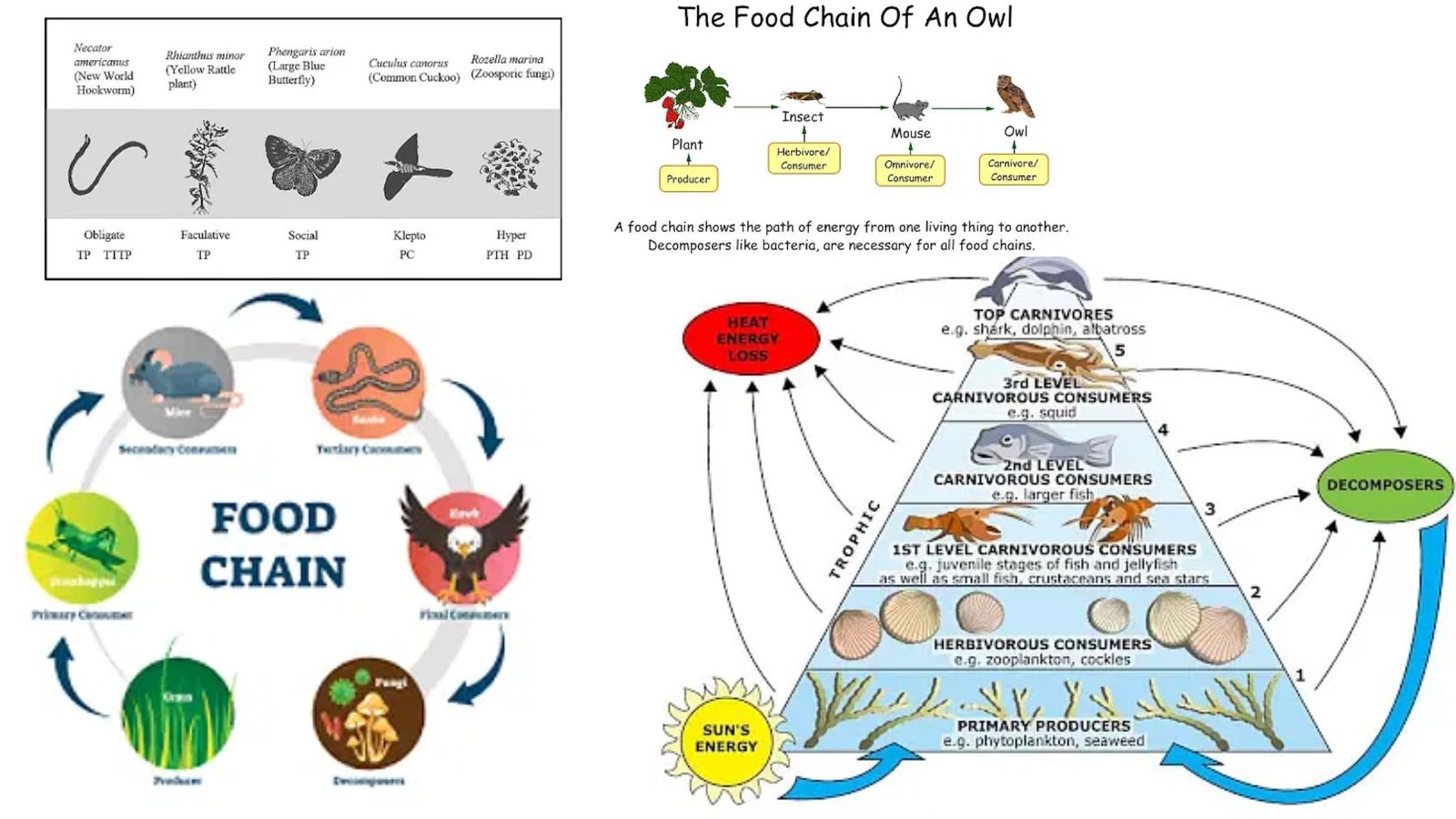
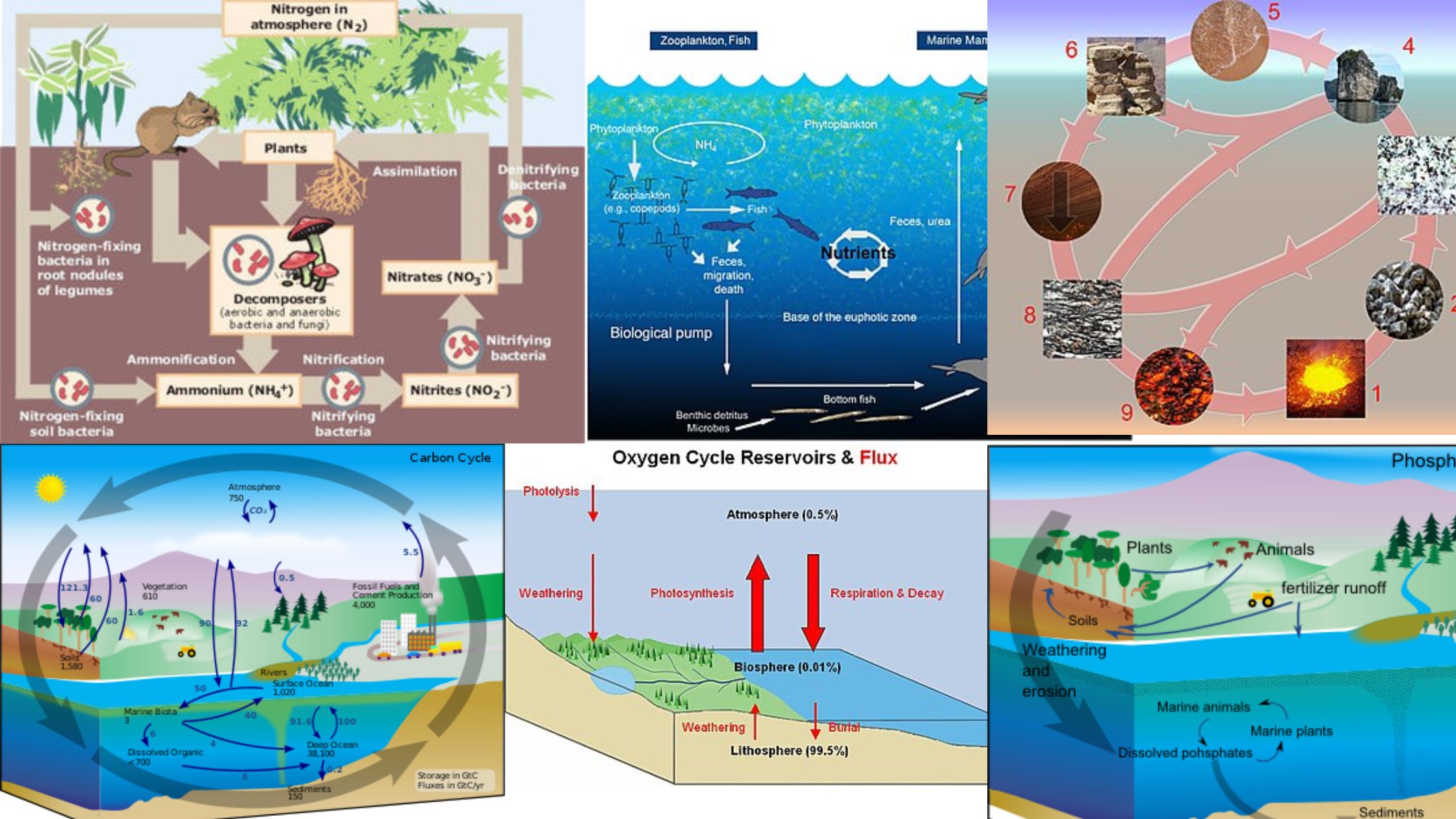
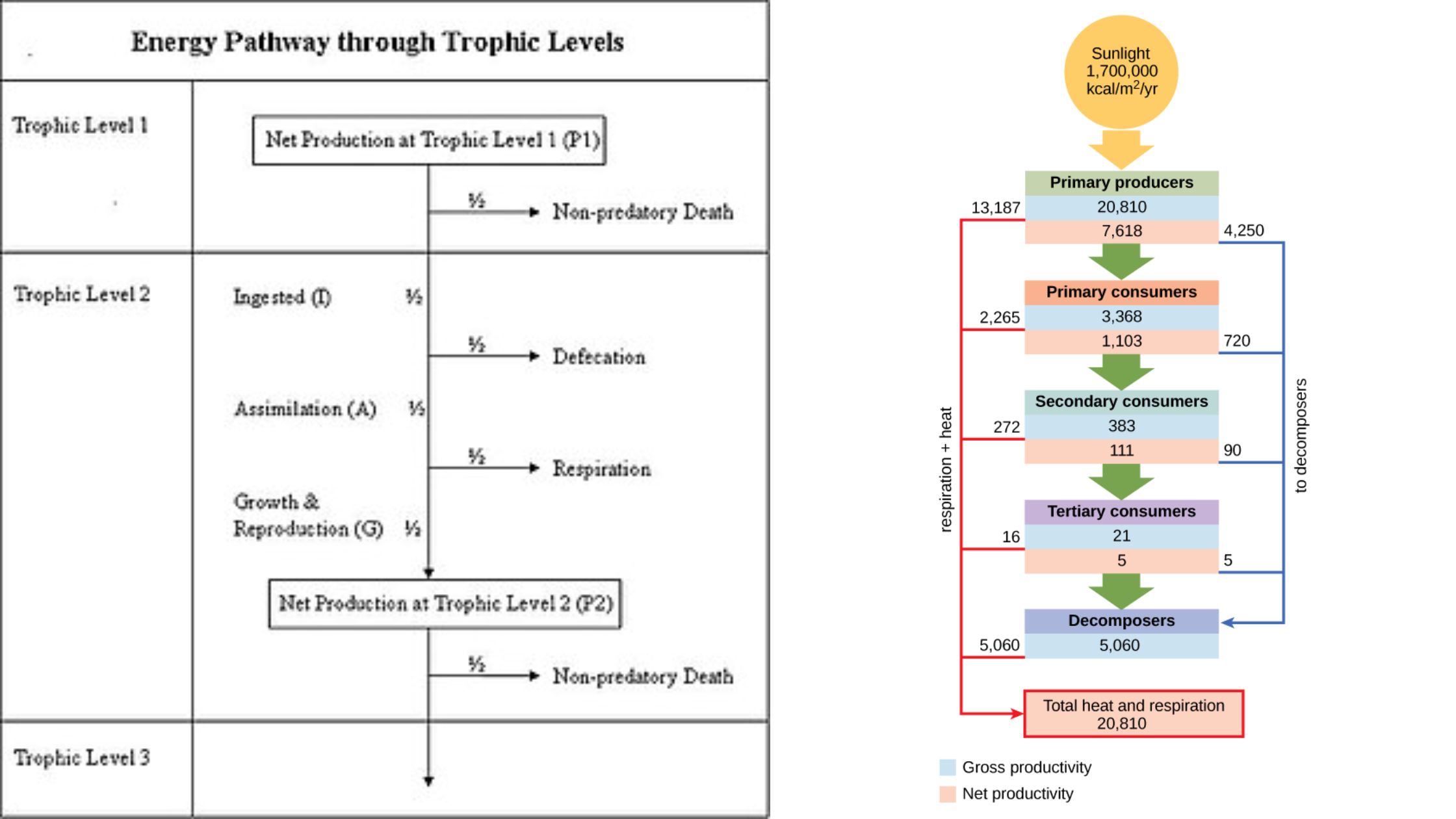
