Through technological advances, The methods for sterilization have changed throughout the decades. There are now many different methods of sterilization employed in laboratories. However, autoclaving using steam is the most popular method for sterilization in the majority of labs. Although autoclaving is a clean rapid, reliable, and cost-effective method of sterilization, without any environmental risks and risks, it is still utilized most often in hospitals. However, there are three commonly employed methods of sterilization that are used: the steam autoclave, unsaturated chemical-vapor sterilizer as well as the dry heat sterilizer. This article will only focus on the Difference between hot air ovens and autoclaves.
Steam sterilization is performed in a chamber that is specialized for pressure called an autoclave, which employs high-pressure steam for sterilizing equipment and other supplies. It is among the most widely used and oldest methods of sterilization of instruments and materials. It is primarily employed in dental offices. Autoclaves are available in many sizes and designs. Another common method for sterilization in a dental offices is to use dry heat. One of the most simple methods for dry heat sterilization is direct burning. While dry heat sterilization is a bit slower than autoclave processes It is a good option for equipment that is prone to be rusty when in a humid autoclave. Let’s examine the two sterilization procedures in more detail.
What is Autoclave (Sterilization by Steam)?
Sterilization results in the destruction of all types of microbial life which is confirmed by the destruction of spores resistant to antibiotics. It is the most effective level of killing of microbes. Autoclaving or steam sterilization is among the most commonly utilized methods of sterilization for dental practices. It is the process of sterilizing instruments that utilizes temperatures, time as well as pressure in order to eliminate all kinds of microbial life. This includes the spores. A autoclave can be described as a chamber of pressure which is a type of vessel that utilizes steam at high pressure to sterilize equipment and other supplies. It is thought to be among the most effective methods for sterilization. It destroys any microorganisms that are pathogenic and not, as well as virus spores and spores. Autoclaving requires at least 121°C (250 degrees Fahrenheit) with a steam pressurization of around 15 pounds/square inch (psi) and 15 minutes to guarantee sterilization.
What are the advantages of Sterilization with Moist Heat?
- It will take shorter time for sterilizing
- Requires low temperatures
- It is easy to monitor and manage.
- Cost-effective and non-toxic
What are the disadvantages from Moist Heat Sterilization?
- It is not possible to sterilize the instrument that is sensitive to heat.
- This can lead to corrosion following sterilization.
- The repeated exposure of instruments could cause damage to the instrument.
What is Dry Heat Sterilization?
Dry heat sterilization (DHT) is another method of sterilization, which uses time and temperatures to kill all types of microbial life. This includes the spores of microbial life and viruses. It is basically sterilization by using an oven. Dry-heat ovens can be utilized to sterilize objects which could rust within the autoclave that uses steam. The oven requires maintenance, but will not cause corrosion or rust to equipment and instruments. The length of time required to sterilize is dependent in part on the temp of your oven. Dry heat sterilization generally lasts about one hour at 340°F or two hours at temperatures of 320 degrees Fahrenheit. It is only suitable for products that have been damaged or not able to withstand moisture-laden heat. The only disadvantage for dry sterilization of heat is that it is slower than autoclaving.
What are the advantages of Dry Sterilization with Heat?
- They are safe and non-toxic.
- Cost-effective and simple to set up
- The chances of corrosion are slim.
- Be eco-friendly
- It is able to penetrate materials with ease.
What are the disadvantages of Dry Sterilization with Heat?
- It takes longer to sterilize.
- The instrument is exposed to greater temperature can pose a risk.
- It requires extremely high temperatures.
Method of Autoclave and Hot Air Oven/Dry Heat Sterilization
Autoclaving and dry heat sterilization are two most commonly employed methods for sterilization in dental procedures, autoclaving is one of the most popular and oldest methods of sterilization of tools and other materials that are commonly used in hospitals. Autoclaving is a method of sterilization of instruments using temperatures, time and pressure to destroy all types of microorganisms, while Dry heat sterilization the process of sterilization using an oven that makes use of time and heat to kill all kinds of microbial life. This includes the spores of microbial life and viruses.
