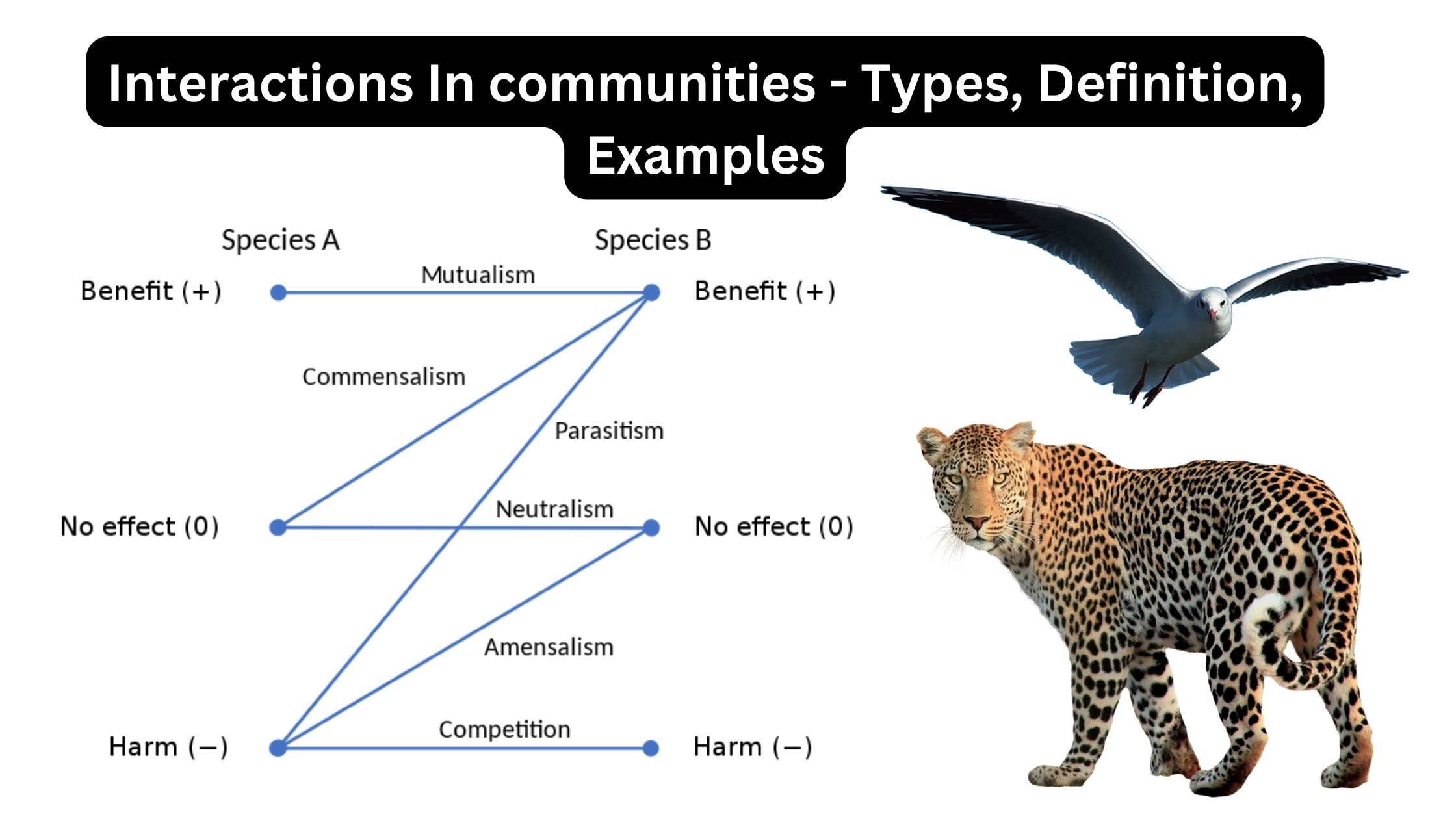
Mutualism – Definition, Types, Examples
What is Mutualism? Mutualism is simply a partnership between two animals that benefits both. This link may exist either inside the species or between species. The organisms involved in this connection are known as symbionts. All living species, including humans, animals, birds, plants, and microbes such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, exhibit interdependence. Mutualism resembles … Read more