Hyaline Cartilage Under Microscope
Image Gallery











Description
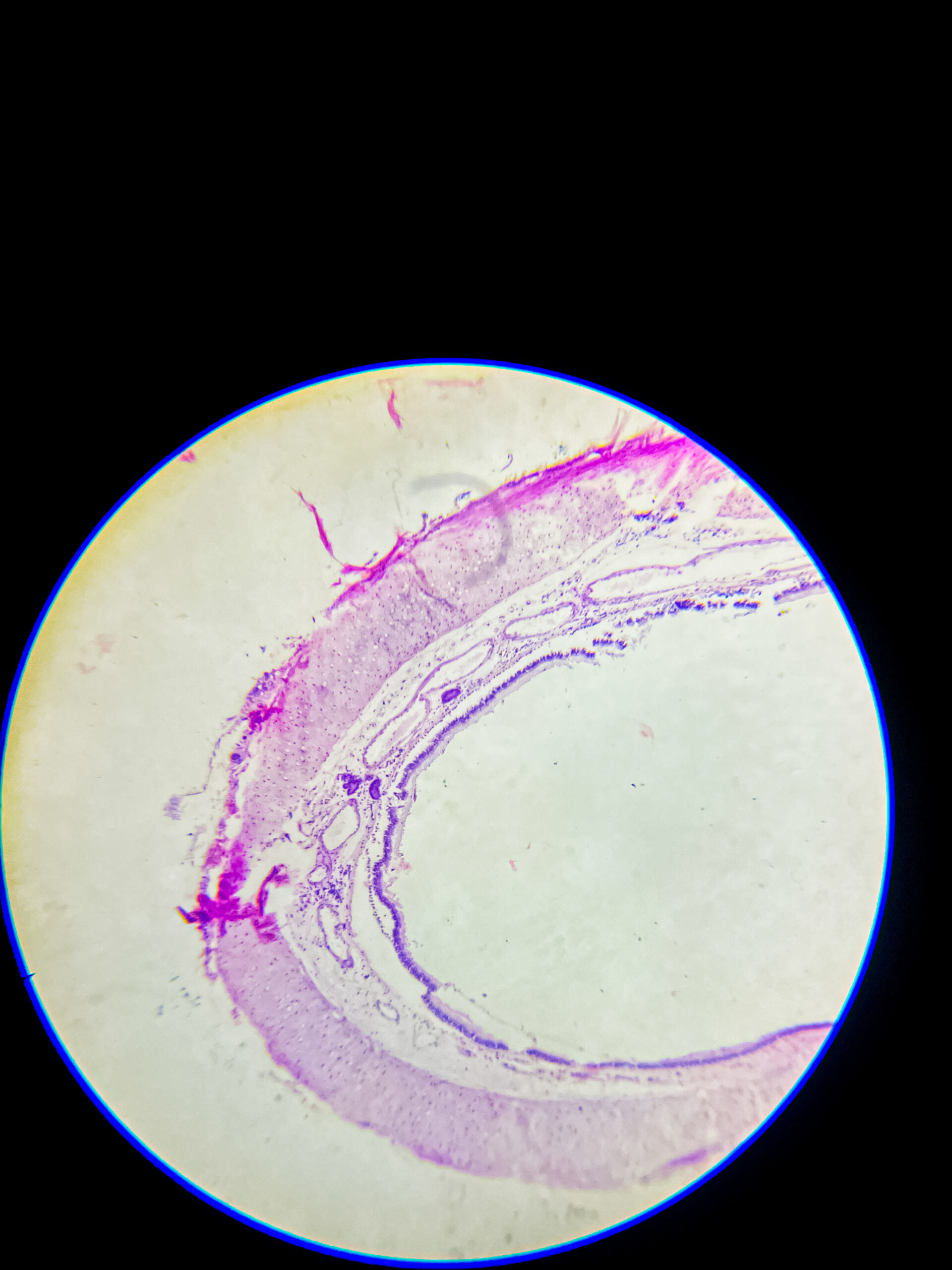
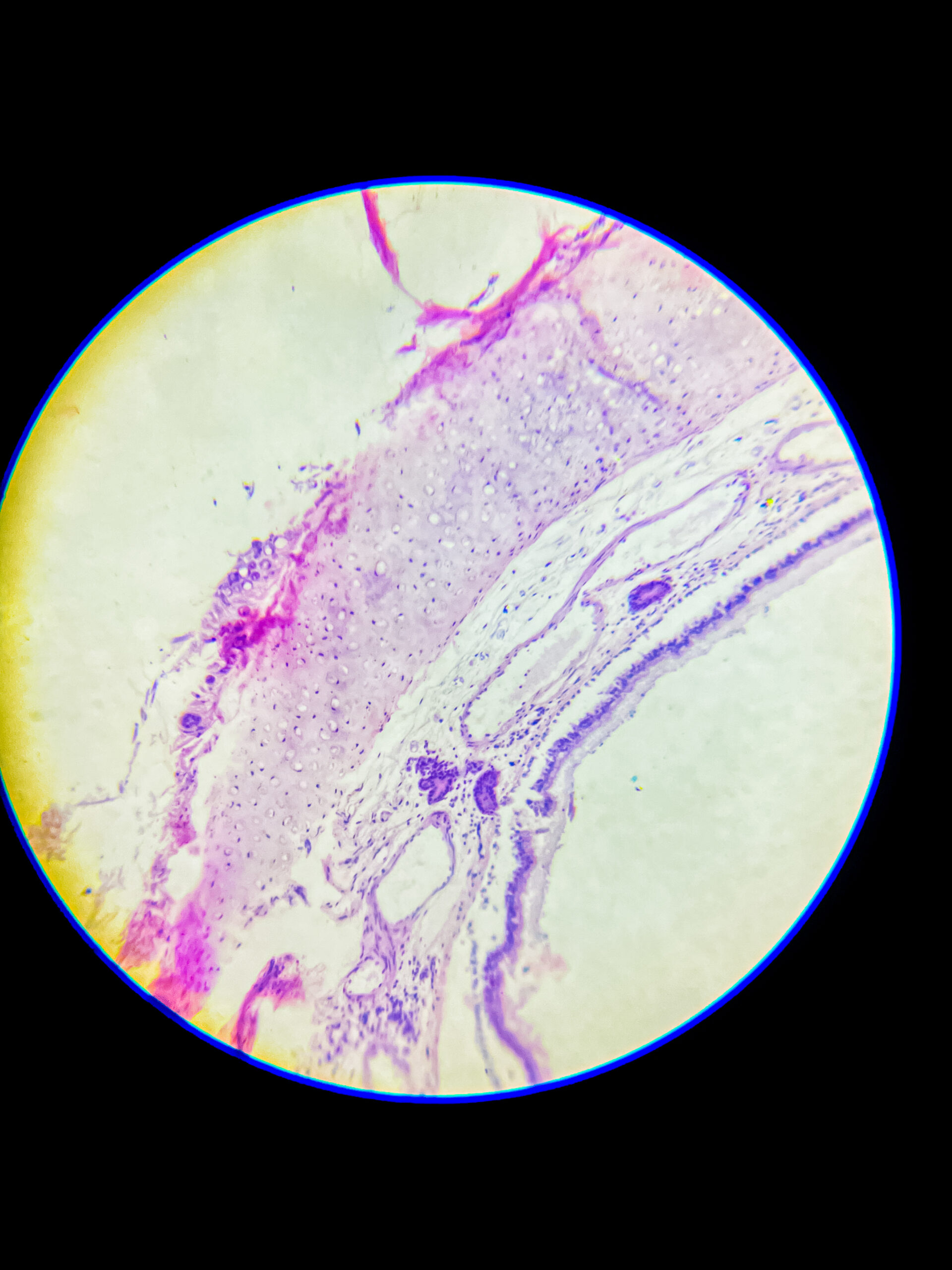
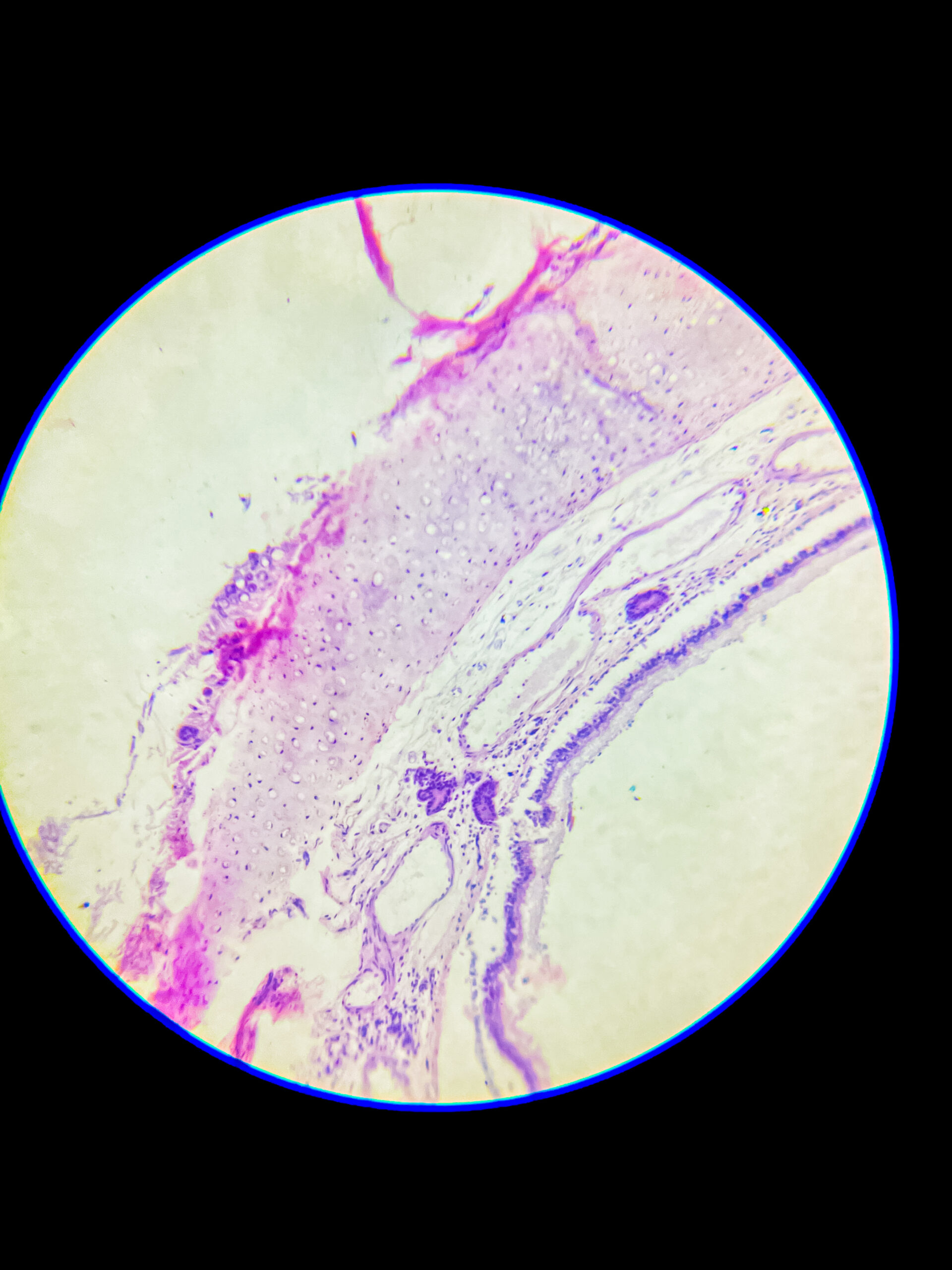