Sterilization Conditions
In order to ensure that the sterilization process is completed The pressure chamber or autoclave is needed to raise the temperature of the steam that is saturated to a minimum 121 degrees Celsius or 250 degrees Fahrenheit using steam pressure between 15 and 16 pounds for each square inch (PSIG) for between 15 and 30 minutes. It is crucial to follow the instructions specific to the autoclave you are working. Dry heat sterilization generally takes around an hour so at 340 degrees Fahrenheit or two hours at 320 degrees. The instruments should be completely dry prior to sterilization. The doors should be closed until the entire process is completed.
Applications of Autoclave vs. Hot Air Oven/Dry Heat Sterilization
Steam sterilization is a viable option for everything that can take moisture and heat, but steam may penetrate tough substances like wraps, containers and PVC tubing. Steam can also harm the rubber and plastic components. They can also be utilized to remove biological wastes. While the dry method of sterilization can be comparatively slower than autoclaving, it’s frequently used to sterilize items that are affected by water or inaccessible to steam. They can be used to remove the pyrogens that are present in glassware, more typically in the pharmaceutical sector. Dry heat is not recommended on rubber products made of soft rubber.
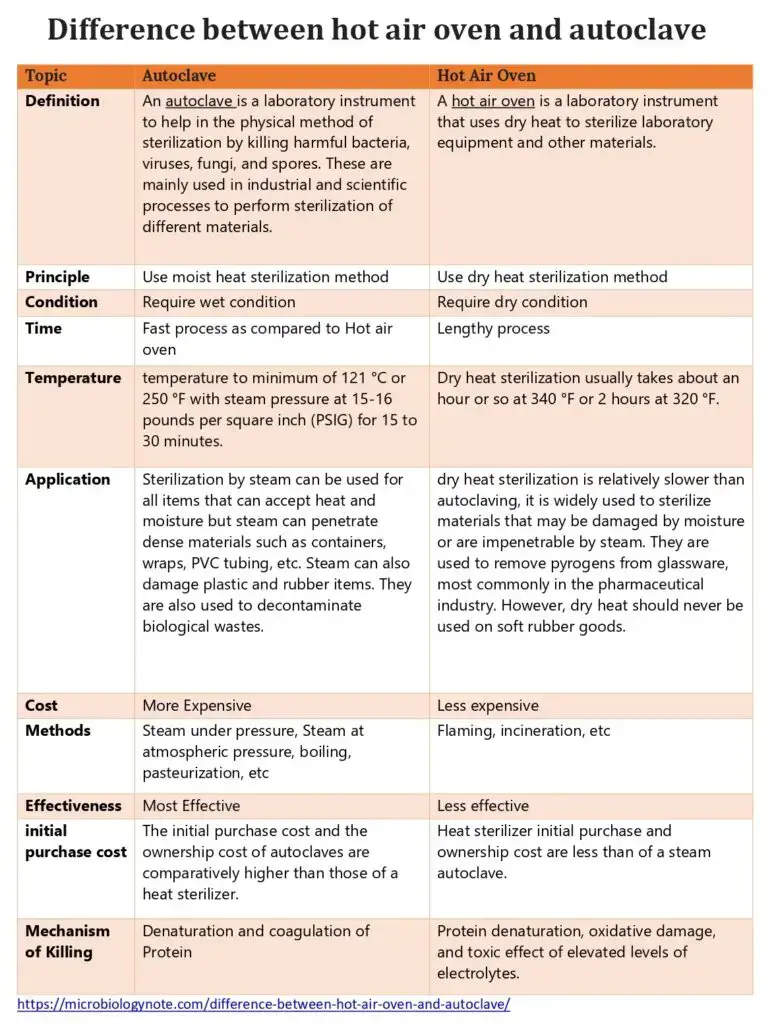
Difference between hot air oven and autoclave
| Topic | Autoclave | Hot Air Oven |
| Definition | An autoclave is a laboratory instrument to help in the physical method of sterilization by killing harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. These are mainly used in industrial and scientific processes to perform sterilization of different materials. | A hot air oven is a laboratory instrument that uses dry heat to sterilize laboratory equipment and other materials. |
| Principle | Use moist heat sterilization method | Use dry heat sterilization method |
| Condition | Require wet condition | Require dry condition |
| Time | Fast process as compared to Hot air oven | Lengthy process |
| Temperature | temperature to minimum of 121 °C or 250 °F with steam pressure at 15-16 pounds per square inch (PSIG) for 15 to 30 minutes. | Dry heat sterilization usually takes about an hour or so at 340 °F or 2 hours at 320 °F. |
| Application | Sterilization by steam can be used for all items that can accept heat and moisture but steam can penetrate dense materials such as containers, wraps, PVC tubing, etc. Steam can also damage plastic and rubber items. They are also used to decontaminate biological wastes. | dry heat sterilization is relatively slower than autoclaving, it is widely used to sterilize materials that may be damaged by moisture or are impenetrable by steam. They are used to remove pyrogens from glassware, most commonly in the pharmaceutical industry. However, dry heat should never be used on soft rubber goods. |
