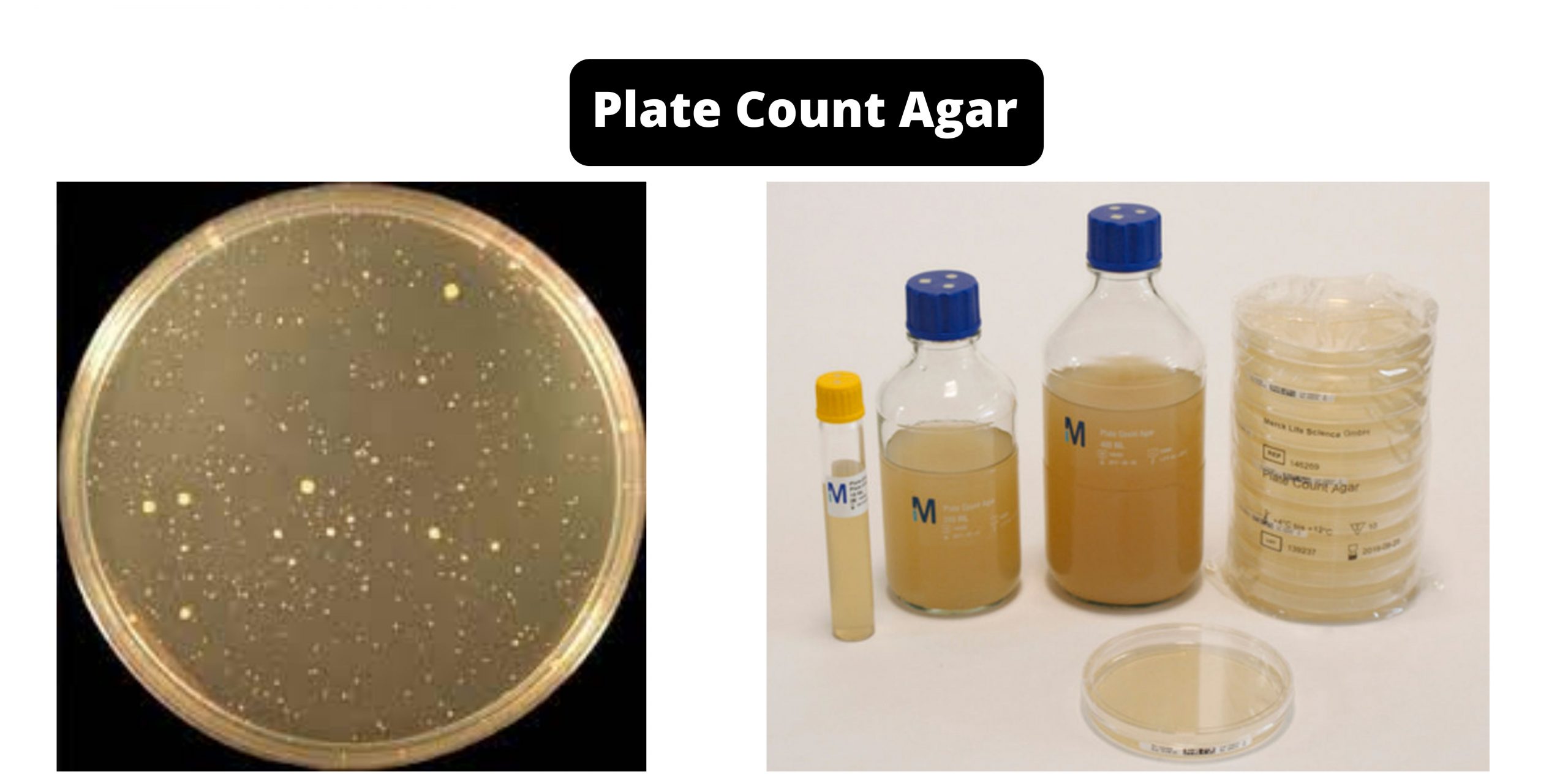
Plate Count Agar (PCA) – Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
PCA, also known as plate count (PCA) is an bacteriological medium that is used to determine the total amount of aerobic live bacteria present in a sample. This is not considered to be a specific medium. The quantity of bacteria is expressed in units of colony-forming units per Gram (CFU/g) in solid samples, and per milliliter (CFU/ml) for liquid samples. The preferred method is to use the pour plate method. The samples are dilute and the appropriate dilutions added to Petri plates. Sterile molten Agar is added to the plates. The plates are rotated with care to ensure an even mixing of the sample with the agar. The plates are then incubated at 20 or 30degC over three days. After incubation, the amount of colonies counted is recorded on the plate using 25-250 colonies, which is believed to provide the most precise results. When calculating the amount of bacteria present within the specimen, the dilution factors is to be considered.