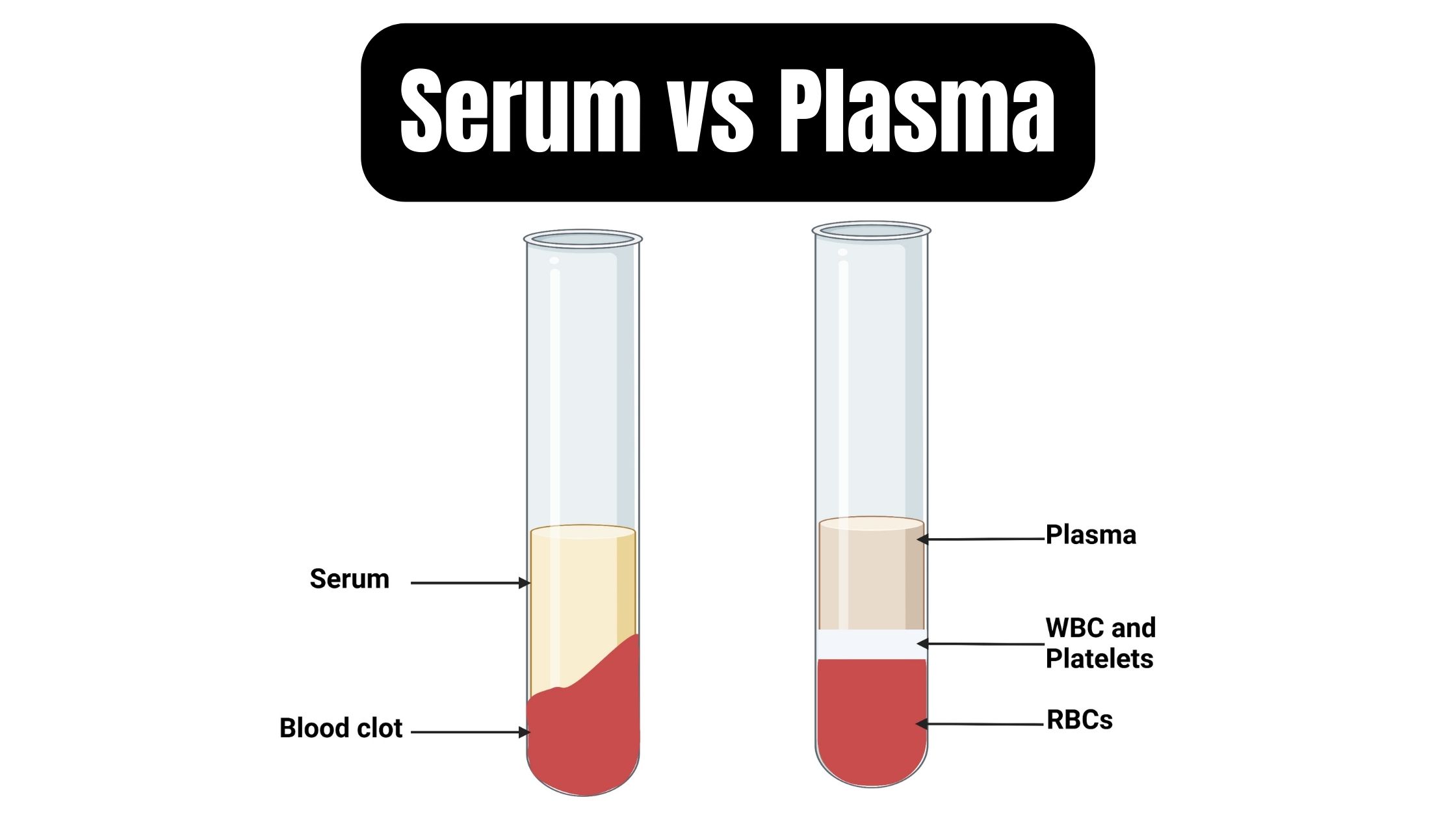
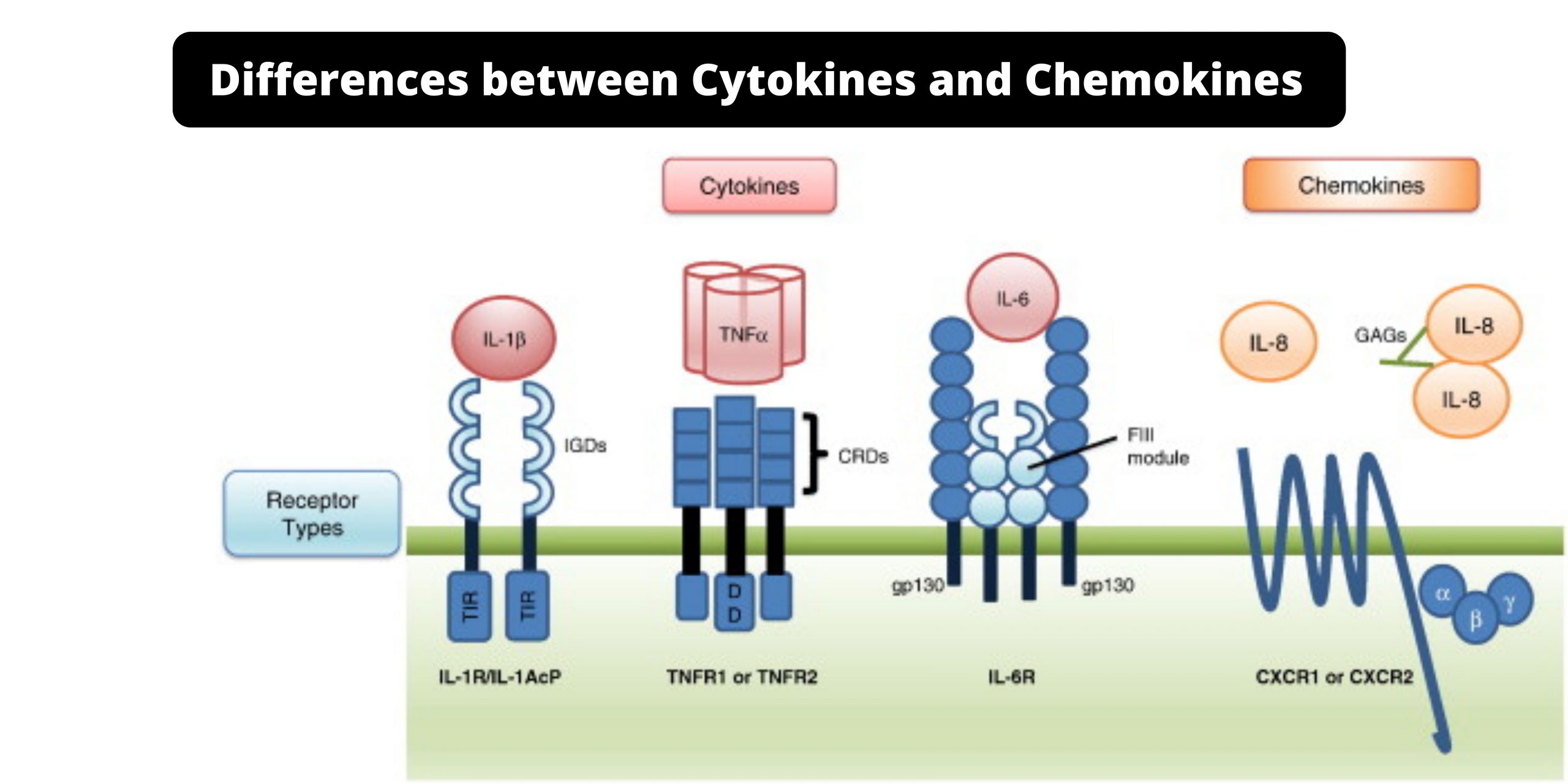
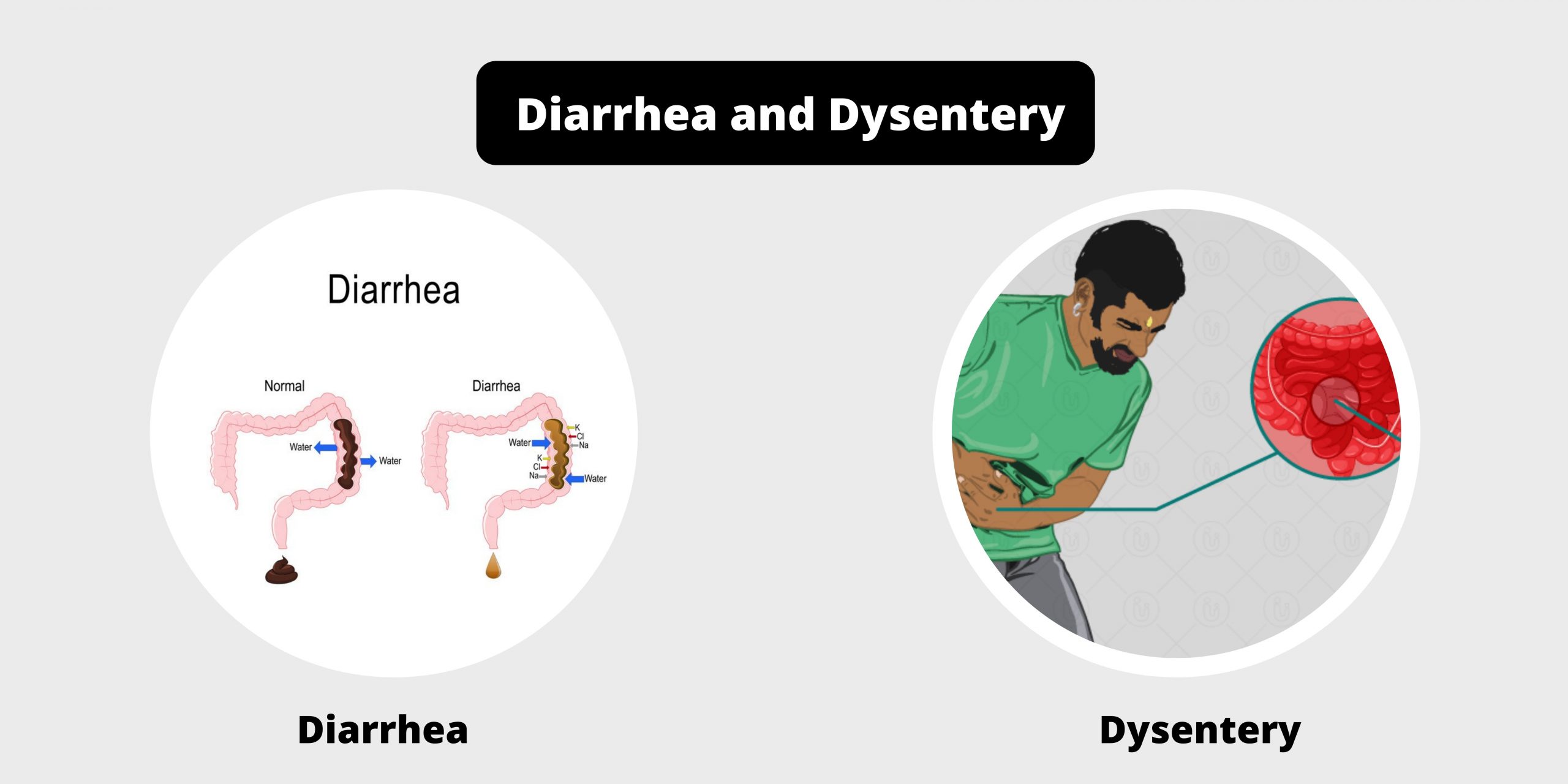
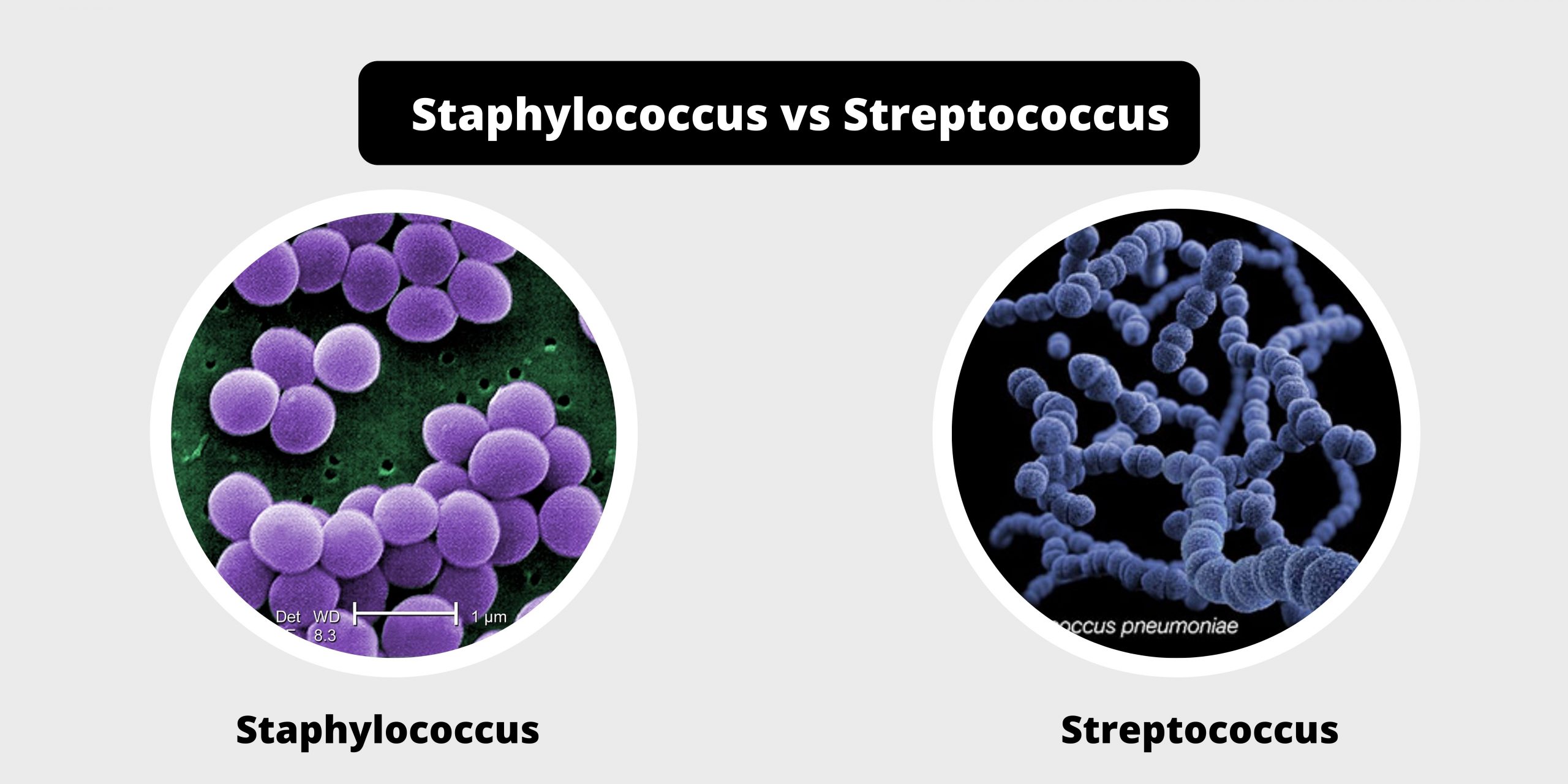
