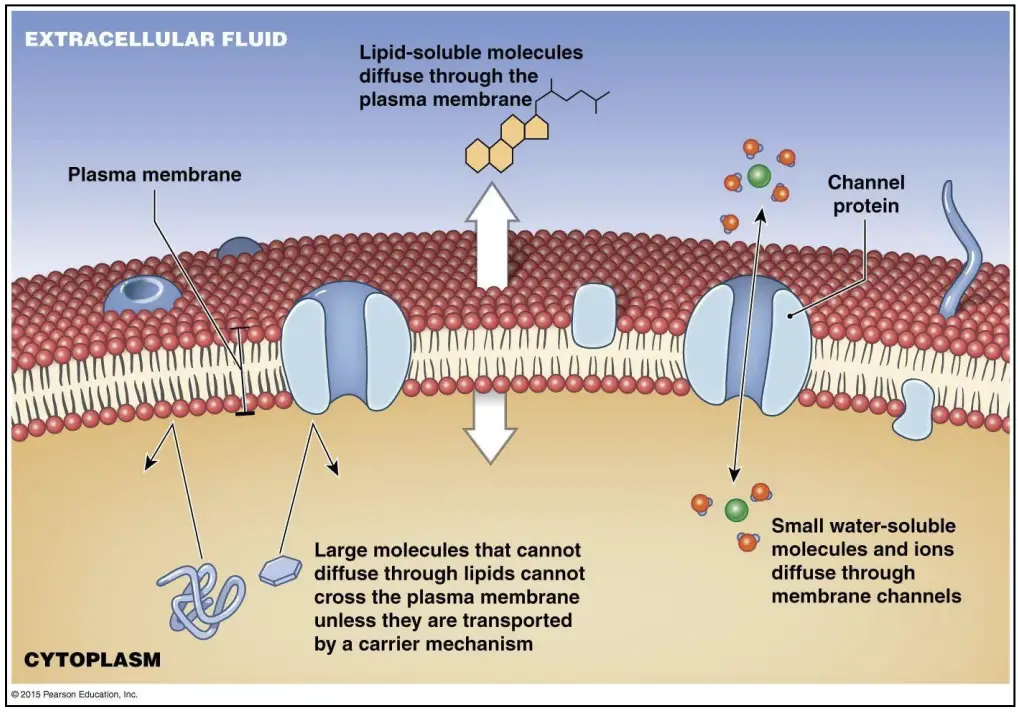
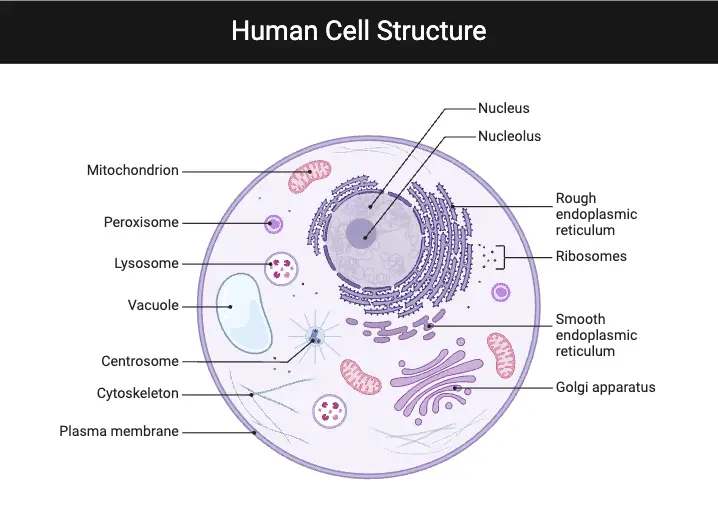
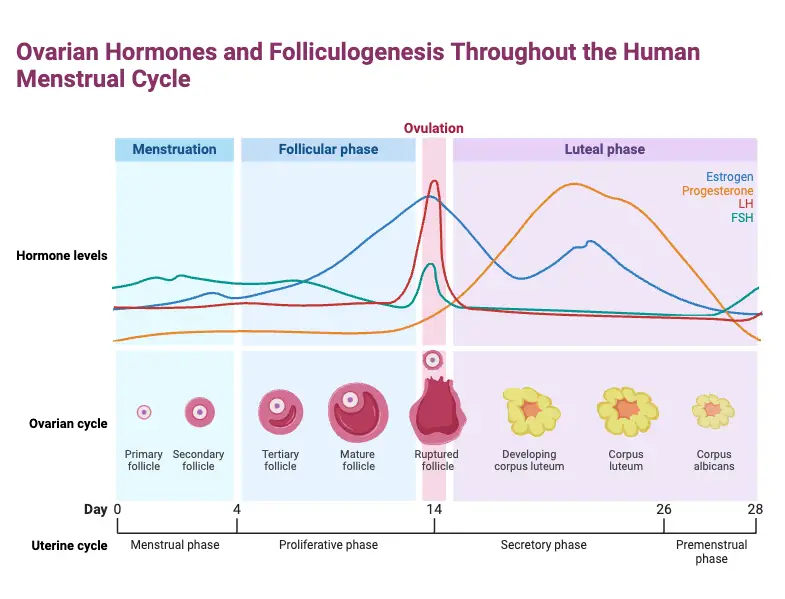
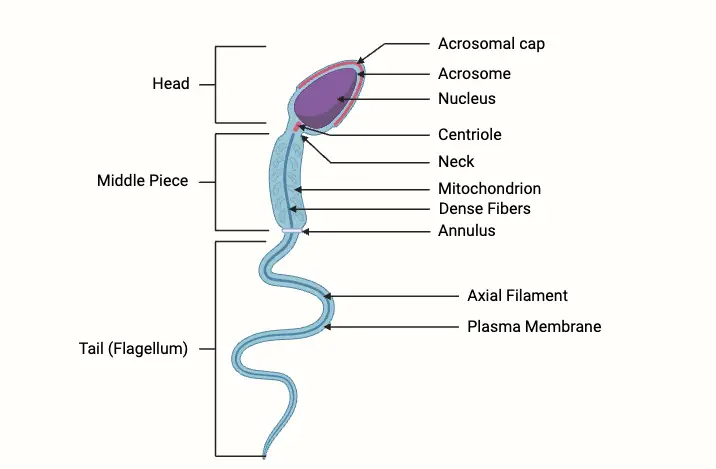
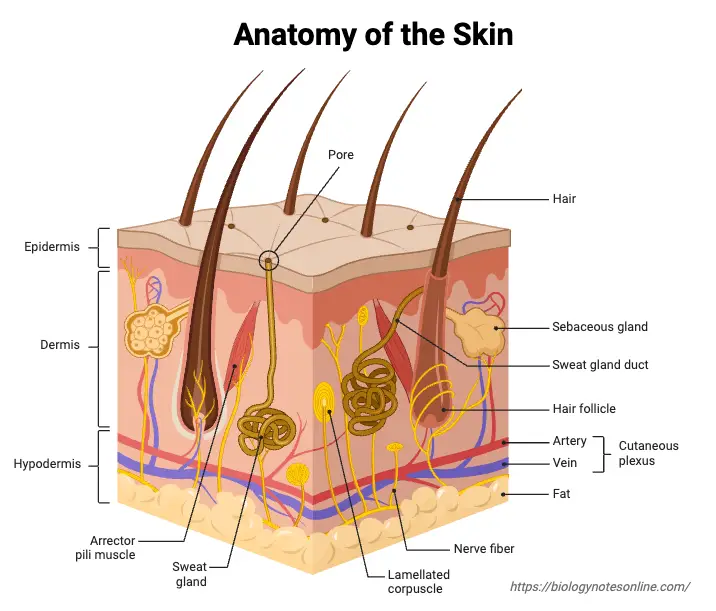