| Cost | More Expensive | Less expensive |
| Methods | Steam under pressure, Steam at atmospheric pressure, boiling, pasteurization, etc | Flaming, incineration, etc |
| Effectiveness | Most Effective | Less effective |
| initial purchase cost | The initial purchase cost and the ownership cost of autoclaves are comparatively higher than those of a heat sterilizer. | Heat sterilizer initial purchase and ownership cost are less than of a steam autoclave. |
| Mechanism of Killing | Denaturation and coagulation of Protein | Protein denaturation, oxidative damage, and toxic effect of elevated levels of electrolytes. |
Major Differences between Autoclave and Dry Heat Sterilizer
- Autoclaves are sterilizing devices which use pressure, temperature and time to eliminate any microbial presence in the instruments. On the other hand, dry heat sterilizers are oven-like machines that make use of temperature and time to kill any microbial growth from the instruments’ surfaces.
- Autoclaves cost more when compared to heat sterilizers.
- The initial cost of purchase and the expense of ownership for autoclaves is significantly more expensive than those of a heating sterilizer. Initial purchase cost and cost of ownership are lower than that of an autoclave steam.
- In autoclaves, at least 121 degrees Celsius or in other words 250 degF is needed to be maintained with the minimum steam pressure that is 15 PSIG over 15 minutes. while in the heat sterilizers for proper sterilization, it is required to reach the temperature to be 320 degrees Fahrenheit, which will take around two hours or you can achieve 340 degrees F to do the same in one hour.
- Autoclaves can carry out sterilization procedures on a variety of materials at the same time and in the fastest manner possible. Heat sterilizers are slower in the process of sterilization and , consequently, require longer to finish the task completely.
Difference between hot air oven and autoclave pdf
References
- http://www.differencebetween.net/technology/difference-between-autoclave-and-dry-heat-sterilizer/
- https://www.labrotovap.com/difference-between-autoclave-and-hot-air-oven-dry-heat-sterilizer/
- https://www.duralinesystems.com/The-Difference-Between-A-Dry-Heat-Sterilizer-and-A-Steam-St-s/583.htm
- https://askanydifference.com/difference-between-autoclave-and-dry-heat-sterilizer/
- https://qa.answers.com/other-qa/What_is_difference_between_autoclave_and_oven
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4157279/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot_air_oven
- https://princesterilization.com/difference-between-moist-heat-sterilization-dry-heat-sterilization/
- https://www.pharmaguideline.com/2016/11/difference-between-sterilization-and-depyrogenation.html
- https://www.westlab.com/blog/2018/02/05/different-sterilization-methods-used-in-the-laboratory