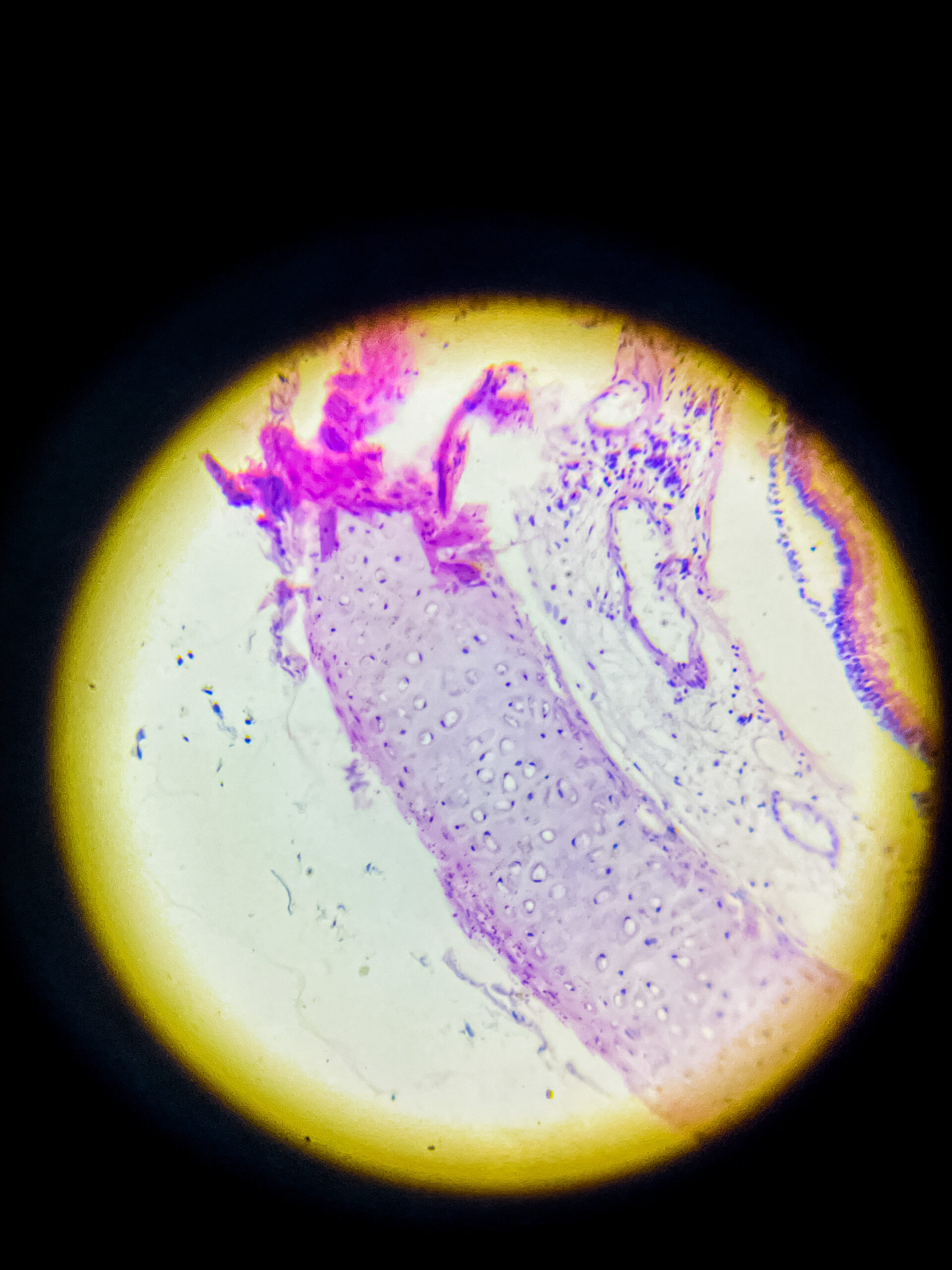
Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue, it consists of a dense network of collagen fibers embedded in a firm, gel-like matrix, mostly it’s made up of type II collagen, it provides smooth surfaces for joint movement, flexibility, and support, it is most common cartilage type in body, that’s found in nose, trachea, larynx, ends of long bones, costal cartilages, and embryonic skeleton.
it’s avascular, so nutrients must diffuse through matrix, no nerves, and no blood vessels, chondrocytes present inside lacunae, surrounded by perichondrium except at articular surfaces.