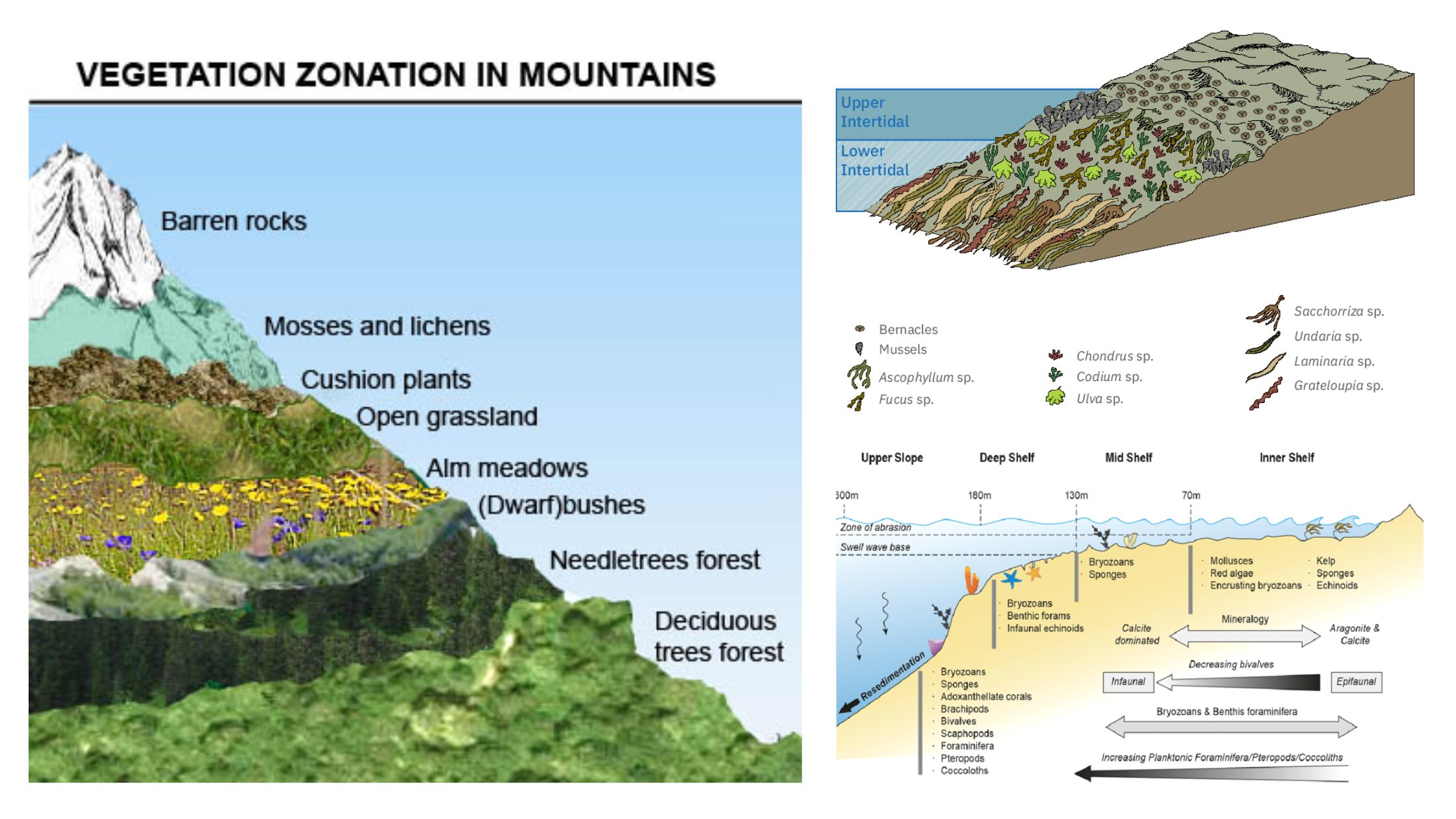
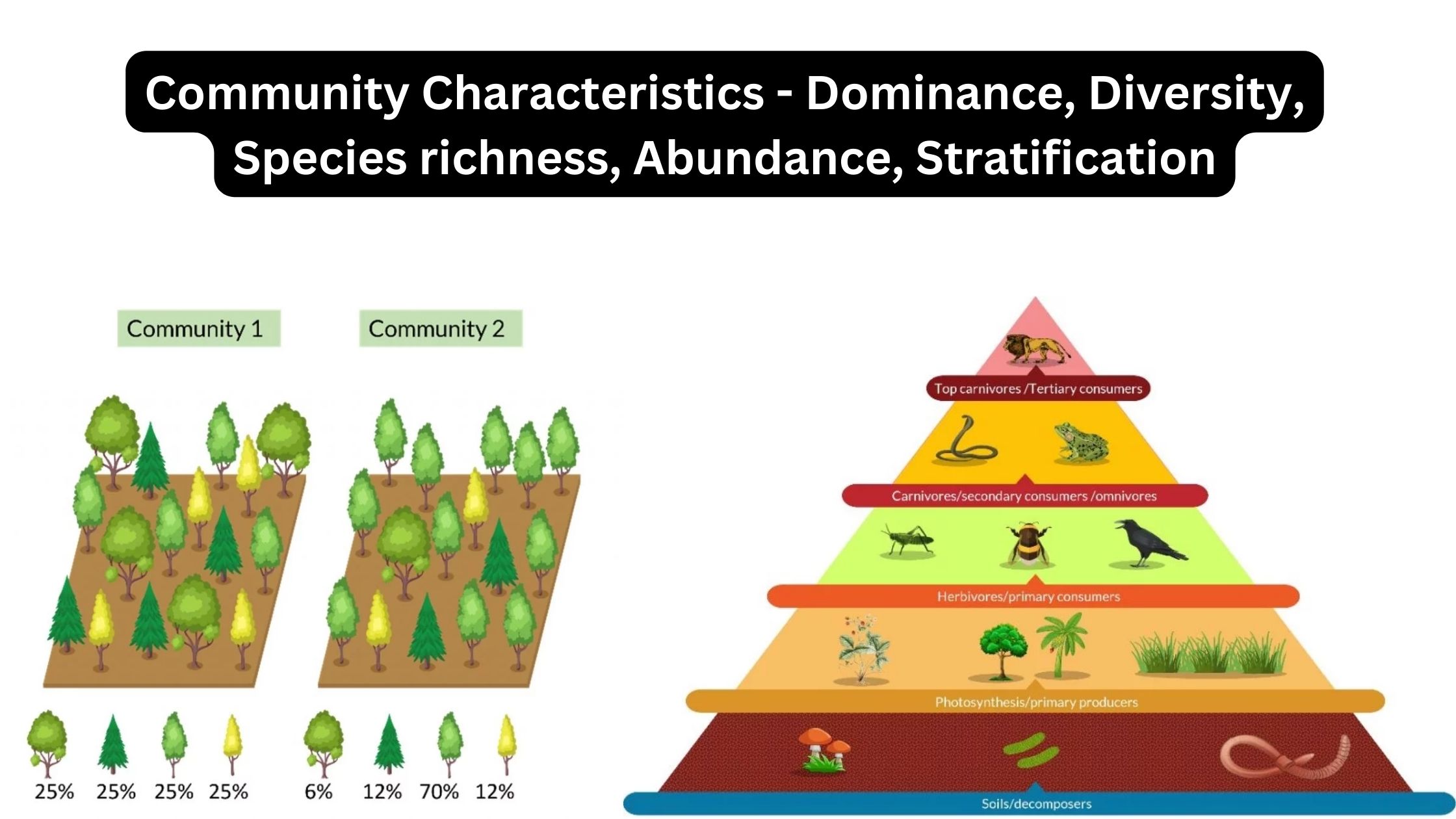
