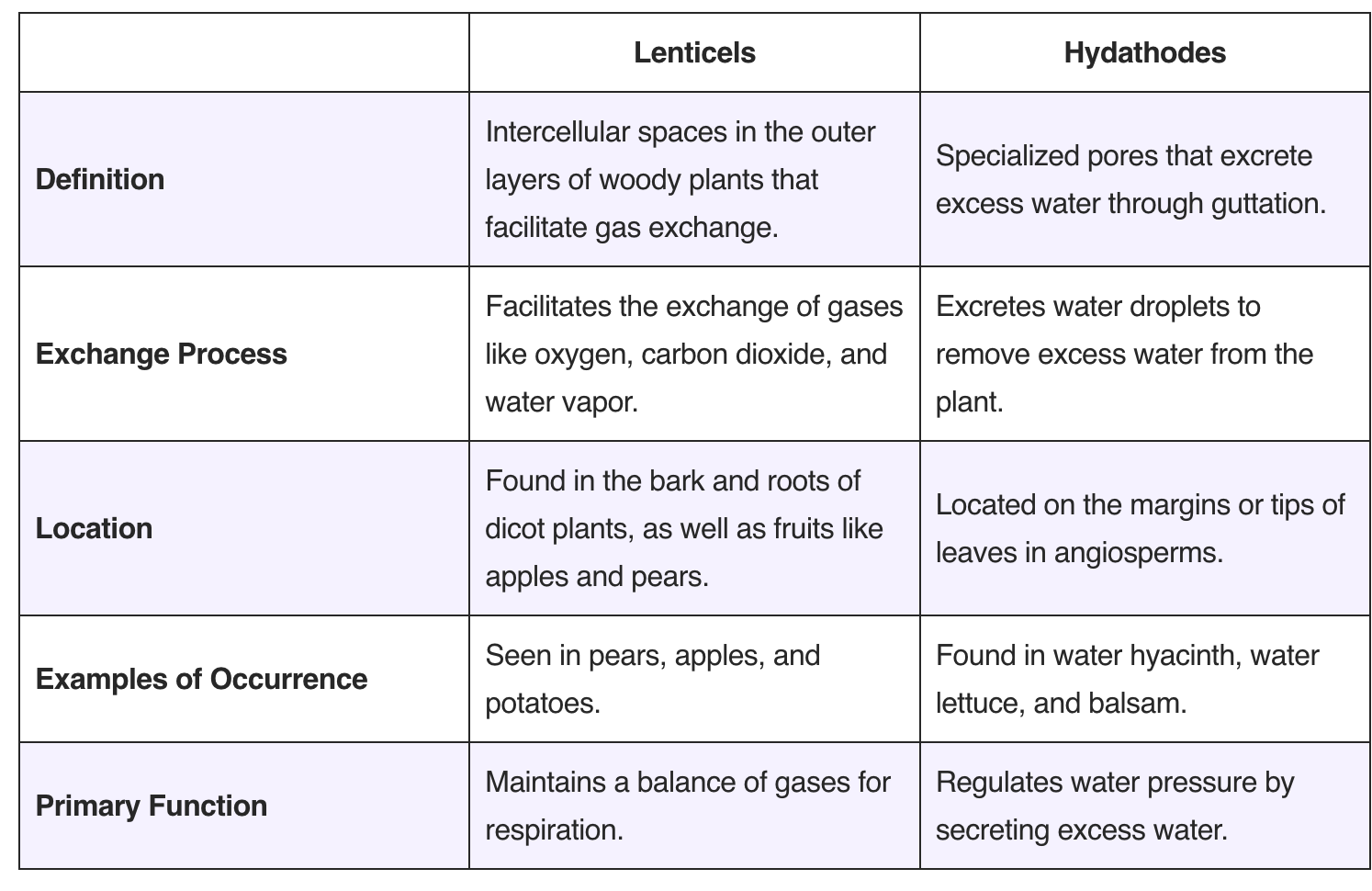
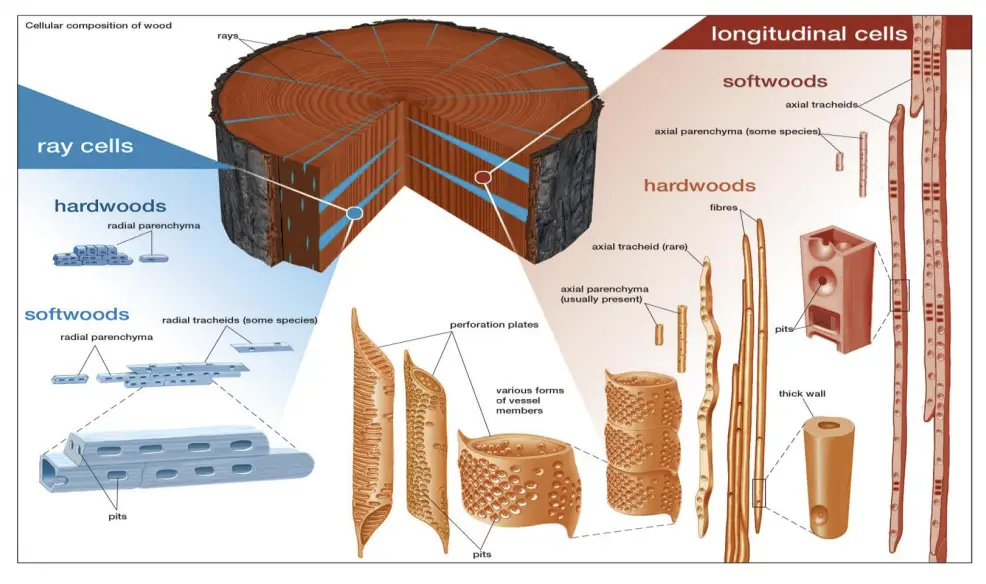
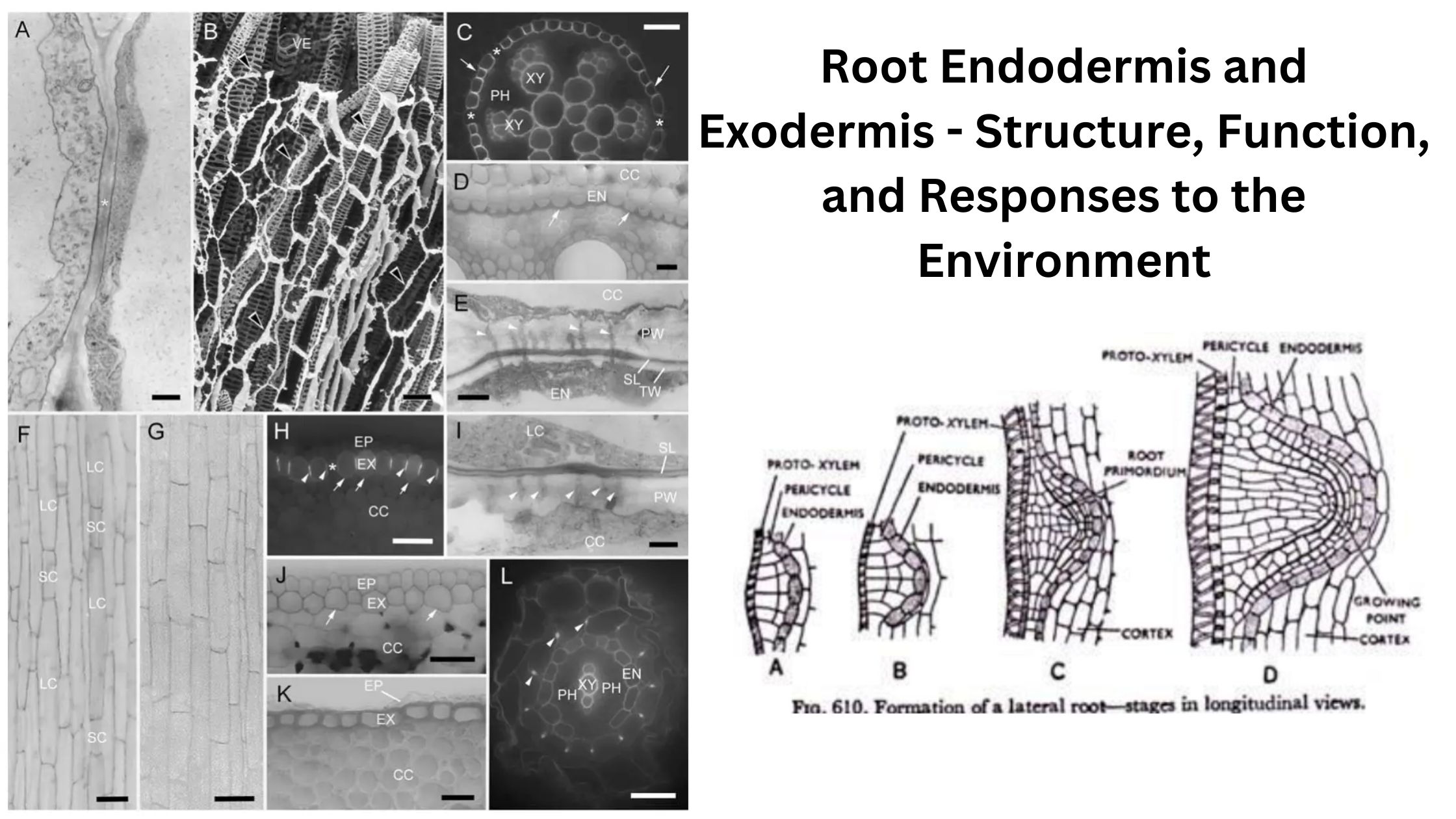