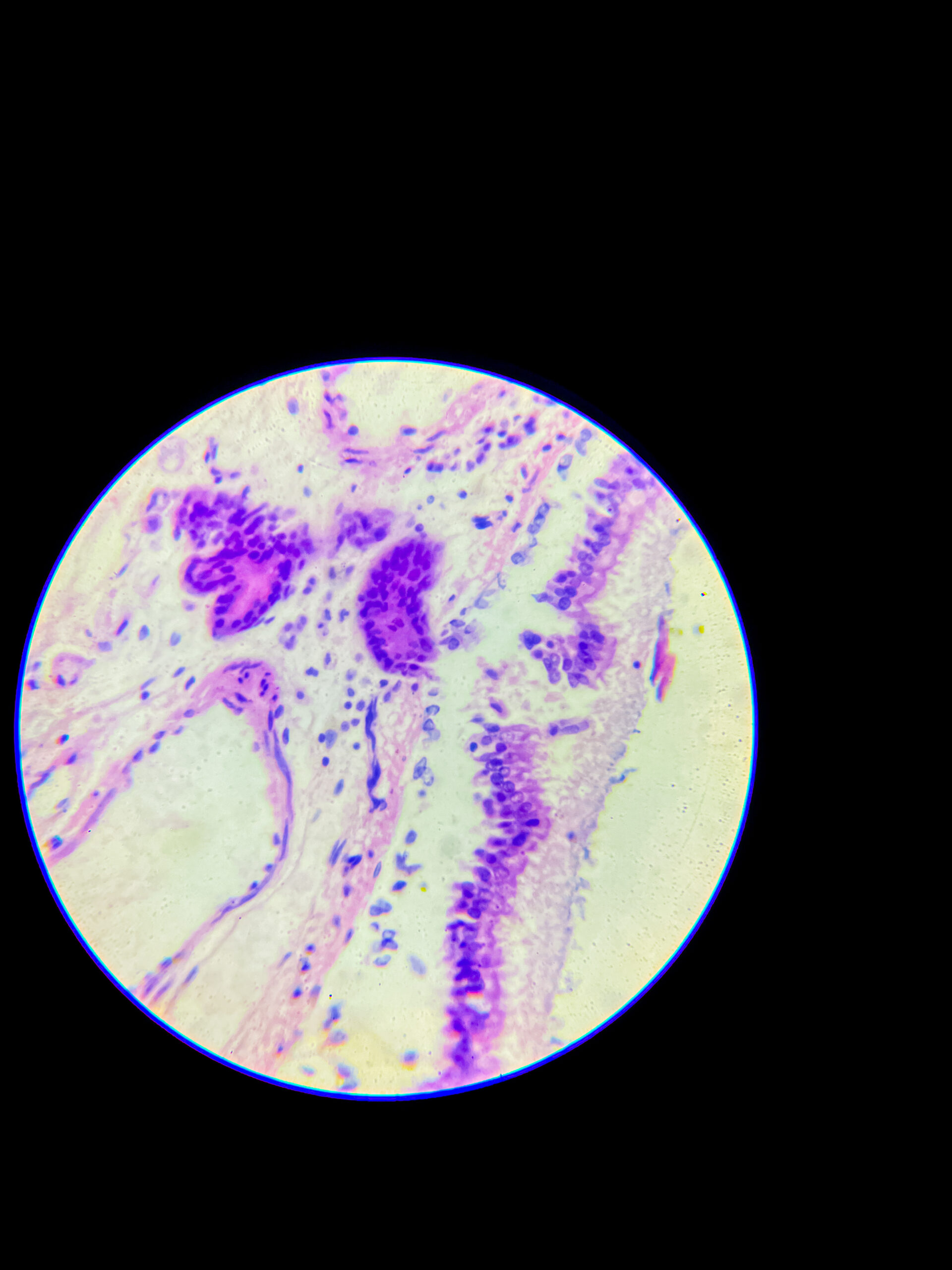
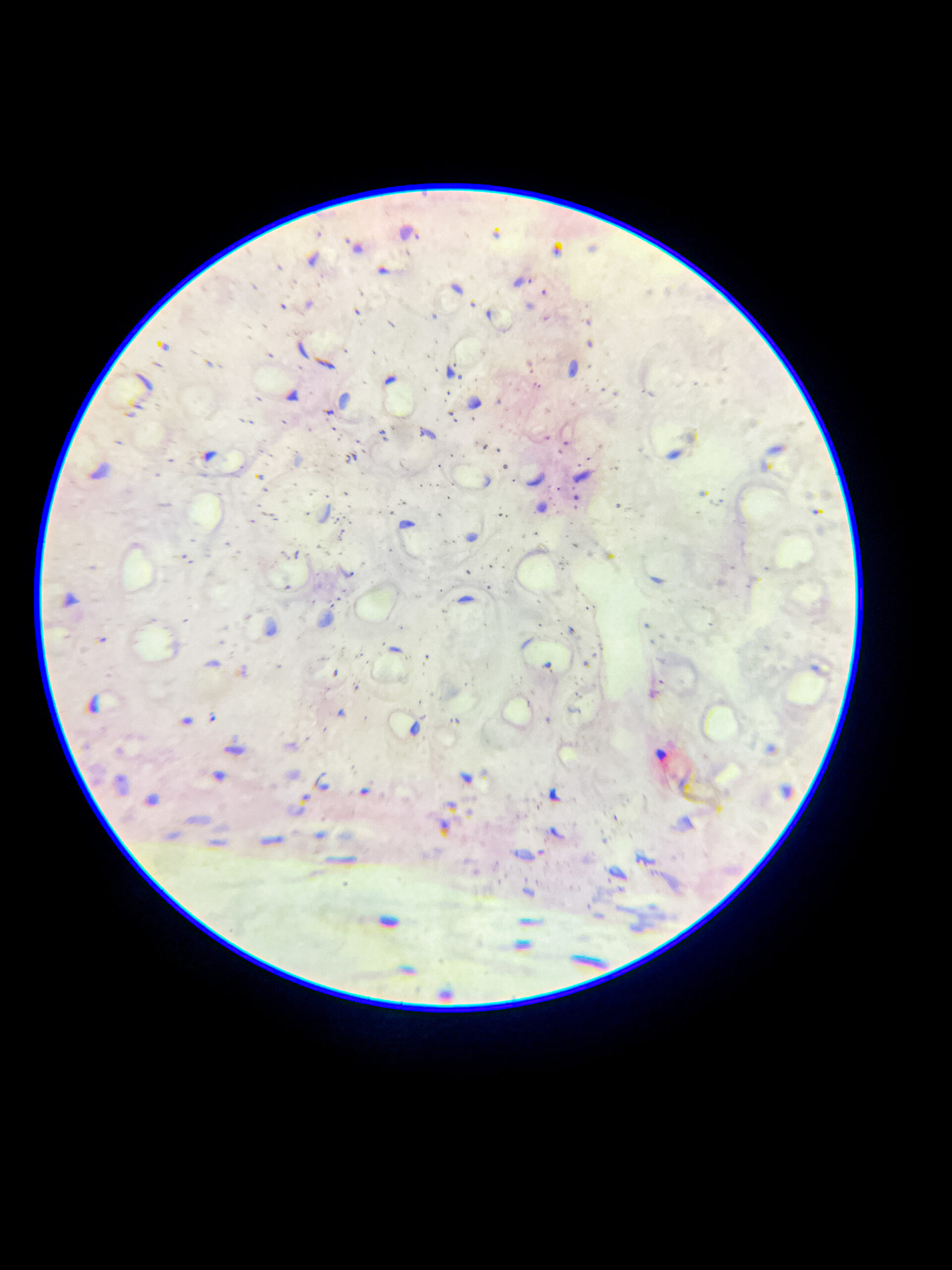
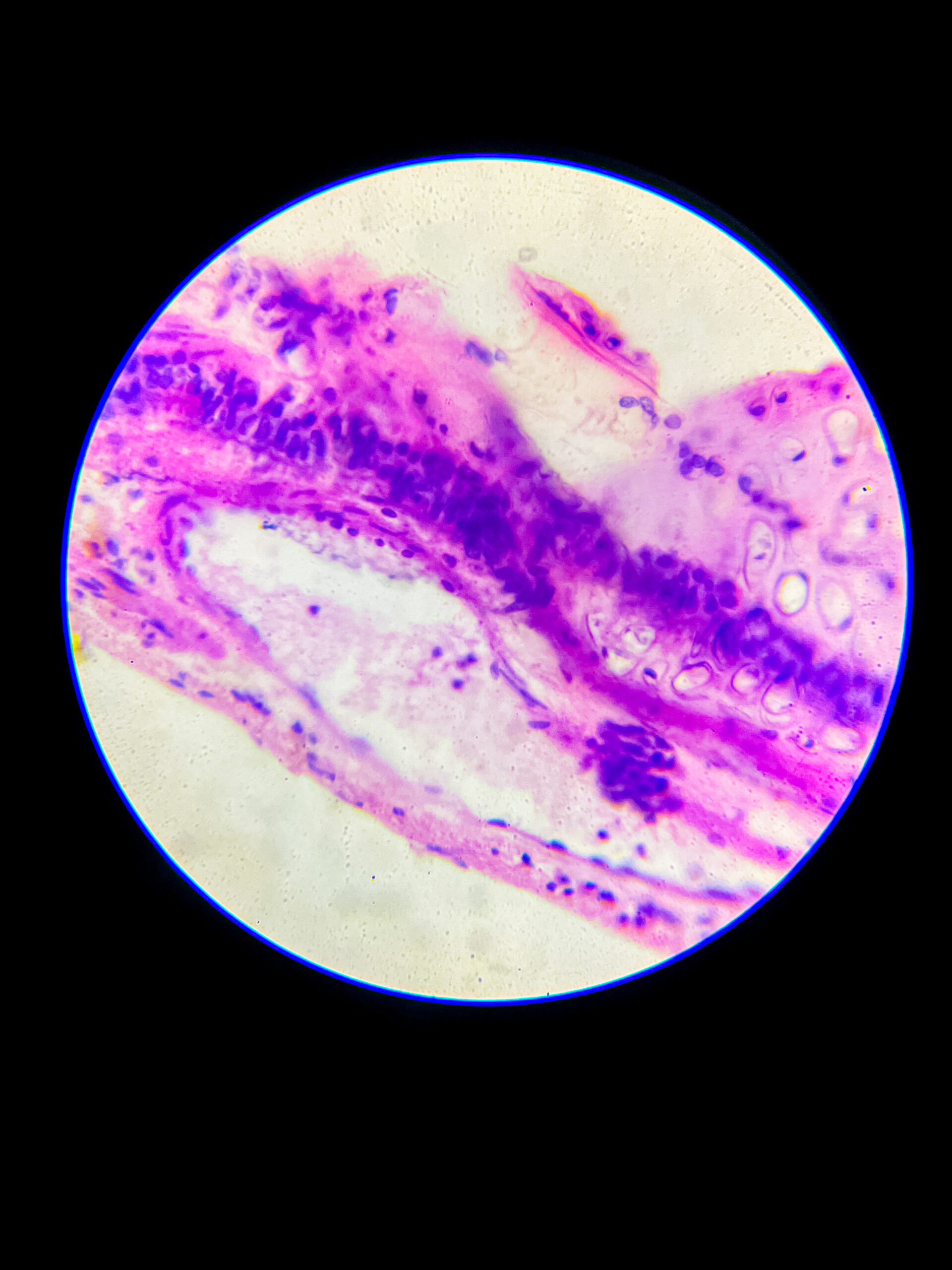
Microscopic appearance – under microscope, hyaline cartilage appears glassy, homogeneous, pale bluish or pinkish if stained, matrix looks smooth and translucent, that’s why called ‘hyaline’ (means glass-like), it’s difficult to distinguish individual collagen fibers because they are very fine and dispersed.
- chondrocytes are visible as round or oval cells, often clustered in groups called isogenous groups, each chondrocyte lies in a small cavity called lacuna, cytoplasm basophilic due to presence of RNA.
- peripheral region shows more elongated or flattened chondrocytes, central region contains round chondrocytes.
