In this article, we will learn about the Economic Importance of Fungi in agriculture, industries, medicine, etc. There are present a huge number of fungi, which has tremendous economic importance to humans.
Every day we benefited or were harmed directly or indirectly by those fungi. They help in yielding antibiotics, maintain the soil fertility, cause crop and fruit diseases, and also helps in the production of many foods in industries. Some of them are also used for research purposes.
There are also harmful effects of fungi such as some of them are responsible for the spoilage of stored goods such as foodstuffs, textiles, leather, rubber, plastic, timber, and even glass.
Economic Importance of Fungi In Medicine
- The most important role of fungi in the Medicine industry is, they help in the production of different antibiotics against pathogenic bacteria or microorganisms. These antibiotics are used to fight back against pathogenic bacteria.
- Besides fighting against the infectious pathogen, some fungal antibiotics are also fed to slaughter animals to promote rapid growth and improve the quality of the meat products.
- Some antibiotics are also used to preserve the freshly killed poultry for long periods of time.
- One most important antibiotic is produced from the fungi, called Penicillin from P. notatum and P. chrysogenum. It is an organic substance lethal to microbes. It kills the gram-positive bacteria.
- The antibiotic Streptomycin also obtained from the fungi called Streptomyces griseus. It destroys the gram-negative organisms, which are not killed by penicillin.
- Many antibiotics such as chloromycetin, aureomycin, Terramycin, etc. are also obtained from actinomycetes. These antibiotics prevent the growth of many pathogenic bacteria.
- Aureomycin is an effective antibiotic for those animal and human diseases that do not respond readily to other antibiotics.
- Soluble antibiotics are also produced from the plasmodia of certain species of Myxogastres. These antibiotics also help to monitor the growth of certain bacteria and yeasts in culture.
- The antifungal agent Griseofulvin is produced from the mycelium of Penicillium griseofulvum. This antibiotic only acts on hyphae by interfering with the wall formation, as a result, it causes hyphal tips to curl and cease to grow. It is also used for the treatment of fungal skin diseases such as ringworms and athlete’s foot disease.
- Sclerotia is produced by the Claviceps purpurea in the ovaries of the flowers of grasses such as rye. The sclerotium is known as the ergot of rye. This Ergot is used in veterinary and human medicine. It has an alkaloids mixture which helps in rapid and powerful contractions of the uterus. It is highly poisonous. The derivative of ergot is known as the lysergic acid (LSD) used in experimental psychiatry.
- The anti-cancer substance calvacin is obtained from the giant puffball Clavatia. This fungus prevents stomach tumors.
Economic Importance of Fungi in Industry
Fungi are used in various industrial processes, such as;
Fermentation of Alcohol
- In brewing and baking industries, yeast is used as the main ingredient. Yeast helps in the fermentation of sugar solutions and produces ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Yeast also used in brewing or winemaking industry to produce alcohol and other by-products such as carbon dioxide.
- Now, carbon dioxide is commercially produced, collected, solidified, and sold as “dry ice”. In bread industry carbon dioxide Causes the dough to rise and Makes the bread light.
- In alcohol industries yeast is an important ingredient. It secretes an enzyme complex known as zymase, which converts the sugar into alcohol. Yeast can not break the starch into sugar directly, because it lacks diastase. So, moulds are employed as starters to help in scarification of the starch. Then yeast is employed in the second stage to act on the sugar.
- Example: Aspergillus flavus is used in the production of African native beer.
Preparations of Enzyme
- There are several enzymes which are obtained from fungi. All of them are commercially available, such as Digestin, Polyzime, Taka diastase, etc. All of these are used in starch dextrinization and desiring of textiles.
- The enzyme amylase is produced by the Aspergillus niger and A. oryzae, which contains two starch splitting components.
- Saccharoymces cerevisiae produces a sucrose hydrolyzing enzyme known as Invertase. In a mixture of glucose and fructose, it helps to hydrolyze the sucrose.
Organic acid Preparation
- The moulds are used to produce several organic acids such as oxalic acid, citric acid, gluconic acid, gallic acid, fumaric acid, etc. All these organic acids are commercially available.
- Aspergillus niger produces Oxalic acid by the fermentation.
- Mould fermentation is responsible for the production of Citric acid.
- Moulds and some species of Penicillium and Aspergillus are used for the production of gluconic acid from sugars.
- In Europe and America Gallic acid is commercially produced from the fungi.
Gibberellins
- Gibberellins are plant hormones which are used to accelerate the growth of several horticultural crops.
- The fungi Gibberella fujikuroi is responsible for the production of these hormones. This fungus causes a disease in rice which is accompanied by abnormal elongation.
Cheese Production
- Some Fungi are used in the refining process of cheese, which are known as cheese moulds. They provide a characteristic texture and flavour to the cheese.
- There are two types of mould refined cheese such as Camembert and Brie types, these are soft cheese and the second one is Roquefort Gorgonzola and Stilton cheese. The Roquefort Gorgonzola and Stilton cheese are green or blue veined cheese.
