30 Comparison between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
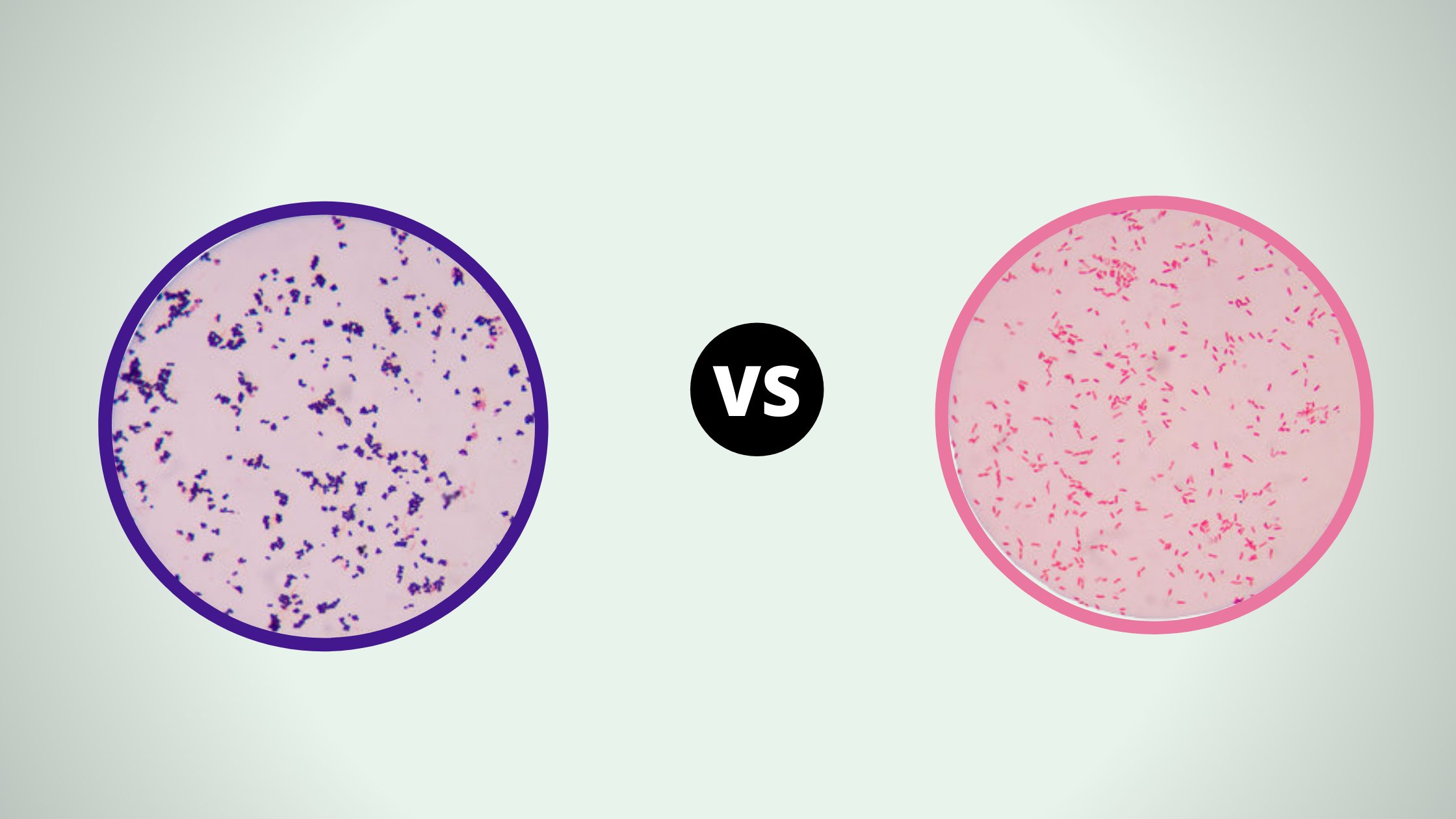
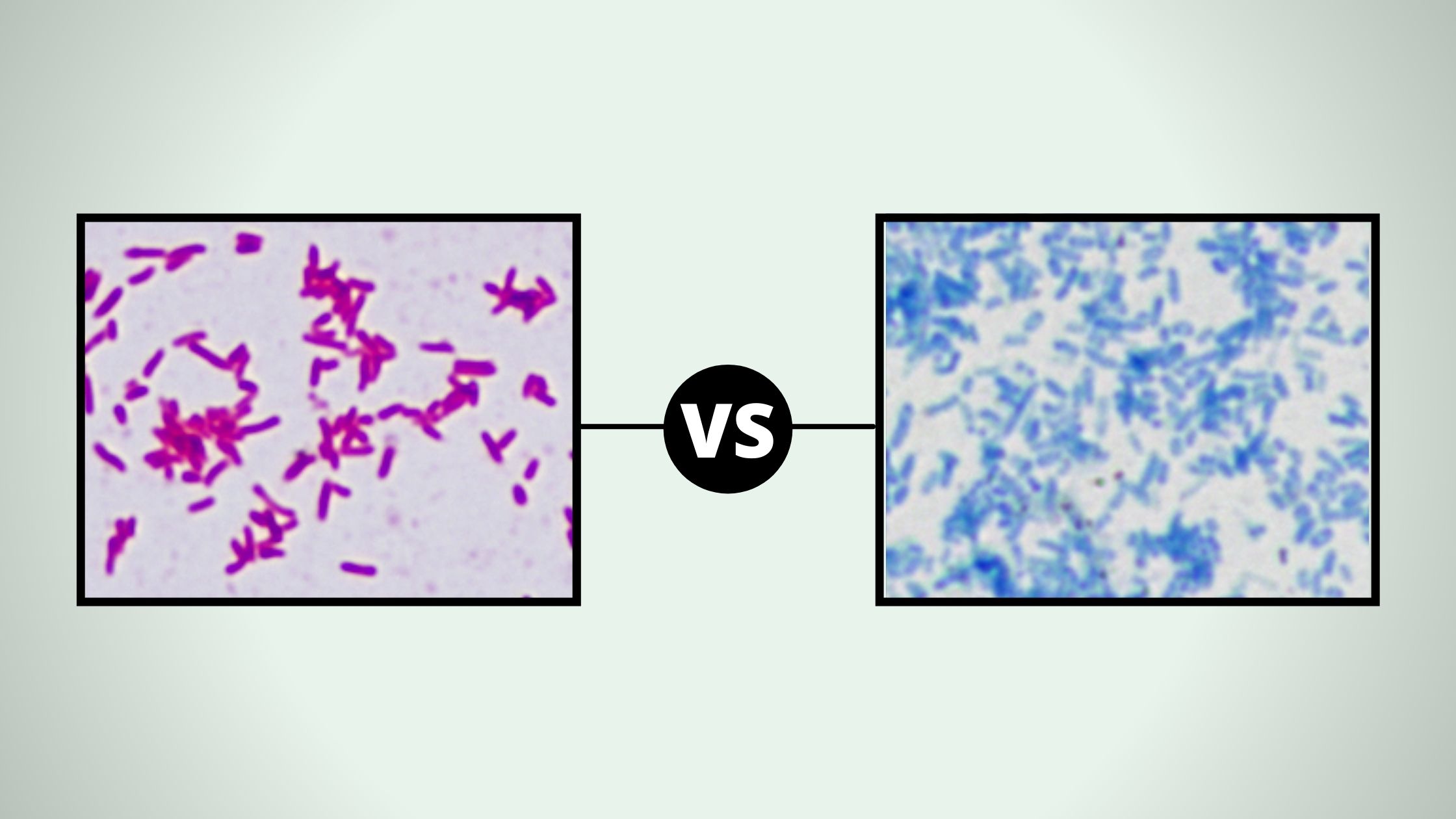
Quick Comparison between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria Serial Characteristics Gram Positive Gram Negative 1 Gram staining Stained purple or blue color (color of primary stain, crystal violet) Stained pink or red (Color of counterstain or secondary stain, safranin) 2 Thickness of cell wall 20-30 nm thick 8-12 nm thick. 3 Smoothness of cell wall The … Read more