Understanding the Genus Concept
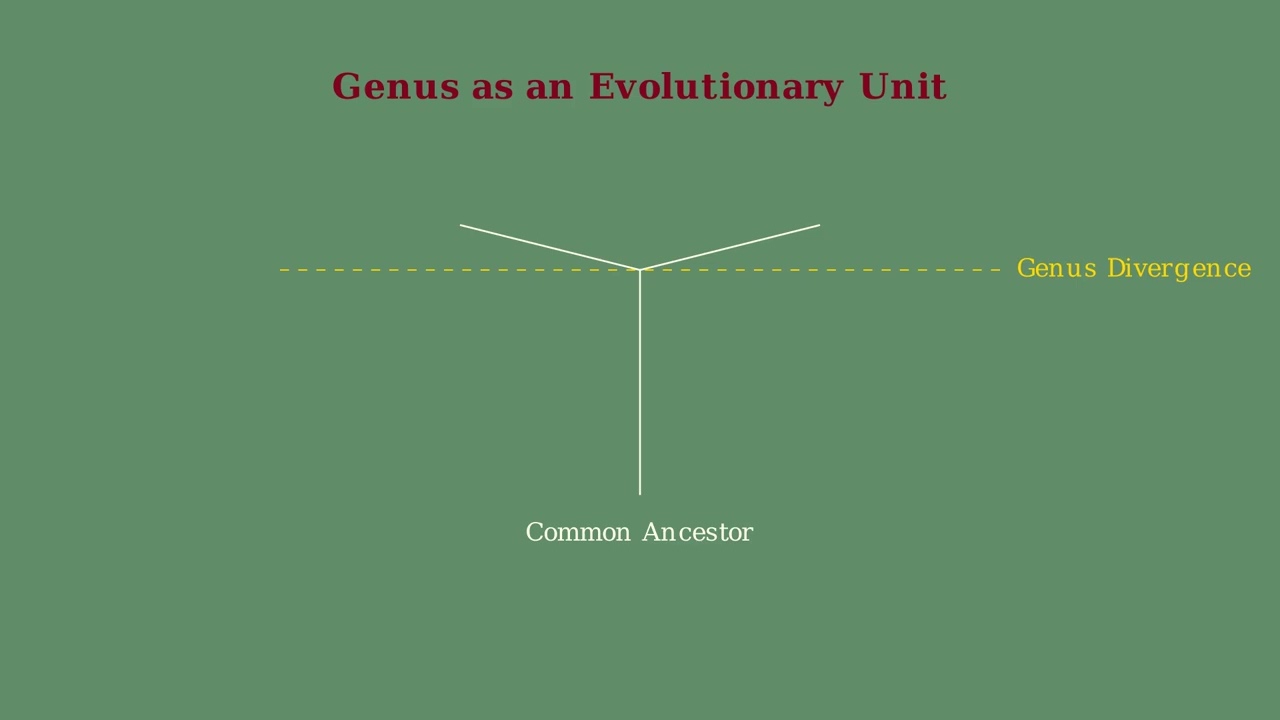
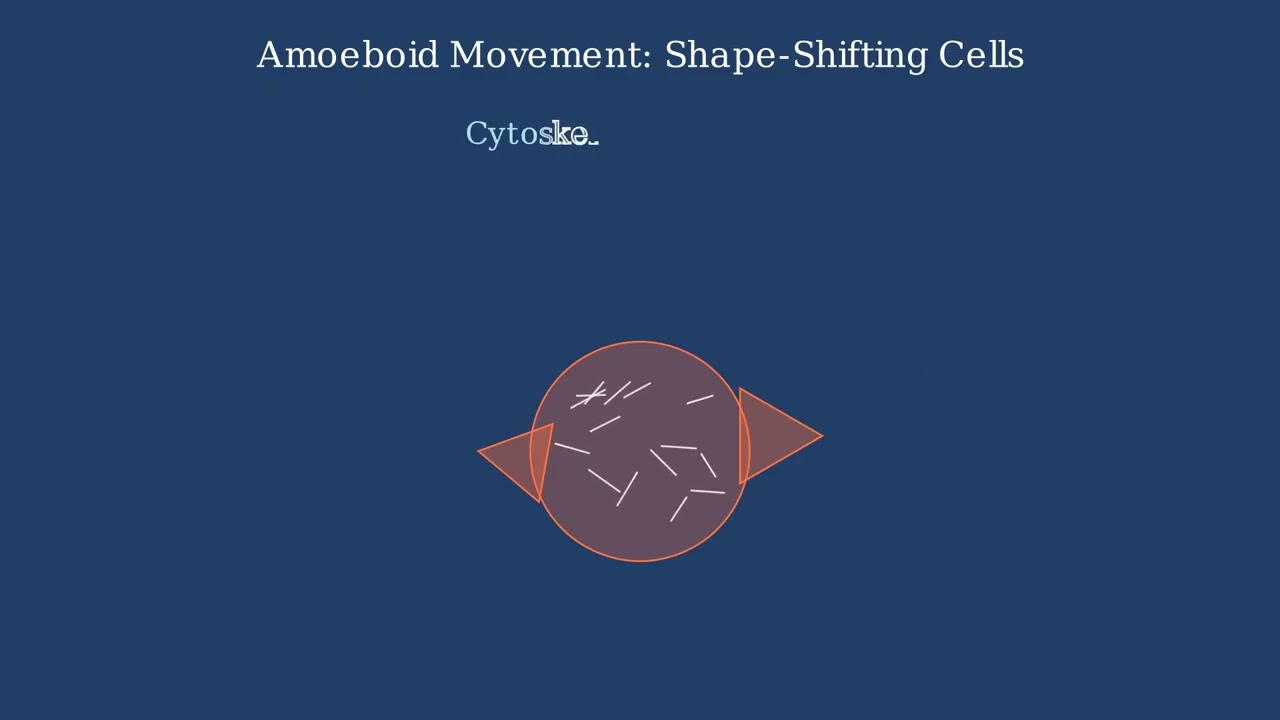
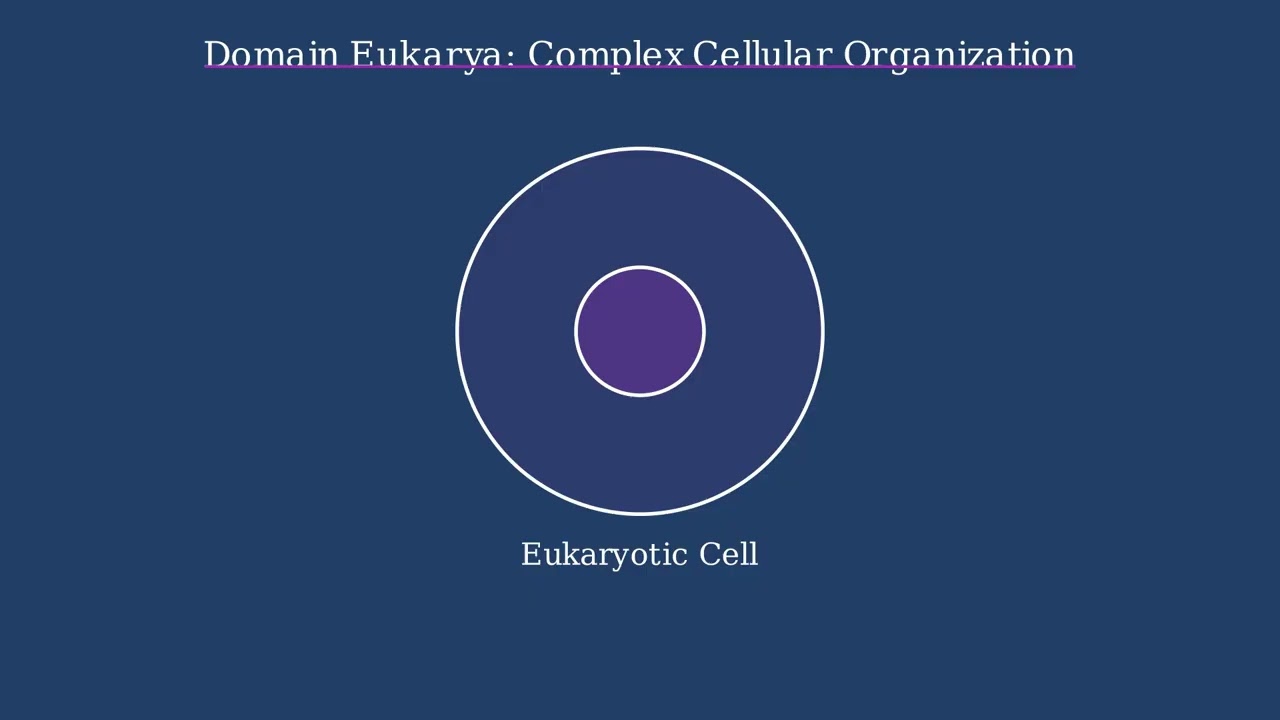
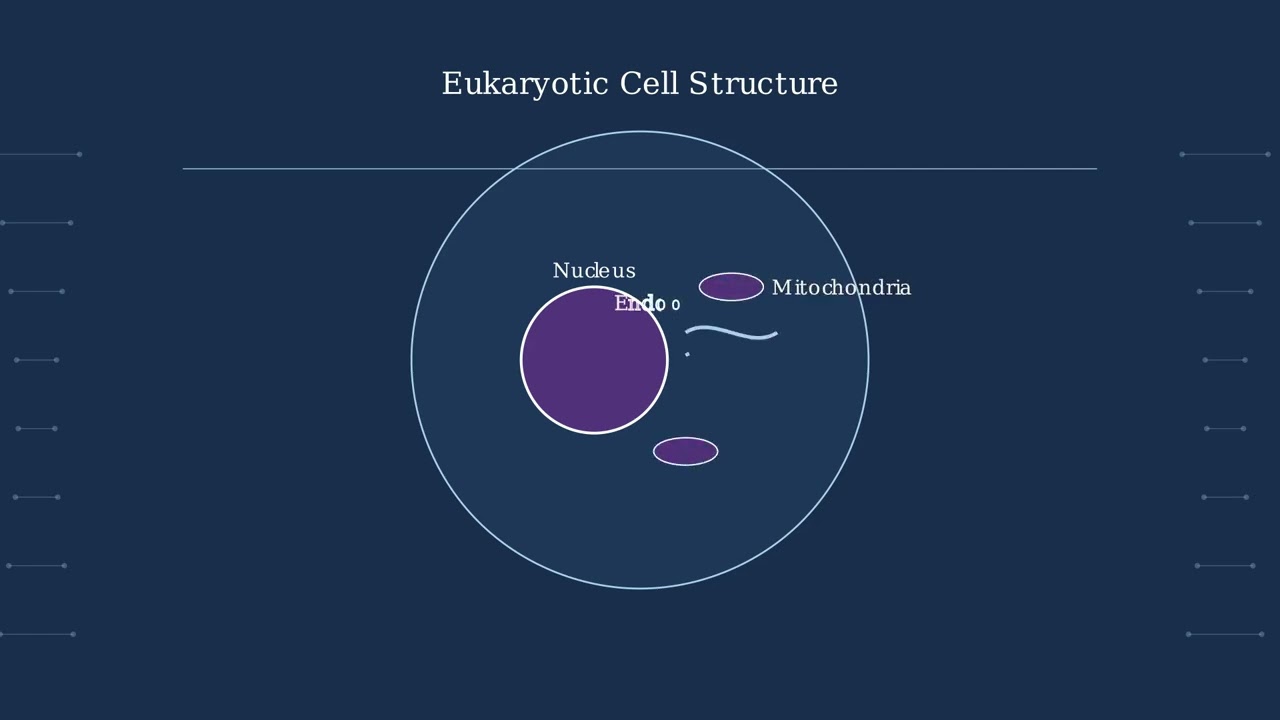
