Describe the following: (a) synapsis (b) bivalent (c) chiasmata Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Describe the following:
(a) synapsis (b) bivalent (c) chiasmata
Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Please login to submit an answer.
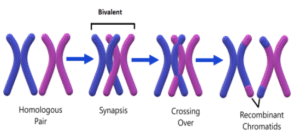
(a) Synapsis
Synapsis is the process during which homologous chromosomes pair up lengthwise during prophase I of meiosis, specifically in the zygotene stage.
This pairing is facilitated by the formation of a proteinaceous structure called the synaptonemal complex.
Synapsis ensures precise alignment of homologous chromosomes, which is essential for accurate genetic recombination and subsequent segregation.
(b) Bivalent
A bivalent, also known as a tetrad, is the structure formed by a pair of homologous chromosomes that have undergone synapsis during prophase I of meiosis.
Each bivalent consists of four chromatids (two from each homologous chromosome).
The formation of bivalents is crucial for the process of crossing over, which leads to genetic variation in gametes.
(c) Chiasmata
Chiasmata (singular: chiasma) are the visible X-shaped structures that represent the points where non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes have exchanged genetic material during crossing over.
They become apparent during the diplotene stage of prophase I in meiosis.
Chiasmata play a critical role in holding homologous chromosomes together until they are separated during anaphase I, ensuring accurate chromosome segregation.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Helpful: 0%