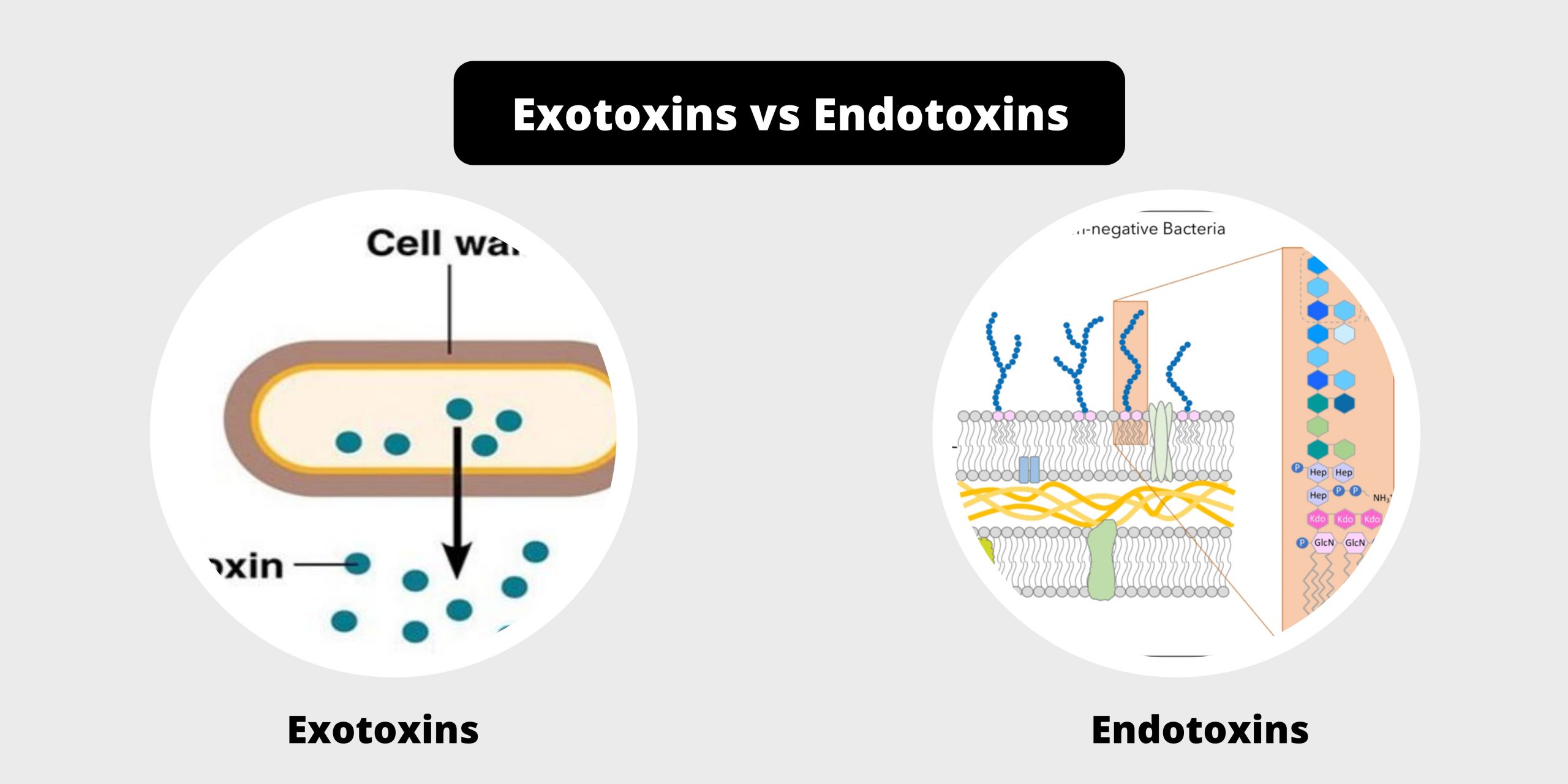
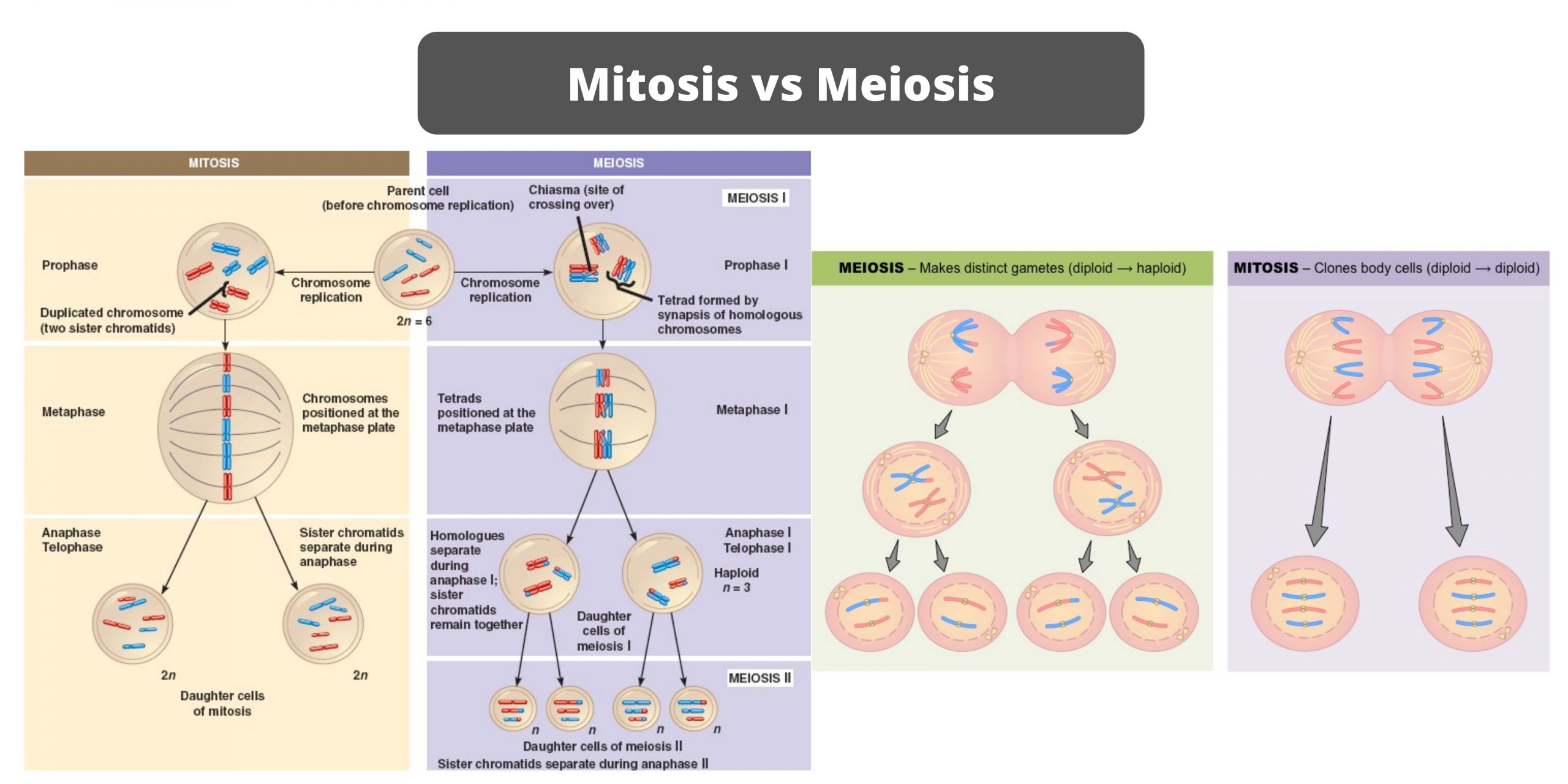
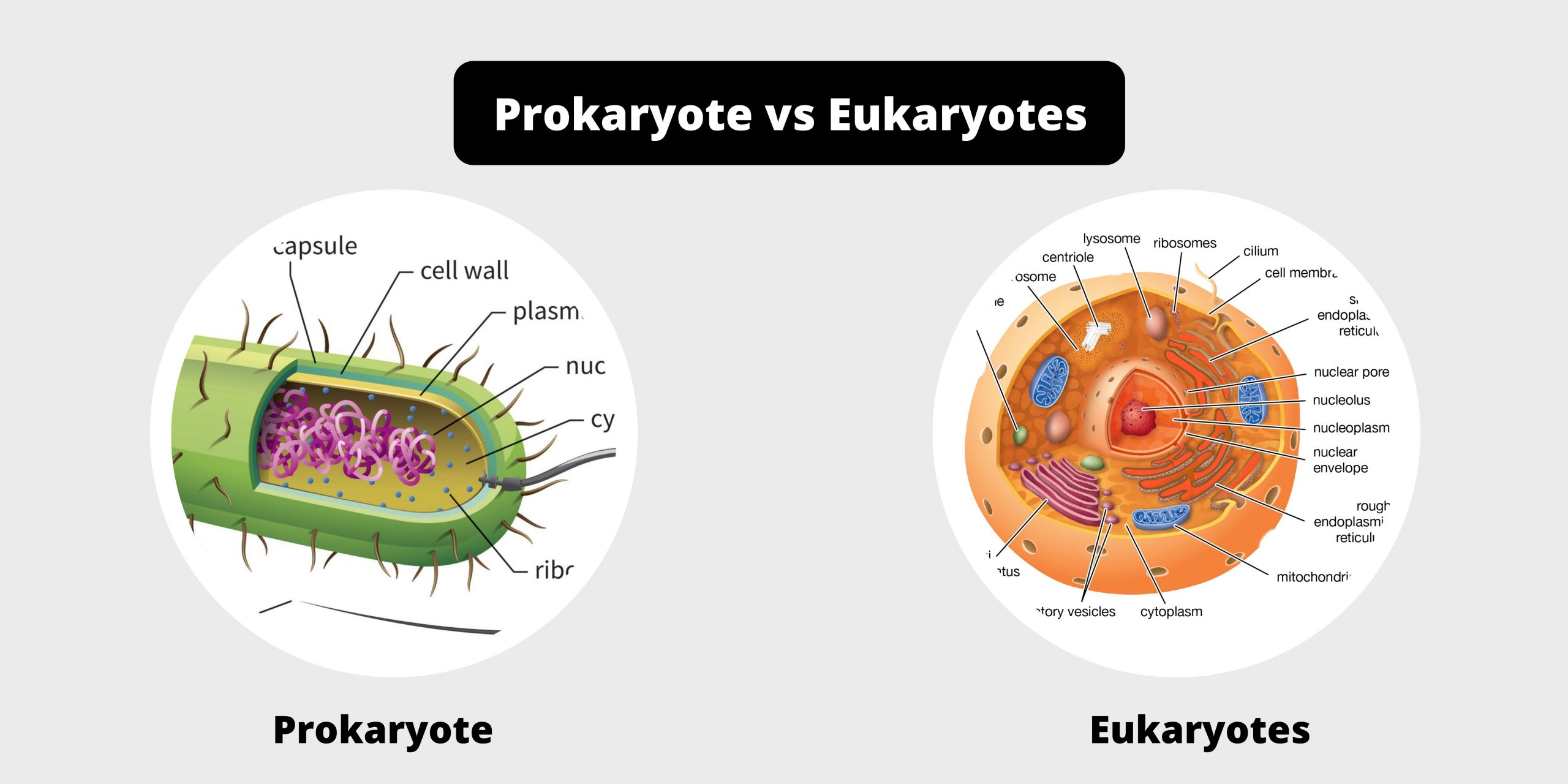
Differences between Serum and Plasma – Serum vs Plasma
Plasma and serum are two blood derivatives which do not have blood cells such as red blood cells white blood cells and platelets. Both are enriched with proteins, drugs hormones, toxins and electrolytes. Both plasma and serum can be used to treat and diagnose. They are separated from blood using centrifugation, which eliminates the blood’s cellular component. Blood is infused with anticoagulants when it has been transfused to stop the clotting. The serum color is amber, while the plasma color is straw. The primary difference between serum as well as plasma lies in the fact that the latter is a protein-rich liquid that separates when blood is coagulated, whereas plasma forms the liquid part of blood that holds blood cells suspended.