Protein Manufacture
- Fungi, special yeasts(Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis) are used for the synthesis of proteins. Yeast contains a high percentage of protein.
- In industrial process, yeast are grown on ammonia and molasses, whcih are serves as the main source of nitrogen and carbon. They produce a product ,known as Food Yeast, which contains about 15% protein and vitamin B.
Vitamins
- Yeast is considered as the main source of vitamin B complex. They are produced from the dried yeast or yeast extracts and sold in the market.
- Ergosterol is a product of many moulds and yeasts which contains Vitamin D.
- The filamentous yeast, Ashby gossypii, helps in the production of Riboflavin.
Fat
- Many fungi contain a high amount of fat such as Endomyces vernalis, Penicillium javanicum and Oidium lactis. However, the production of fat from these fungi is a costly process.
Others
- Some fungi are used for the fermentation of Cocaobeans.
- Certain dyes and reagents are produced from the fungi.
Economic Importance of Fungi in Agriculture
Fungi has both harmful and beneficial effect on agriculture such as;
1. Harmful Effect
Fungi are responsible for many diseases of our crop, fruit and other economic plants. These diseases are responsible for tremendous economic losses.
It is estimated that our economic plants which are grown for food or commercial purposes are attacked by about 30 thousand different diseases(including bacterial and virus).
Plant Diseases
a. Damping off disease
This disease is caused by a species of Pythium and only found in commercial crops, for example tomatoes, com, cotton, mustard, peas, beans, tobacco, spinach, etc.
b. The potato blight
This disease causes great damage to the potato tubers. In 1845, in Ireland it destroyed the entire potato crop. Except potatoes it also infects egg plants, tomatoes, etc.
c. Downy mildews of grapes
In France, it destroyed all the vine yards and caused heavy losses to the crop. This disease can be treated with Bordeaux mixture, which has an effective fungicide against this disease.
d. Ergot disease of rye
This disease is found in cereal crops—rye. It forms a poisonous sclerotia in the rye kernel which is known as ergot of rye. This is highly poisonous to man which can cause hallucinations, insanity and finally death.
e. Apple scab
This disease is only found in apple crops, which decreases the quality as well as quantity of the fruit.
f. Brown rot of stone fruits
This disease is found in fruit crops such as apricots, cherries, plums and peaches.
g. Smut diseases
This disease is found in corn, wheat, oat and other cereal crops, which reduce the yield and quality of grain.
h. Red rot disease of sugarcane
This disease is found in sugarcane, particularly in the northern parts of the country.
i. Rust diseases
This is found in our cereal crops and forest timber. Black stem rust, yellow rust and orange rust are Some of them, which has a serious threat to our wheat crop.
j. Blackarm, Wilt and root rot of cotton
This disease is found in cotton, which is an important commercial crop of our country.
k. Pore fungi
These are mainly wood rotters which destroy timber and lumber.
Except plant fungi also cause disease in human beings and domestic animals. The cause disease in lungs, external ear, some of them are lived in mucous membranes of throat, bronchi and lungs and cause infection of mouth and lungs.
Some examples of fungal disease are skin discoloration, athlete’s foot disease (caused by Trichophytoneae), ‘ringworm’ and barber’s itch.
Some species of Aspergillus such as A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. niger are human pathogens.
Except causing disease in plants and animal fungi also has other harmful effects such as;
a. Destruction of timber
Some fungi reduce the mechanical strength of the wood such as Polyporus, Serpula lacrymans, Fusarium negundi, Coniophora cerebella, Lentinus lapidens and Penicillium divaricatum.
b. Destruction of textiles
Some fungi grow on cotton and woolen textiles and cause destruction, such as Alternaria, Penicillum, Aspergillus, Mucor and Fusarium. Spp. of Stachybotrys.
c. Destruction of Paper
Polyporus adustus, Polystictus hirsutus can destroy the Paper pulp wood. Some fungi such as Chaetomium, Aspergillus, Stachybotrys, Alternaria, Fusarium, Dematium, Mucor, Cladosporium etc. are responsible for extensive damage to paper of books, newspapers and paper industry.
2. Beneficial Effects
- Some soil fungi maintain the soil fertility. They help in decay and decomposition of dead bodies of plants and extract the nutrients from them by releasing enzymes such as cellulose and lignin.
- These enzymes produce simpler compounds such as carbon dioxide, water, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide, etc. from fatty carbohydrate and nitrogenous constituents.
- Some of these simple compounds return to the soil and rest are released to air, where they can be reused by the plants for the production of foods.
- Some fungi live in association with roots such as mycorrhizae, they provide nutrients to the plants from soil.
- Gibberella fujikuroi produces a growth hormone known as Gibberrelin which accelerates plant growth.
- Some fungi such as Empusa sepulchrasis, Metarrhizium anisopliae, Cordyceps melothac etc. are used to control the insect.