Difference between Lenticels and Hydathodes
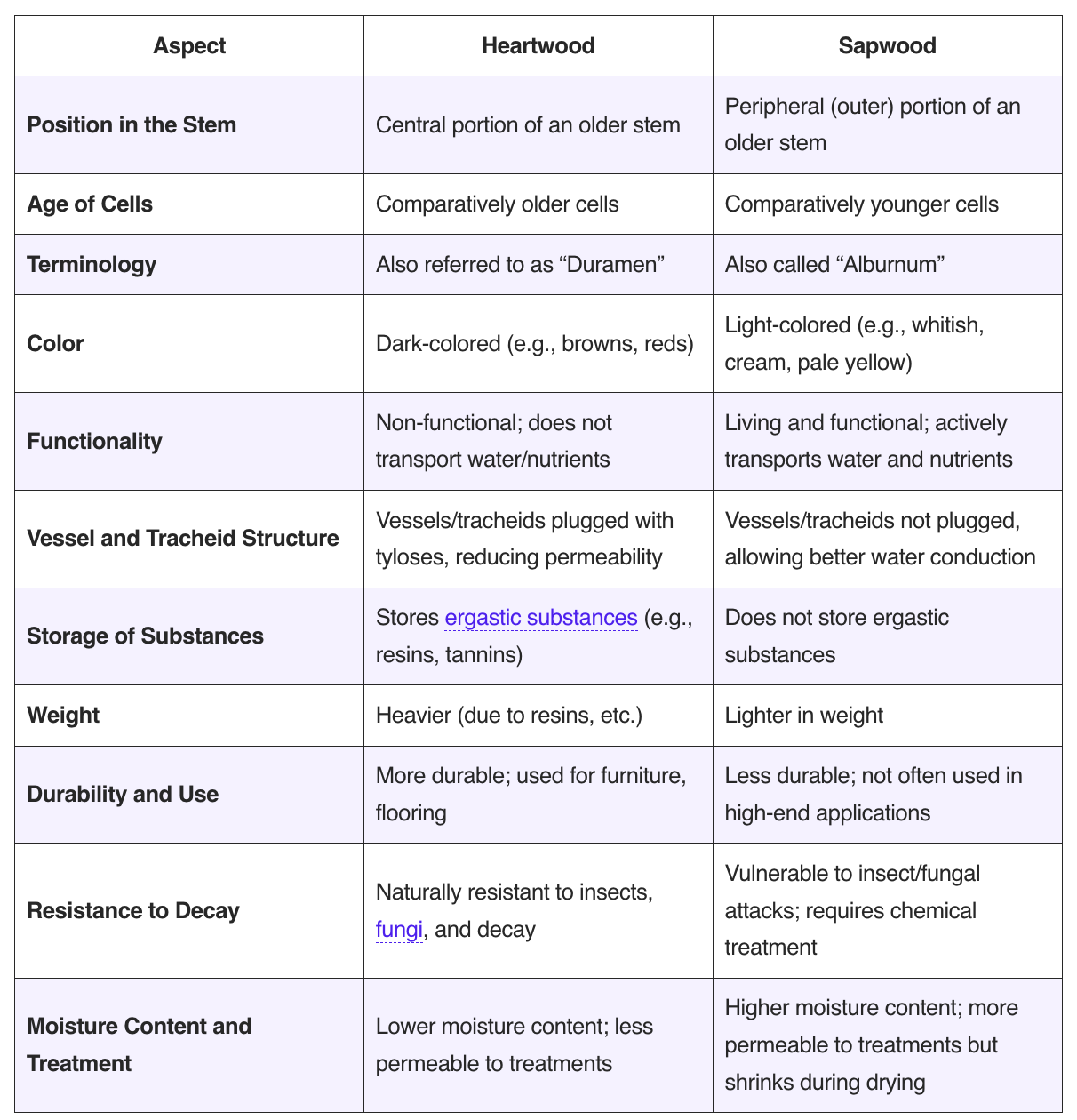
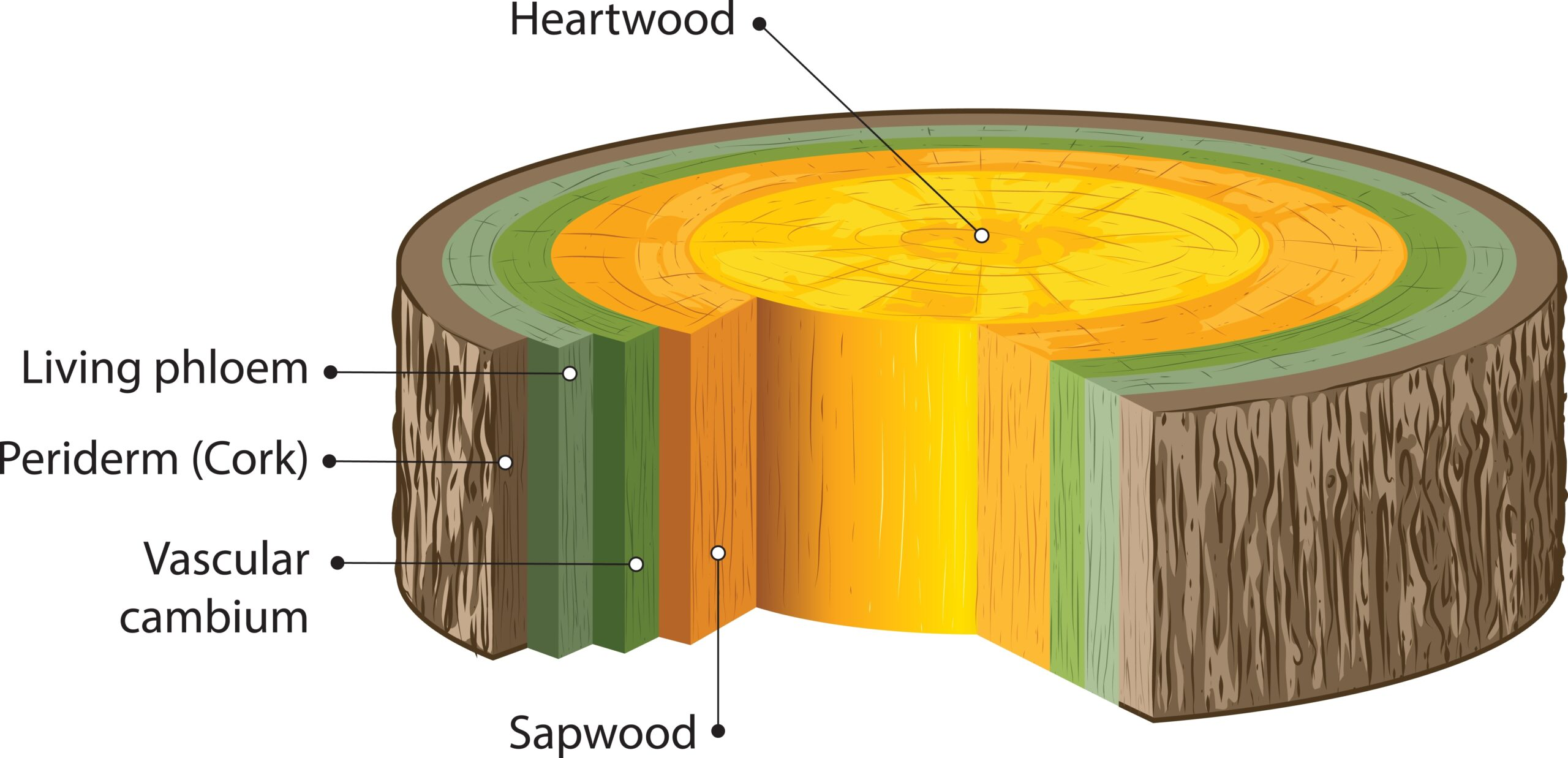