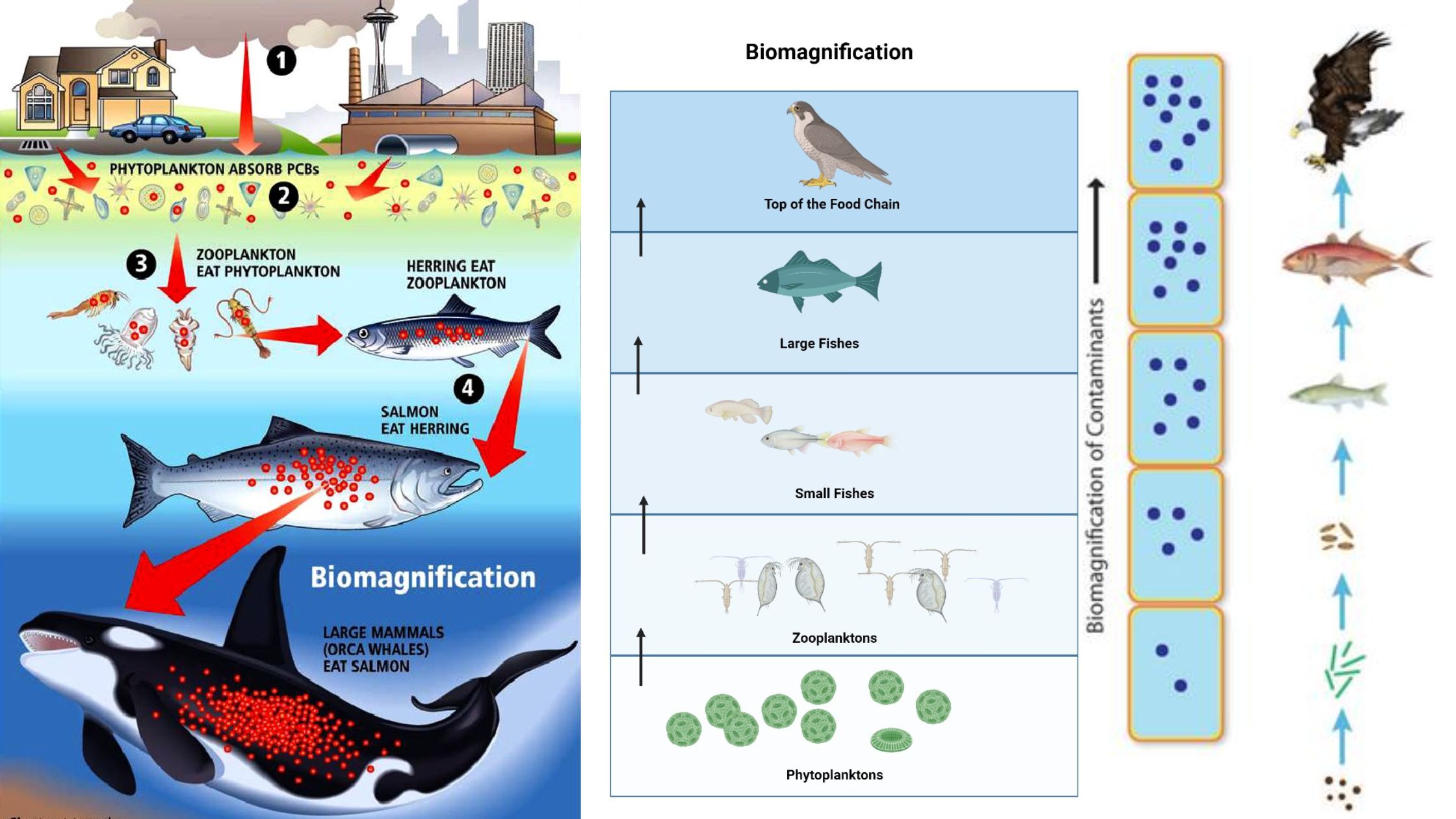
Grazing Food Chain – Definition, Types, Examples and Features
What is Grazing Food Chain? Definition of Grazing Food Chain The grazing food chain is a type of food chain in which energy flows from photosynthetic producers to herbivores and then to carnivores. It starts with green plants that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and is characterized by the consumption of plant material by … Read more