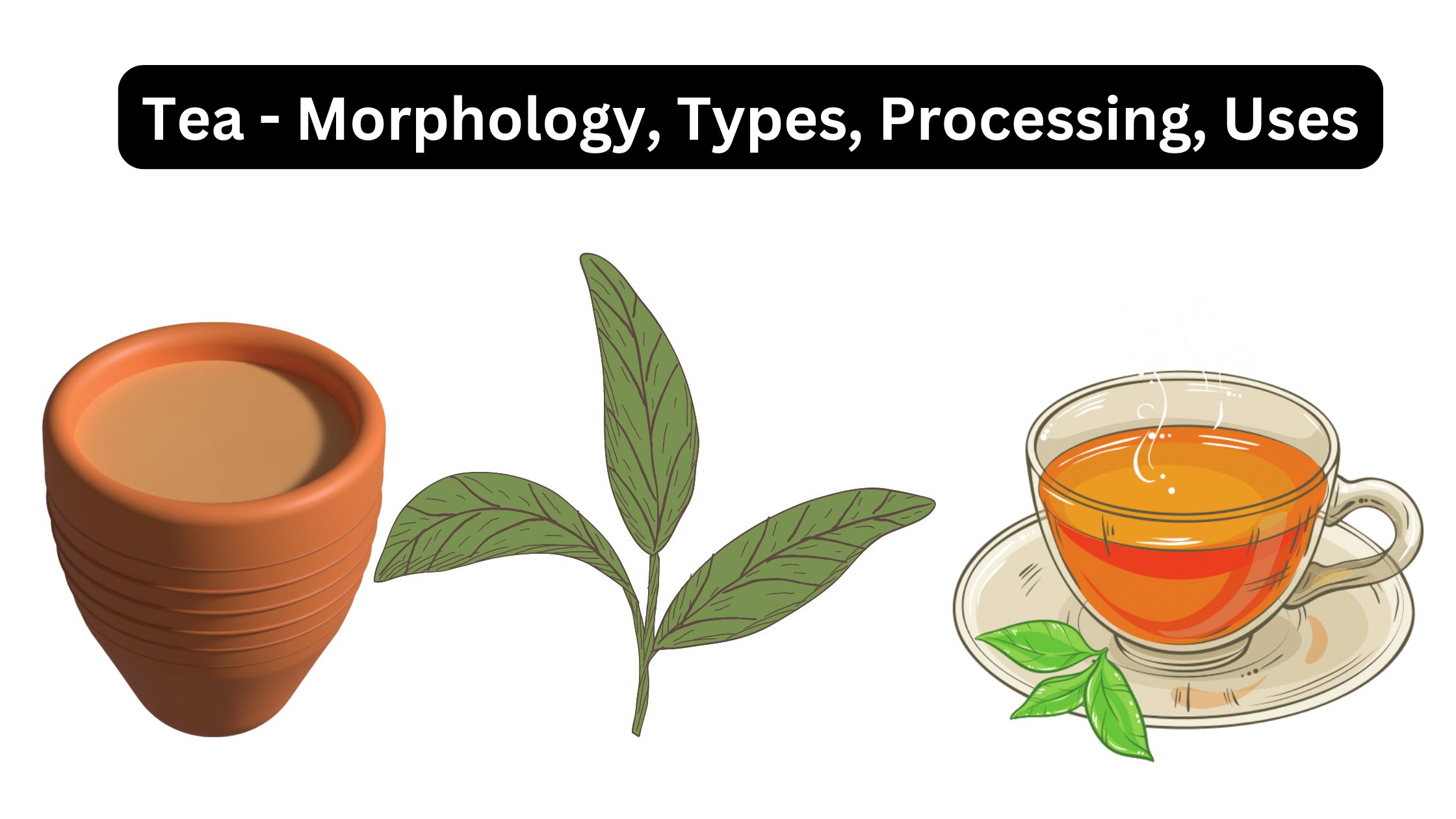
Tea – Morphology, Types, Processing, Uses
What is Tea? Types of Tea Tea is classified into several distinct types, primarily based on the processing techniques used after harvesting the Camellia sinensis leaves. Each type of tea varies in terms of oxidation, fermentation, and the preservation of specific chemical compounds such as polyphenols and catechins. Below is a detailed explanation of the … Read more