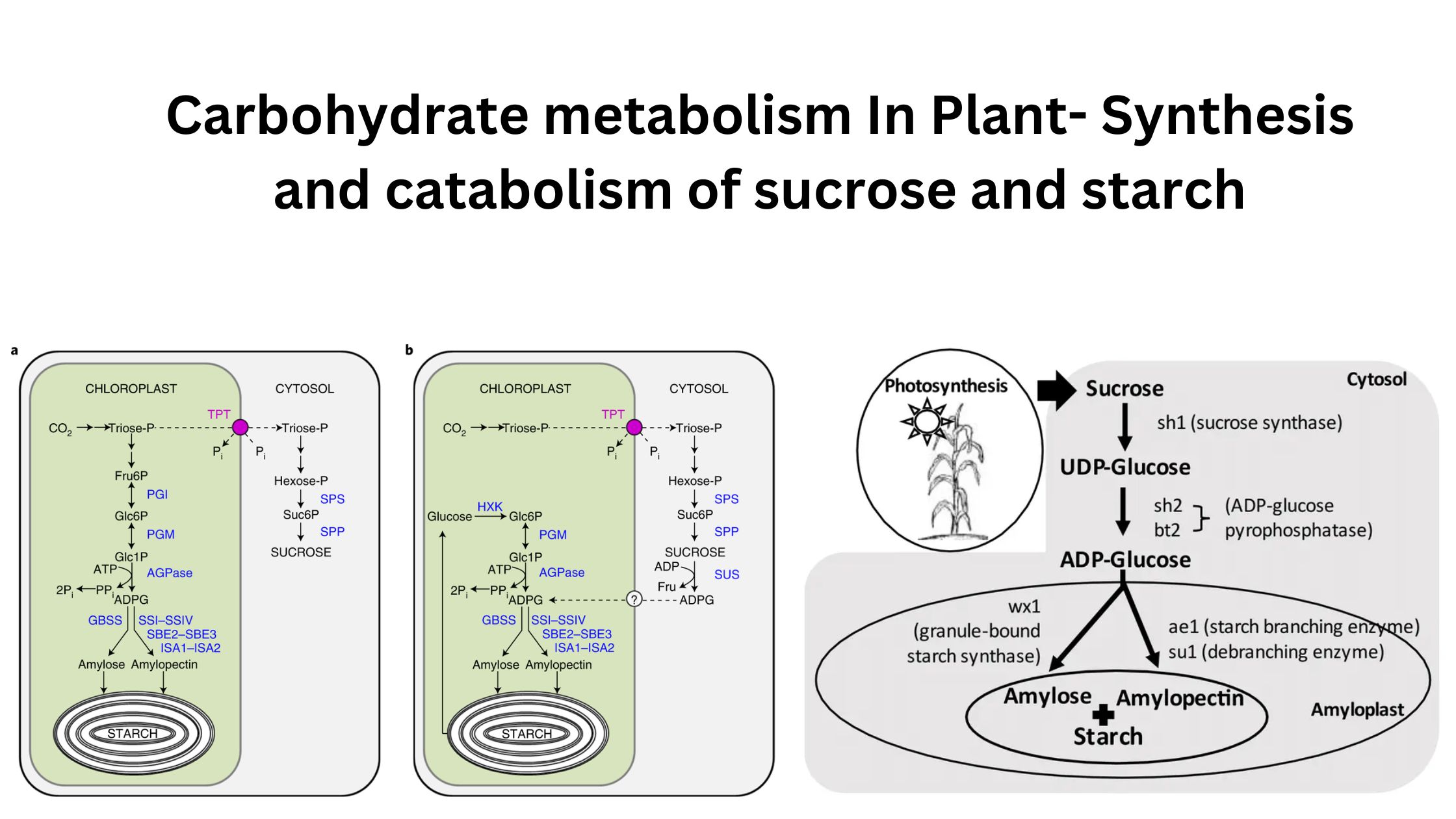
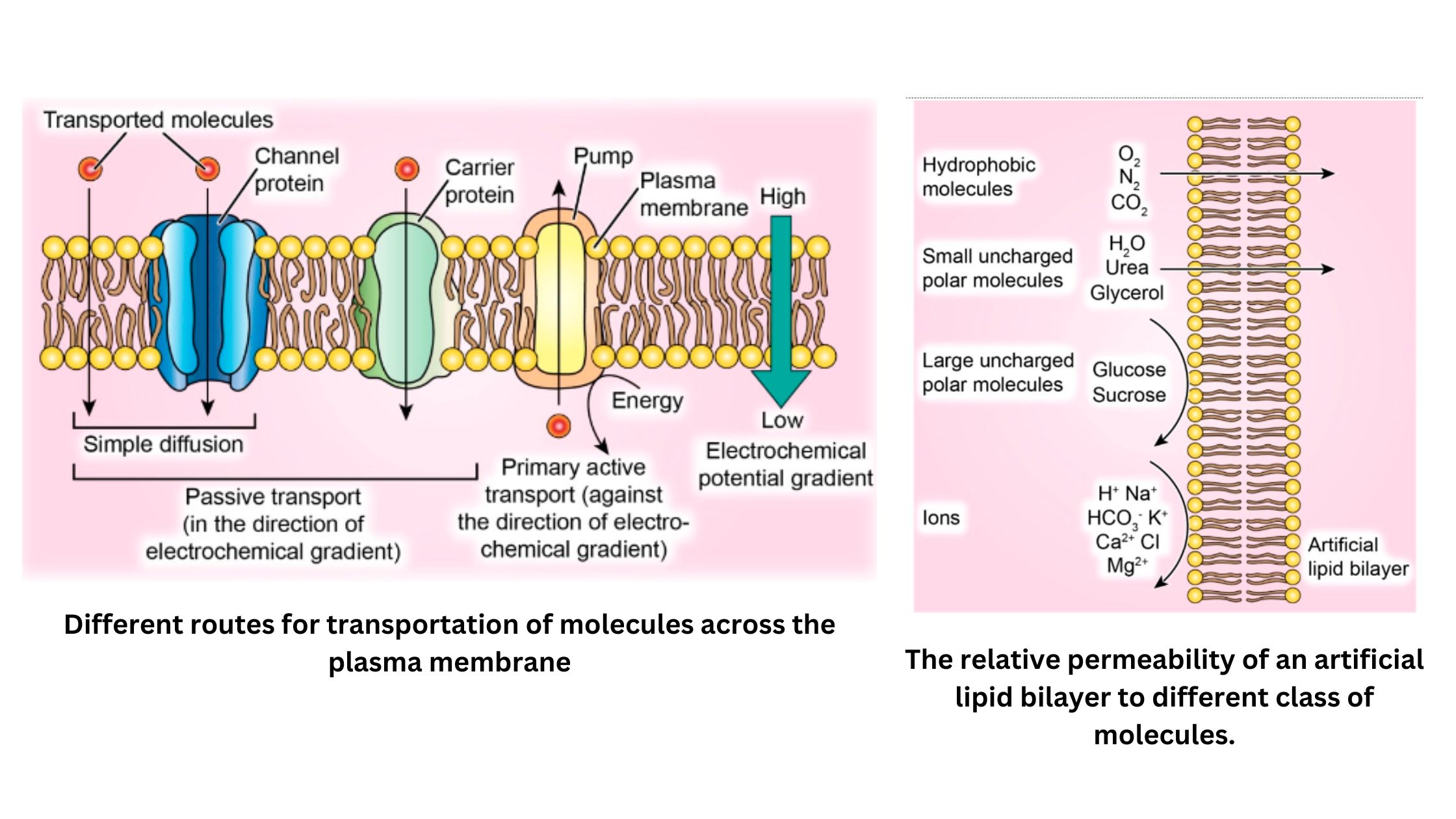
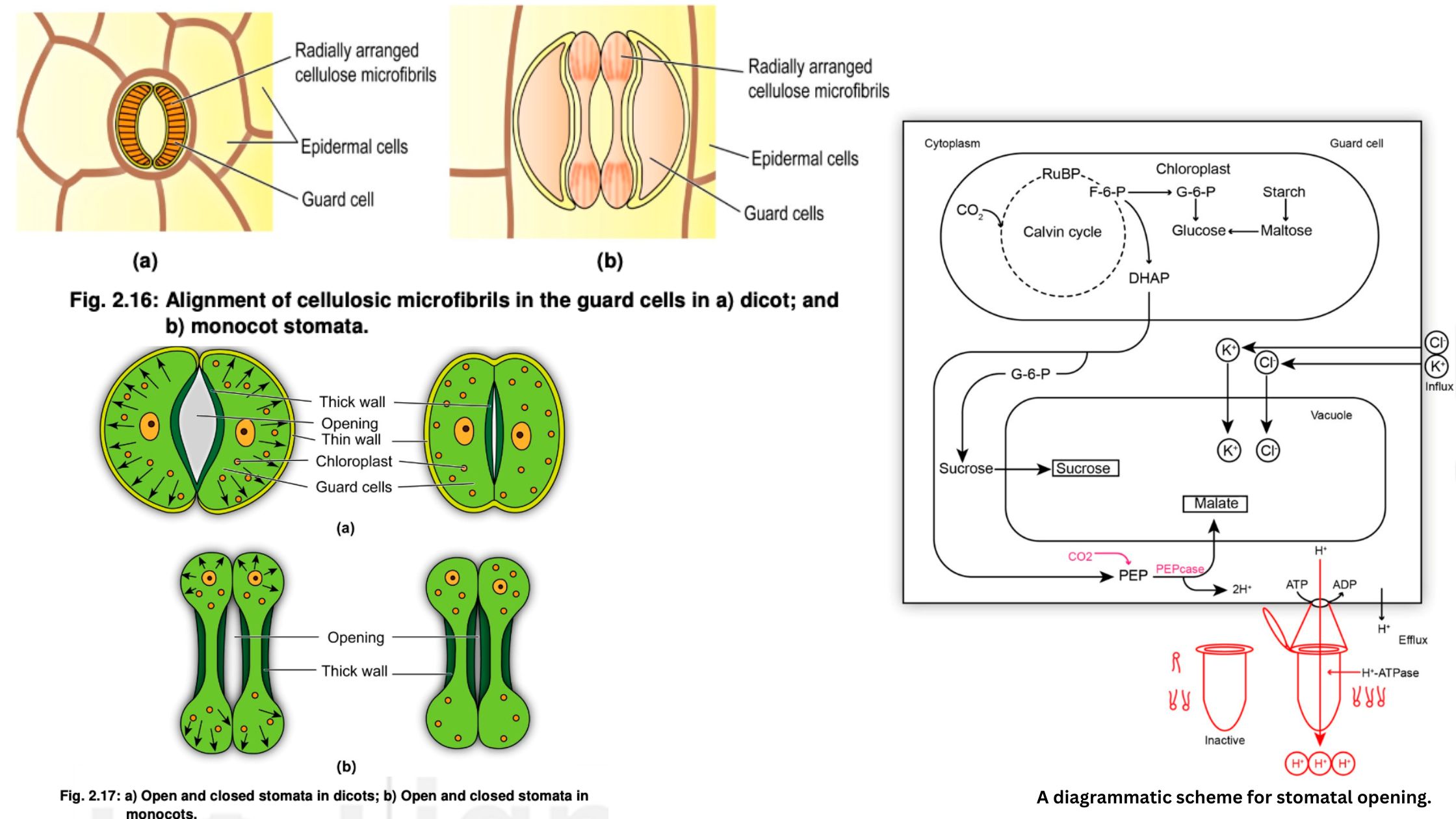
Transpiration – Types, Mechanism, Factors, Significance
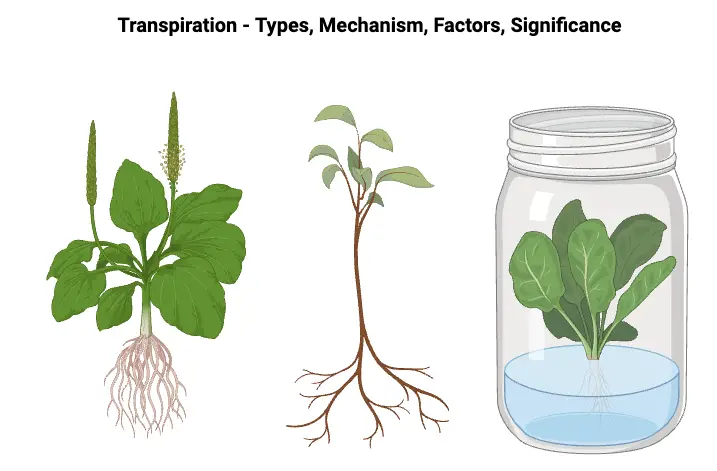
What is Transpiration? Types of Transpiration Transpiration in plants occurs through several distinct pathways, each playing a specific role in water movement and evaporation. These pathways are classified into four primary types: stomatal, cuticular, lenticular, and bark transpiration. Factors affecting Transpiration Transpiration is influenced by a variety of factors that can be classified into two … Read more