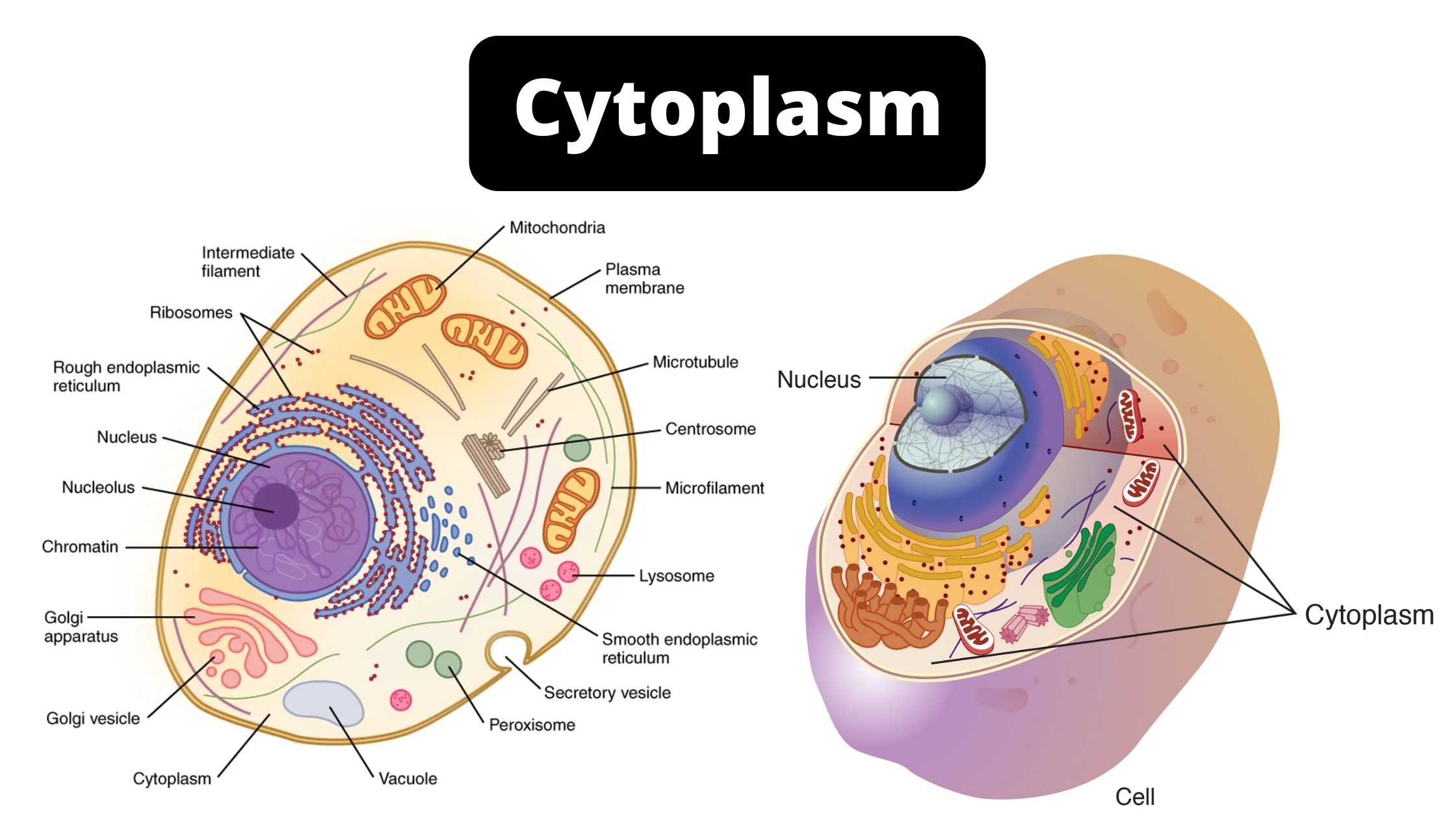
Cytoplasm – Functions, Structure, Definition, and Diagram
The cytoplasm, a highly viscous substance (gel-like) that is enclosed within the cell membrane. It is composed of water (about 85%), proteins (10-15%), lipids (2-4%) and nucleic acids, inorganic salts, and polysaccharides in smaller amounts. Depending on the cell’s configuration, cytoplasm might also contain occasional inclusions (e.g. stored nutrients and pigments).