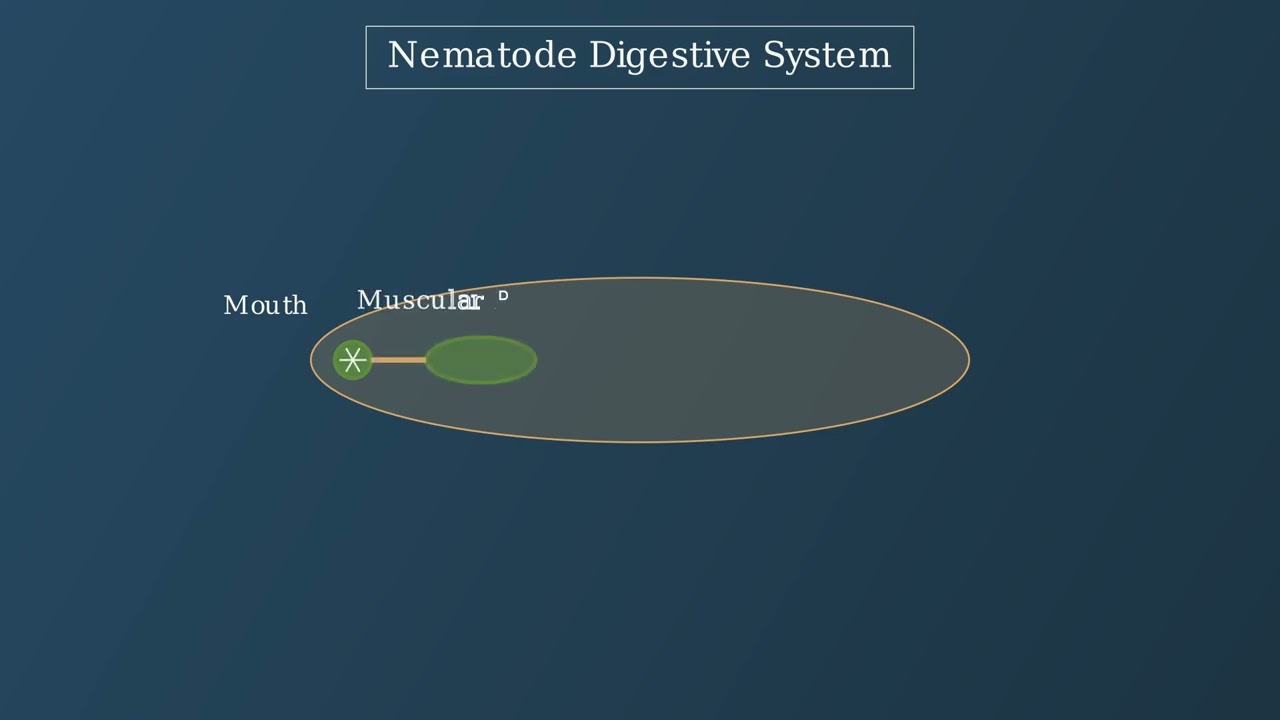
Genus in the Taxonomic Hierarchy Taxonomy provides a hierarchical classification system for all living organisms. The genus level occupies a critical position in this hierarchy, sitting between family and species. A genus groups closely related species that share specific derived characteristics from a common ancestor. For example, humans belong to the genus Homo in the … Read more