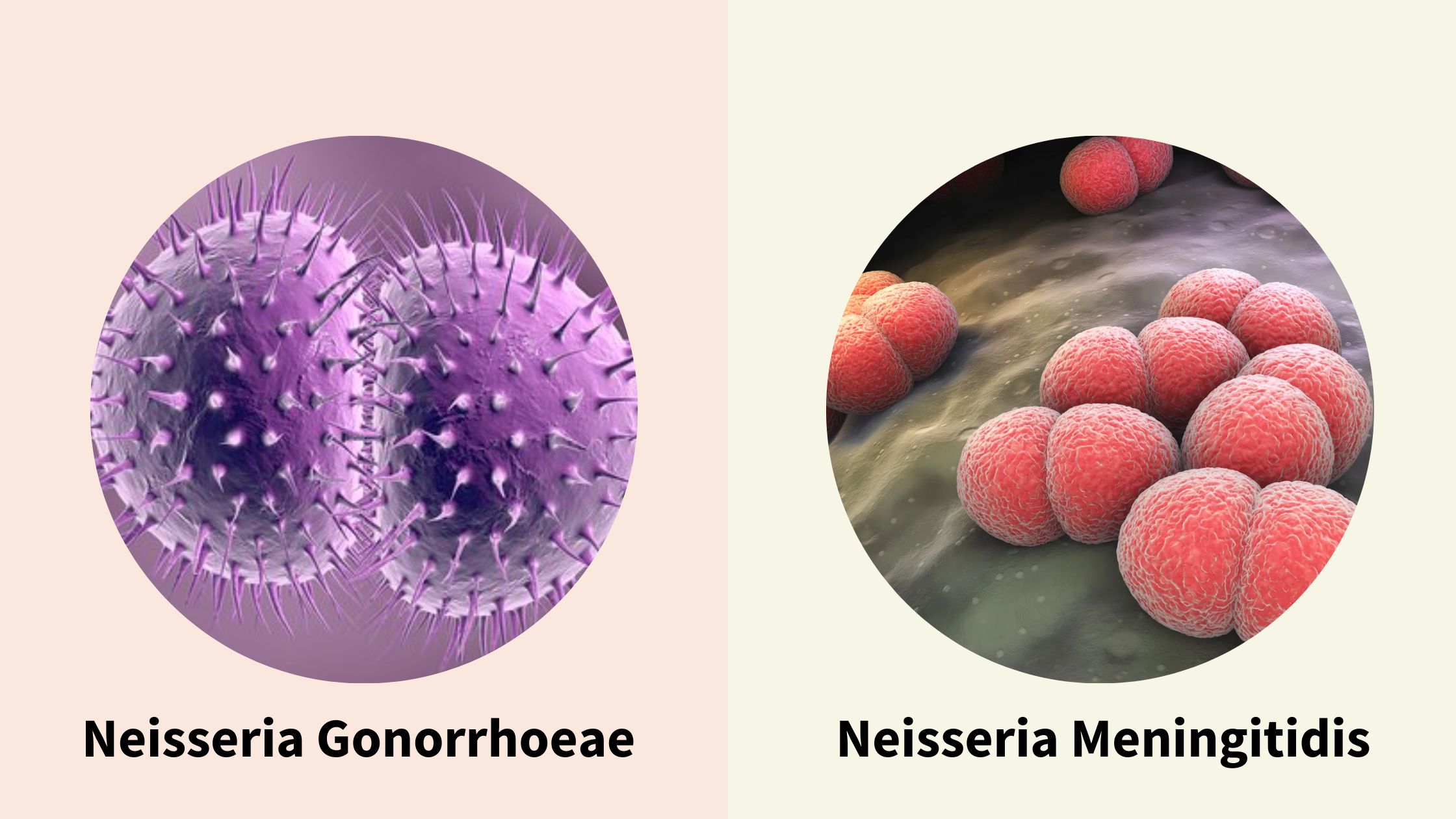
What is the Difference Between Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Neisseria Meningitidis
What is Neisseria Gonorrhoeae? Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a bacterium that can cause the sexually transmitted infection (STI) called gonorrhea. It is transmitted through sexual contact and can infect the genital tract, anus, and throat. Symptoms of gonorrhea can include painful urination, discharge from the genitals, and painful or swollen testicles in men, and abnormal vaginal … Read more