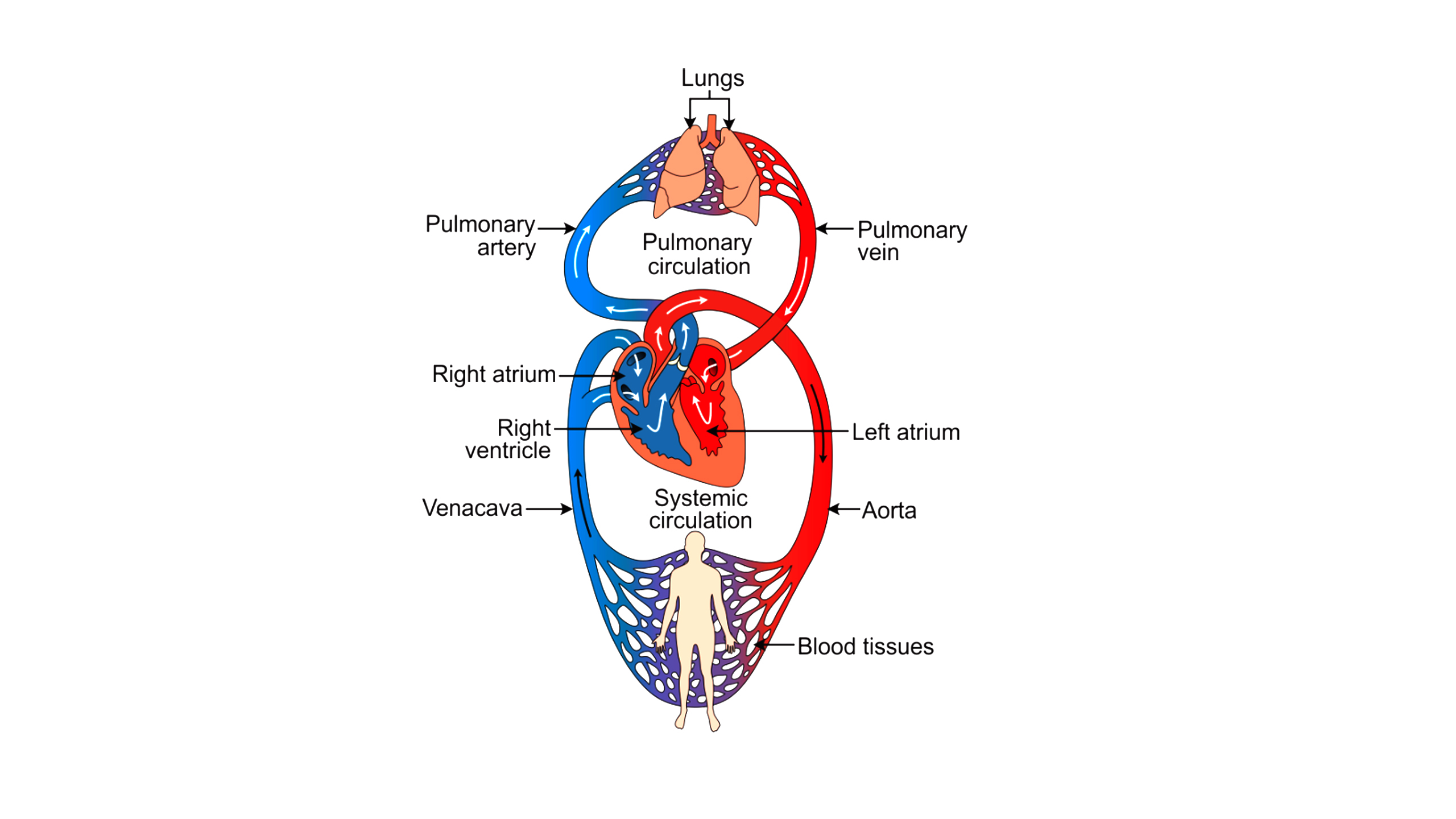
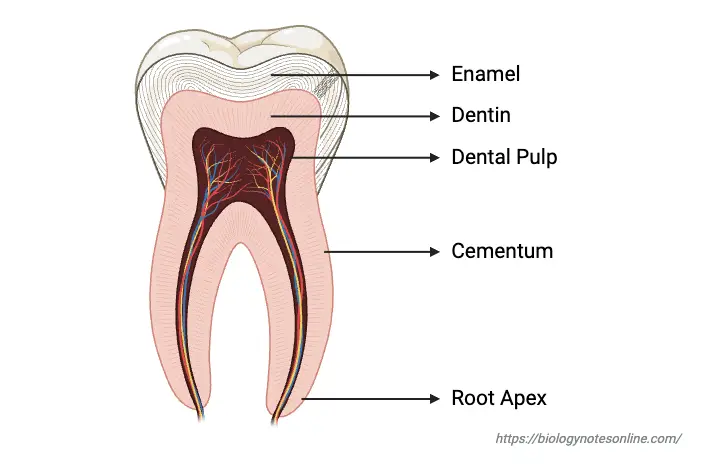
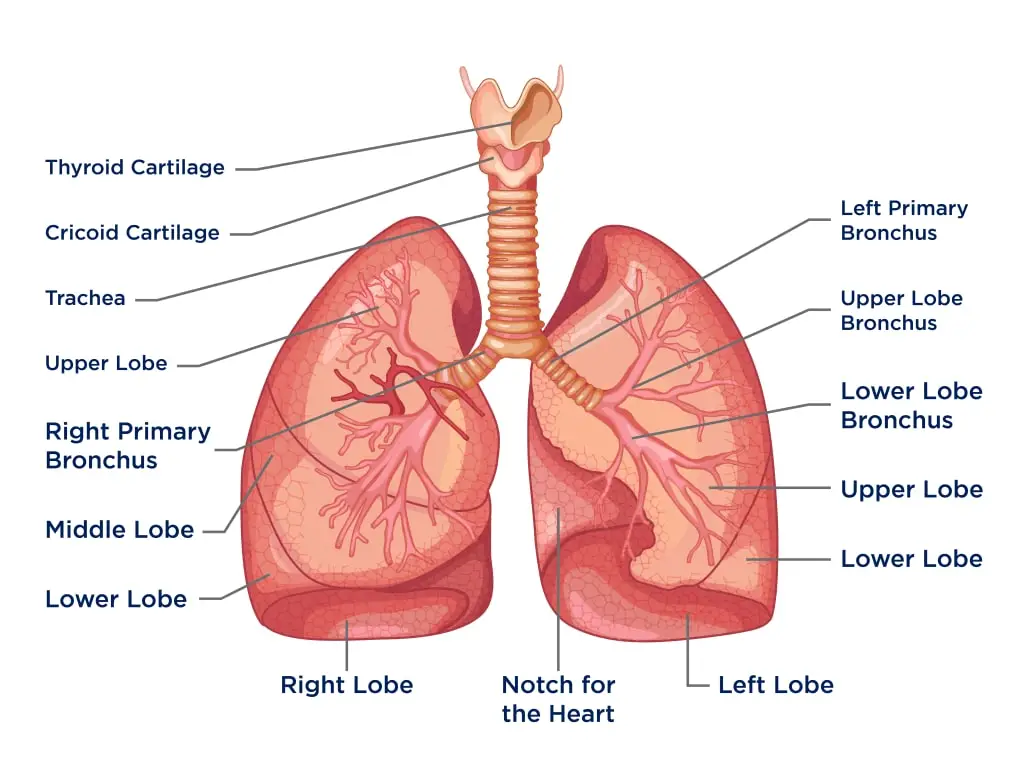
Biological Membrane – Classification, Structure, Functions
Membranes are thin, flexible layers that act like barriers or filters, separating different spaces or substances while allowing certain things to pass through. Think of them as sheets or films—some natural, others human-made. In living things, cell membranes are crucial. They wrap around cells, controlling what enters or exits, like nutrients in and waste out. … Read more