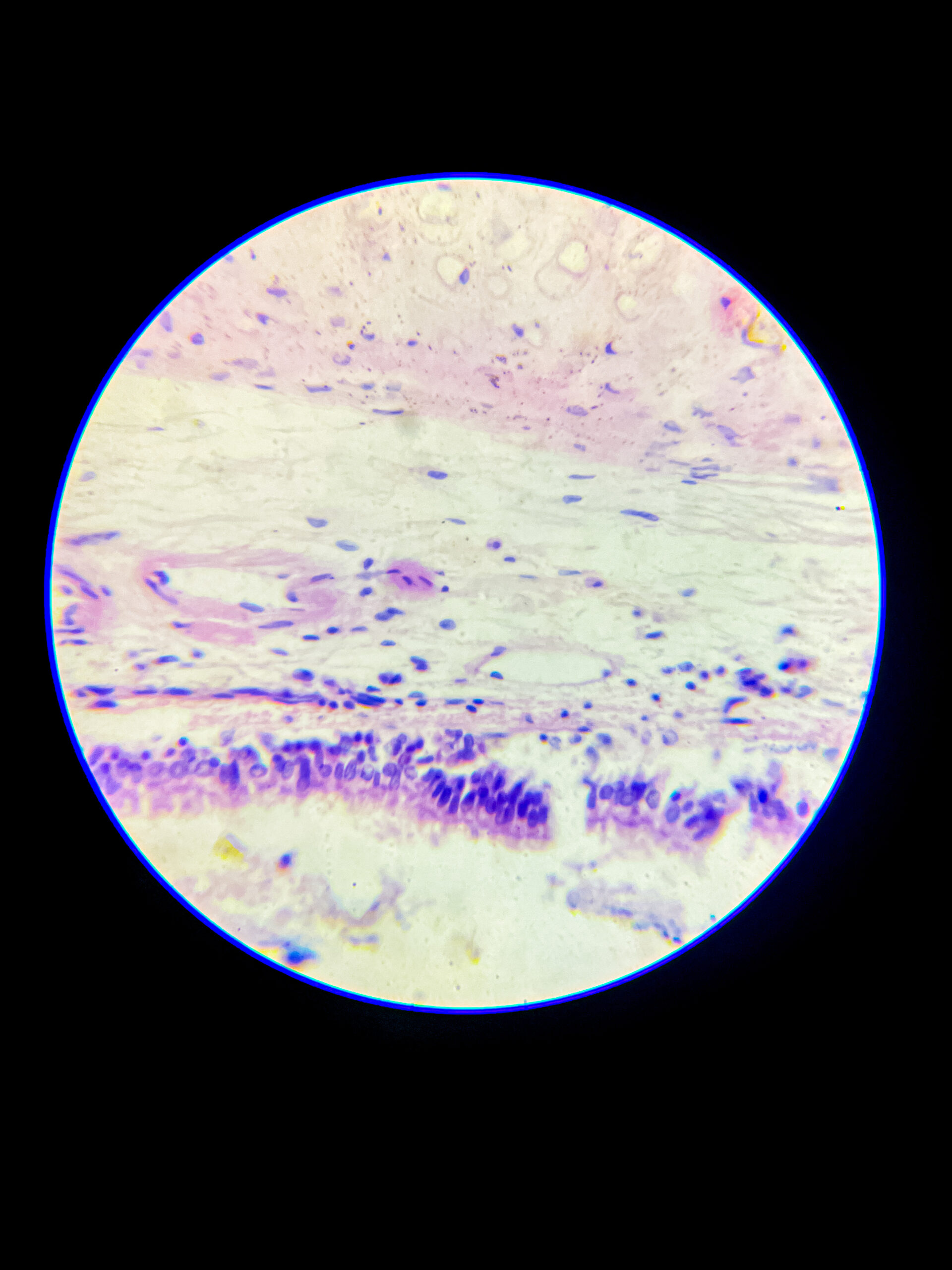
- perichondrium, a dense connective tissue layer, can be seen around the cartilage except at articular surfaces.
- no blood vessels or nerves present inside the tissue, that’s why repair is slow.
Staining features – with H&E stain, matrix looks smooth and light purple, chondrocyte nuclei dark blue, lacunae white or empty spaces, sometimes cytoplasmic shrinkage causes a clear halo around cells.
Summary of key features under microscope –
- smooth, glassy, homogeneous extracellular matrix
- chondrocytes inside lacunae, sometimes grouped
- fine collagen fibers not visible individually
- surrounded by perichondrium (except joints)
- avascular, aneural, slow healing
Common errors – sometimes matrix may show artifact spaces, nuclei of chondrocytes can look shrunken, misinterpretation as empty lacunae occurs if cells are not present in some sections.
Equipment
Compound Microscope
Magnification
40x, 100x, 400x, 1000x
Staining Technique
Sourav Pan (2025). Hyaline Cartilage Under Microscope. Biology Notes Online. Retrieved 23/02/2026 from https://biologynotesonline.com/community-image/hyaline-cartilage-under-microscope/
Helpful: 100%