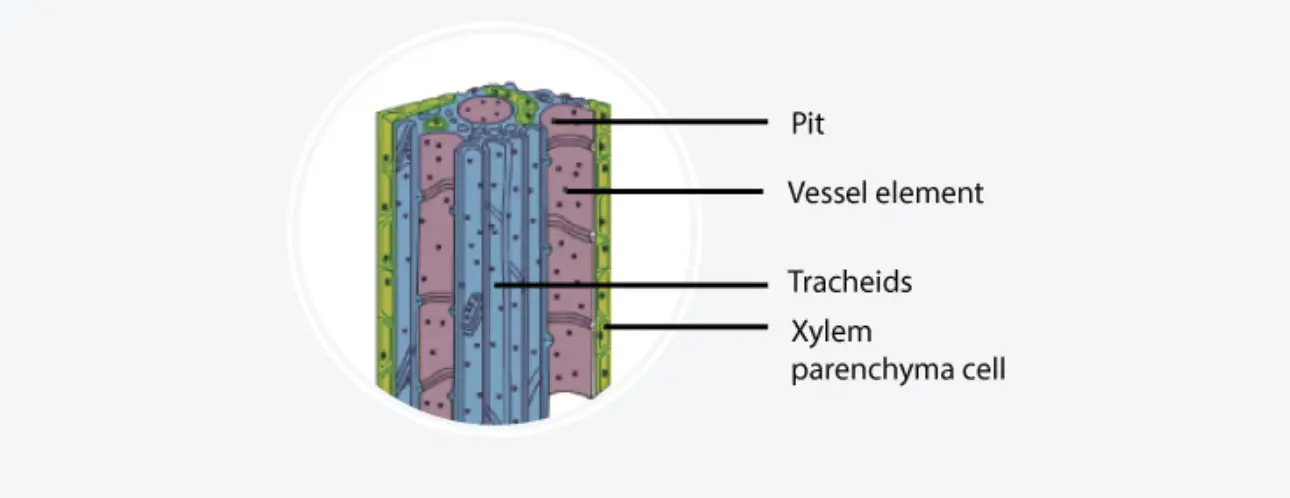
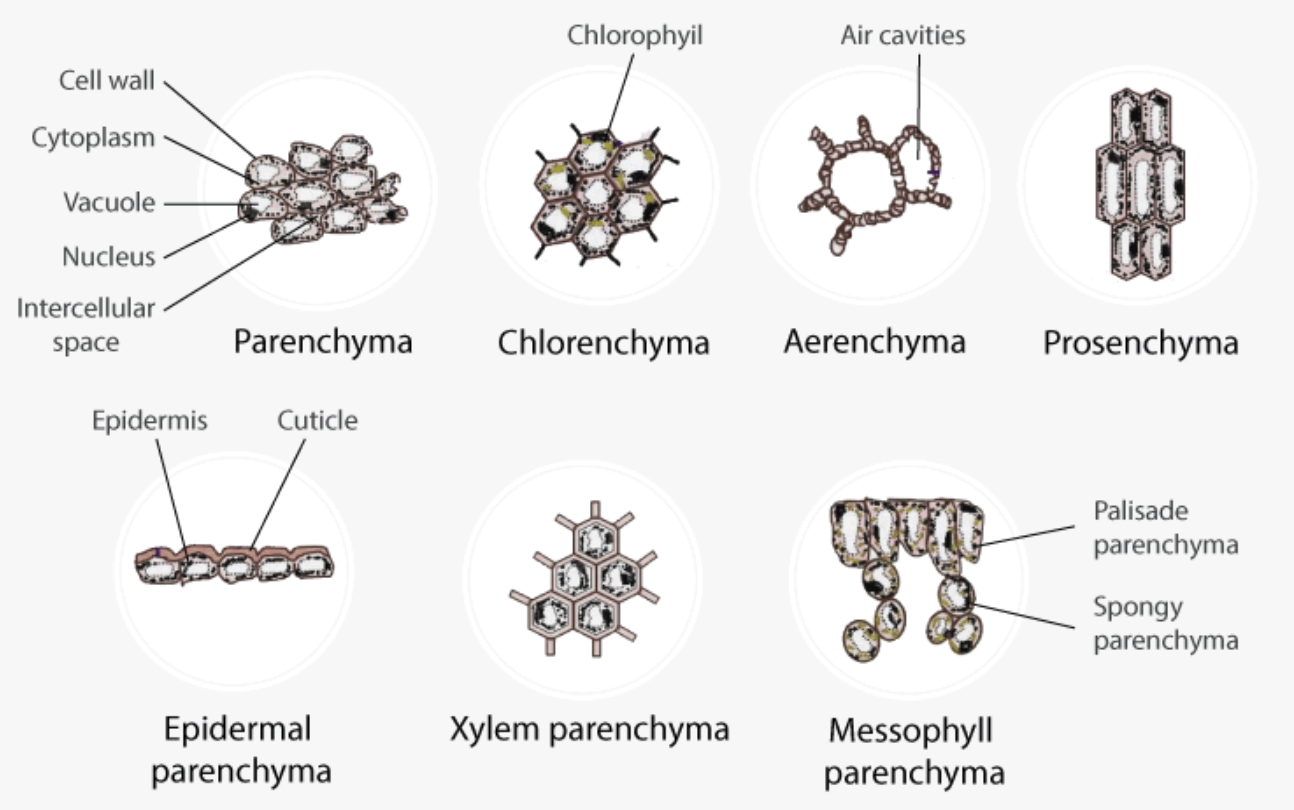
What are Lenticels? What are Hydathodes? Difference between Lenticels and Hydathodes Lenticels and hydathodes are both specialized structures in plants, yet they serve distinct functions and are located in different regions. Understanding their differences is essential for comprehending how plants regulate gas exchange and water balance. Below is a detailed comparison of these two structures: … Read more