- Some fungal inhabitants of the soil help to fight against disease caused by the soil borne fungi. For example Trichoderma lignorum and Gliocladium fimbriatum inhibit the growth of the mycelium of Pythium. They suppress the causative agent of damping off disease of the seedlings, and promote the growth of plants.
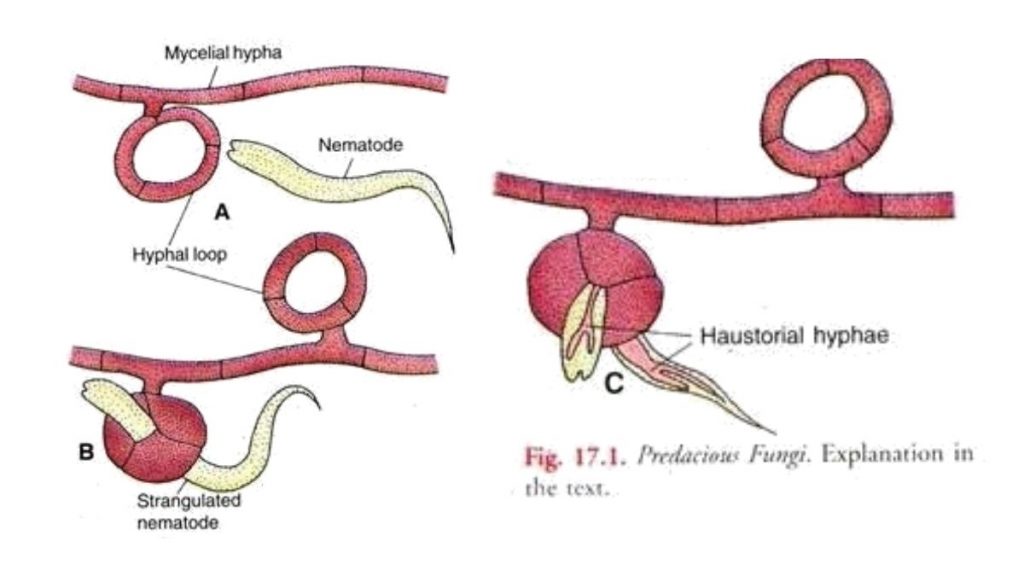
- Some predacious fungi trap and destroy the nematodes (eel worms). They form loops on the mycelium (A) which act as nooses. When nematodes try to pass through this loop they are trapped. After that mycelium absorbs nutrition from the captive by sending a special hyphae.
- Predacious fungi also produce a sticky conidia. When nematodes pass through the soil, conidia stick to their bodies. After that conidia germinates and produces hyphae which then penetrate into the tissues of the host and absorb nourishment.
- Beauveria bassiana is used as a nematicide against borers, thrips, and aphids.
- There are other fungi which are used against soil borne fungal pathogen such as Trichoderma viride and T. harzianum
Economic Importance of Fungi in Food and as Food Producers
- It is estimated that over 200 species of fungi are edible. These fungi have a great economic value as food.
- Some name of edible fungi are field mushroom Agaricus campestris (dhingri), Podaxon podaxis (Khumb), the honey coloured mushrooms, the fairy ring mushrooms, the puff balls (Lycoperdon and Clavatia), morels (Morchella, guchhi), and truffles.
- Fungi has a higher amount of nutritive value. Yeasts and some filamentous fungi contain a huge amount of vitamins B-complex.
- Some mushrooms are fatally poisonous, which can cause only discomfort.
- Some fungi are considered as the ideal organisms for the study of the laws of heredity. Because they can complete their sexual life cycle in a few days, such as red bread mold, Neurospora sitophila and others.
- Now slime molds (Physarum polycephalum) are widely used for the study of DNA synthesis, meiotic cycle and the mechanism of protoplasmic streaming. They are considered as the excellent experimental organism.
- Some fungi also causes spoilage in food stuffs such as citrus fruits are spoiled by Penicillium digitatum; Mucor, Aspergillus, Penicillium, Oidium and Fusarium responsible for the spoilage of milk and milk product; Aspergillus responsible for bread spoilage; Oidium lactis responsible for fishy odour of butter; Mucor sp., Penicillium, Neurospora, Fusarium, Aspergillus etc. are responsible for the spoilage of meat.
- Some fungi such as Aspergillus flavus, A. fumigatus, A. parasiticus and Penicillium islandicum produce a most potent carcinogenic agent called Aflatoxins on dried foods and groundnut meal.
- Aflatoxin prevents the transcription by binding with the DNA. They cause liver cancer in animals and human beings.
- Some Mushrooms produce toxins which can cause diarrhoea vomiting, liver damage, complete unconsciousness etc. Some examples of toxin producing mushrooms are Amanita phalloides, spp. of Helvella and some species of Inocybe.
- Ergot toxins producing fungi, Claviceps purpurea carry several poisonous alkaloids such as ergotamine, ergometrimine, ergocrystinine, ergocrystinine and ergonovin. These are responsible for diarrhoea, abdominal pain, vomiting and psychiatric disturbances.
Yes, I love this place