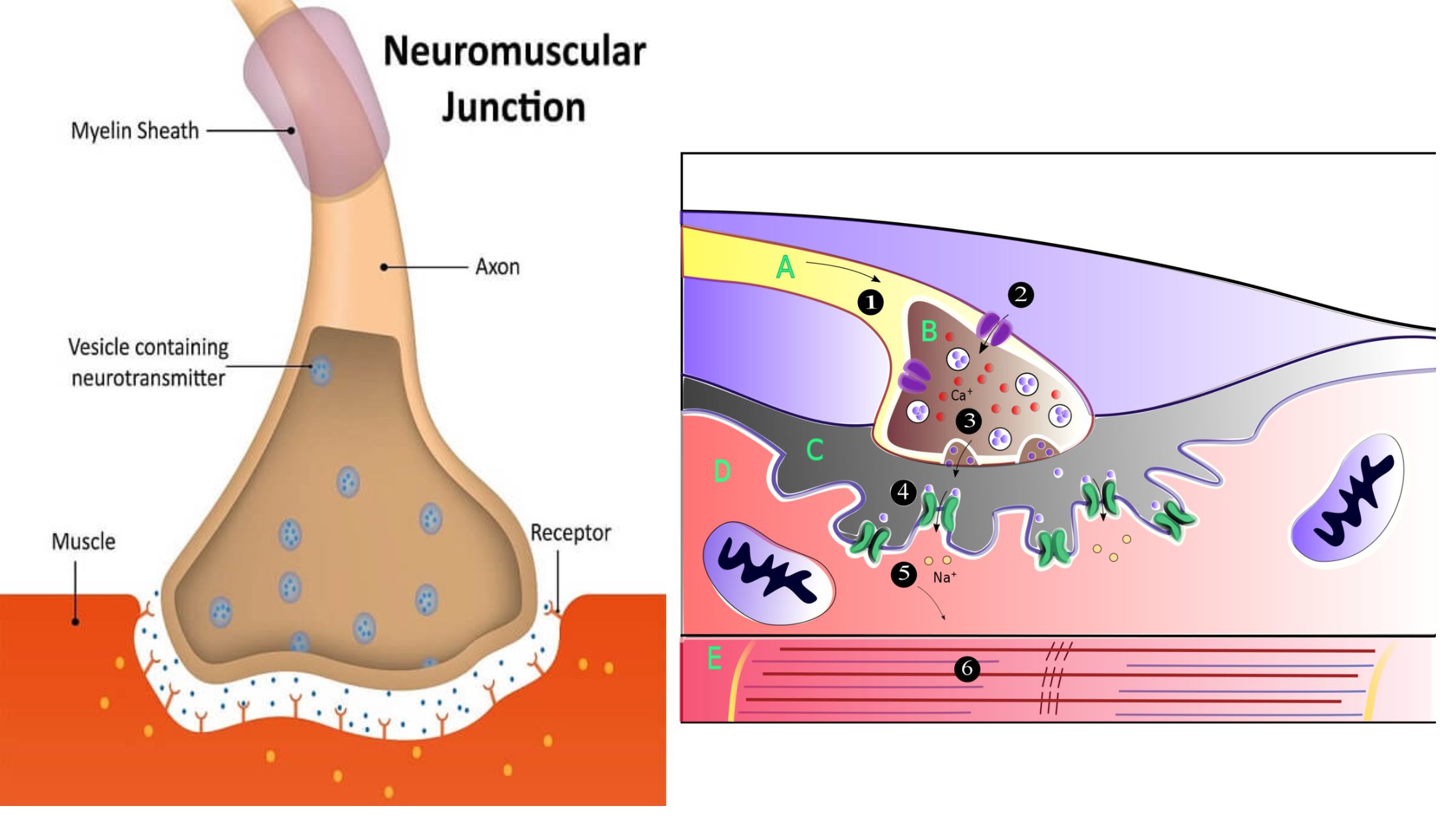
Muscle Cell – Definition, Structure, Functions, Examples
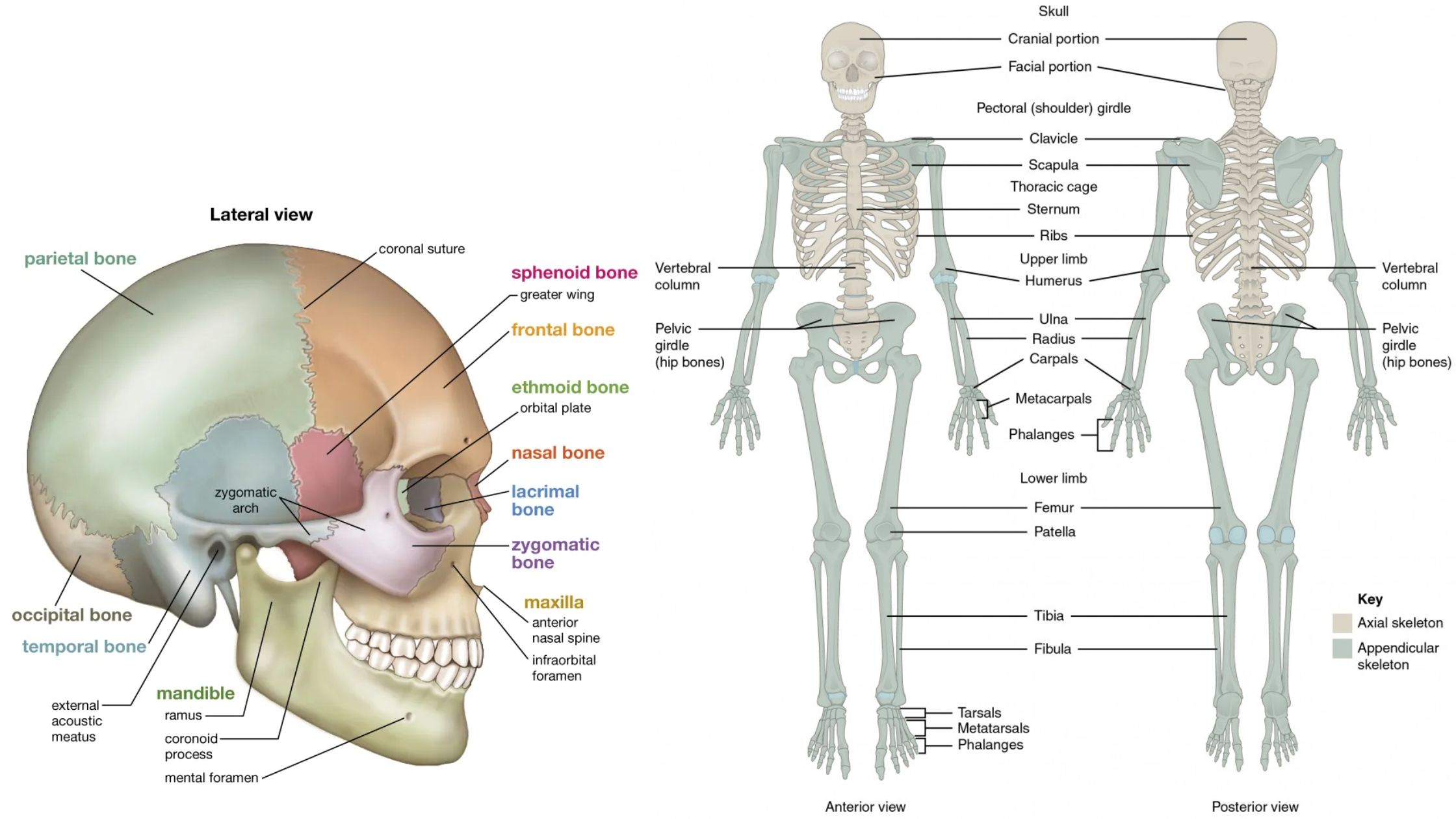
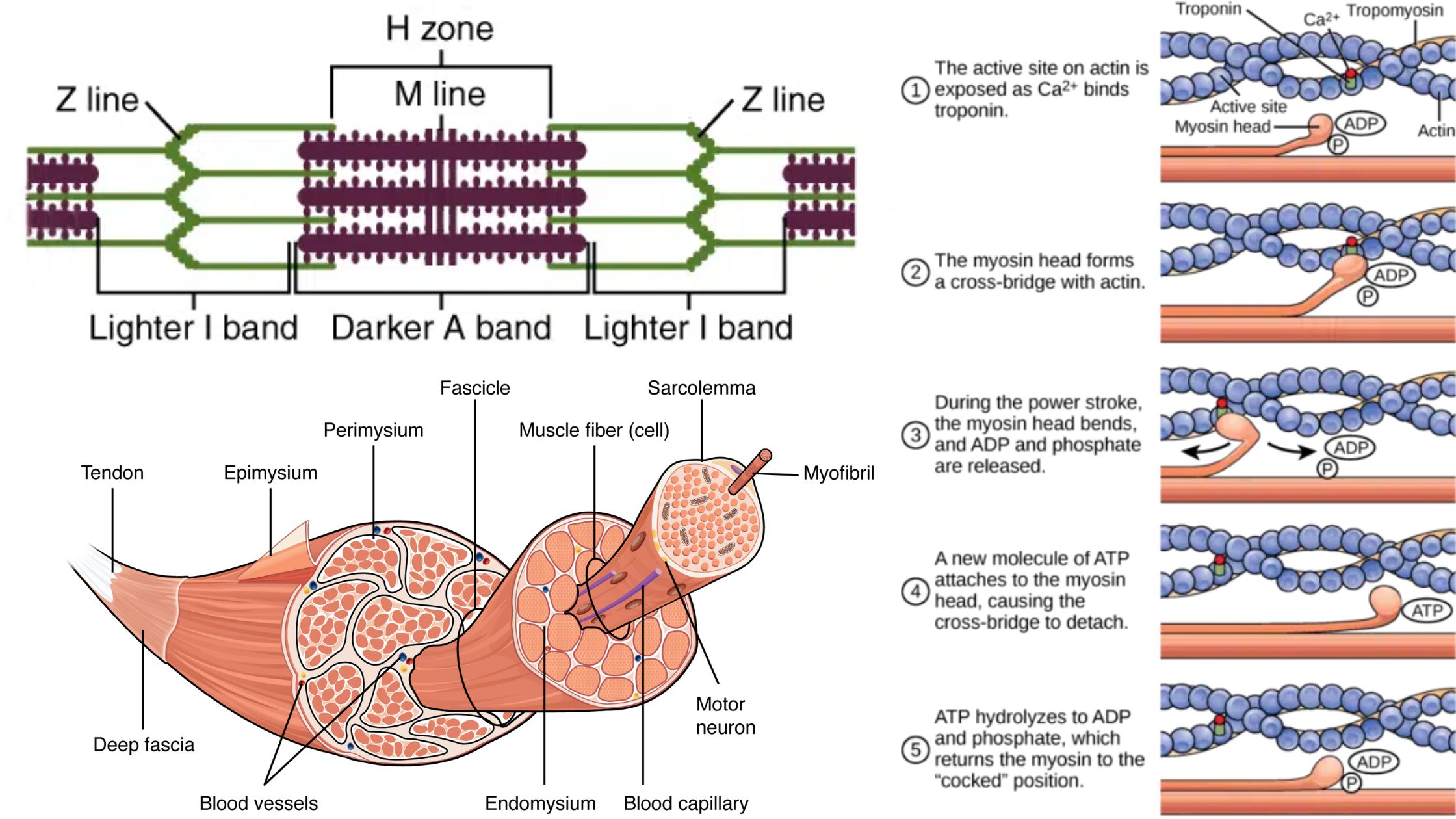
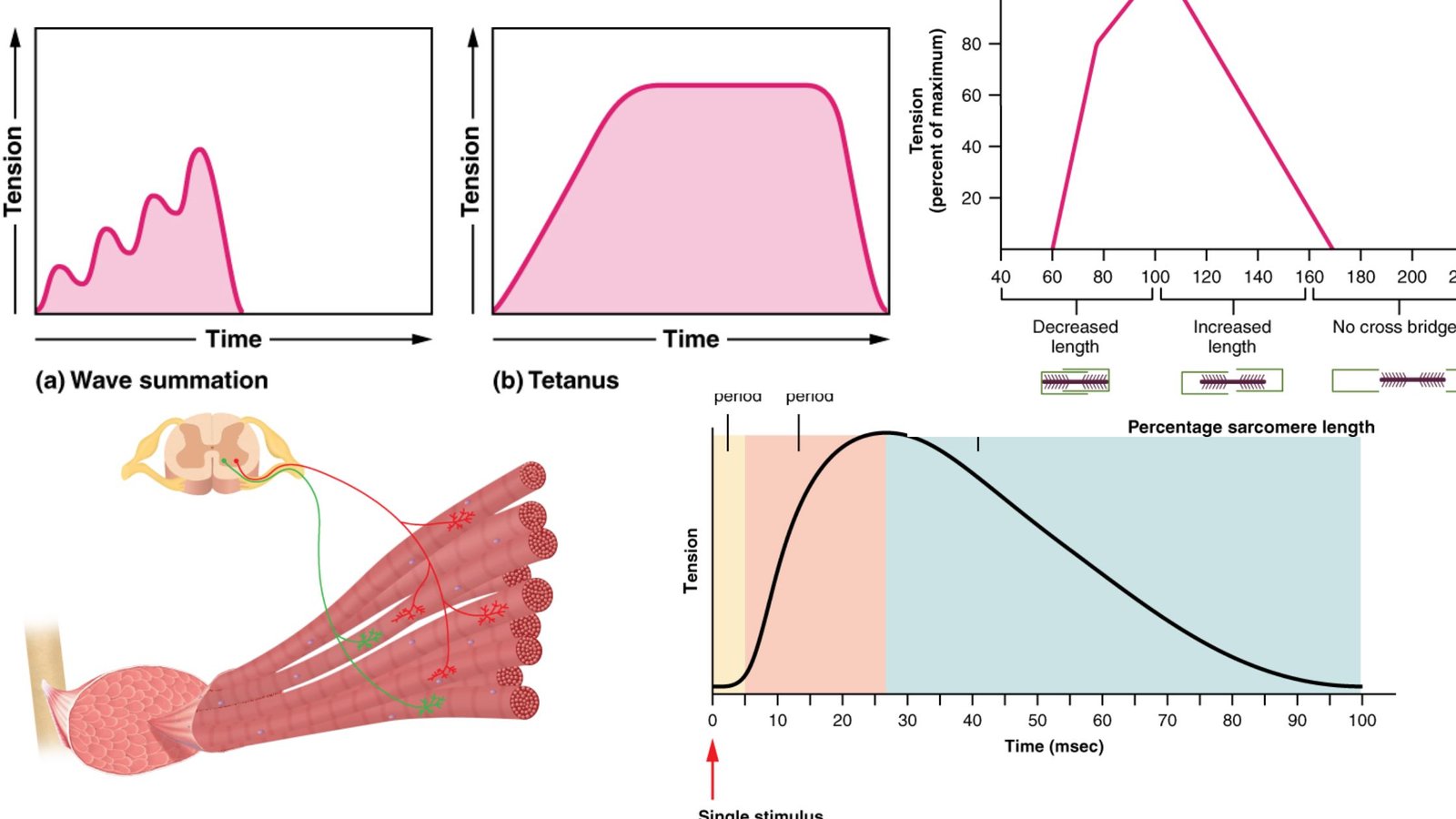
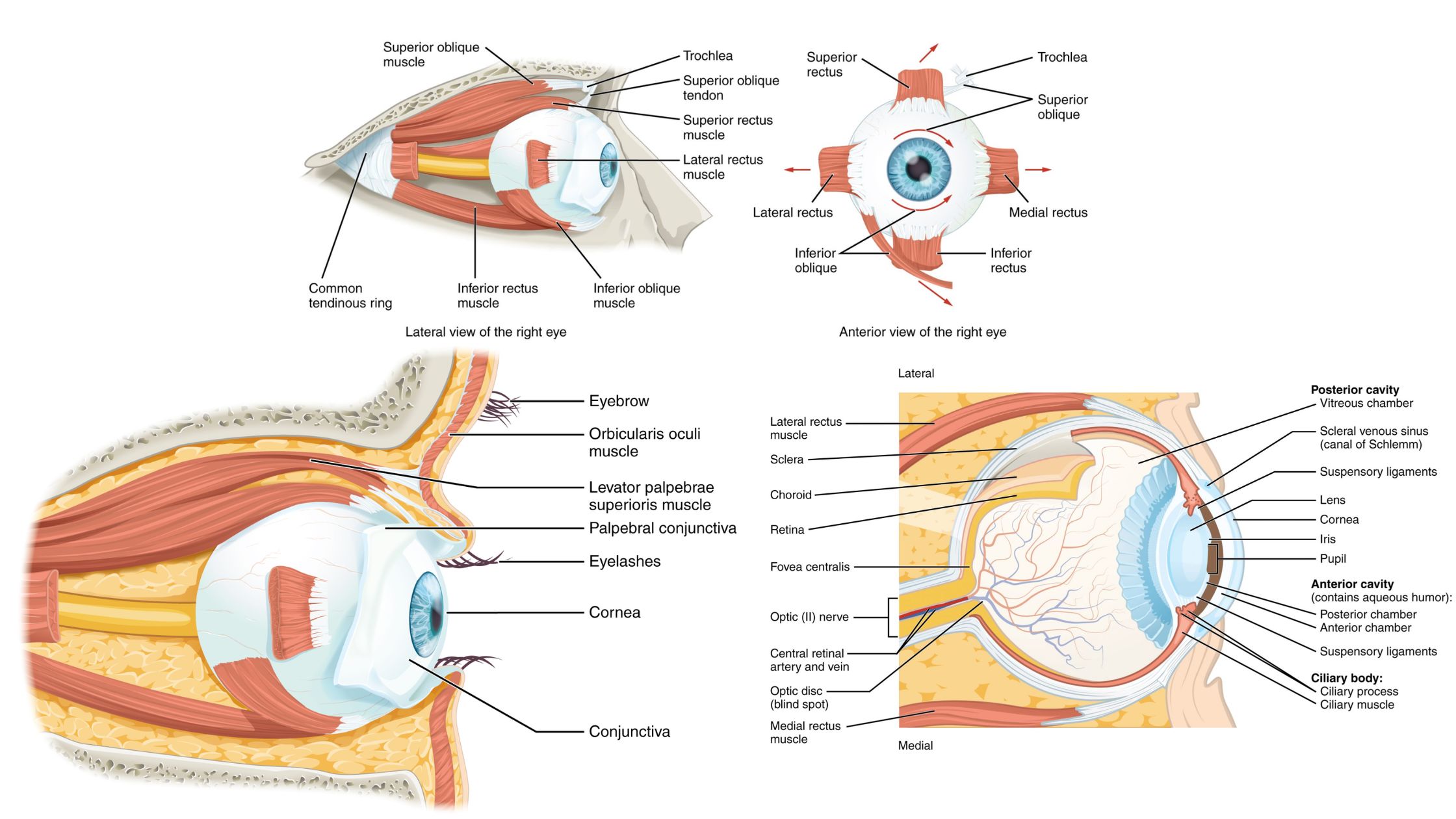
What is Muscle Cell? Definition of Muscle Cell A muscle cell, or myocyte, is a specialized animal cell designed for contraction, facilitated by organized motor proteins, primarily actin and myosin. These cells can be found in various forms, including skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues, each serving distinct functions within the body. Structure of Muscle … Read more