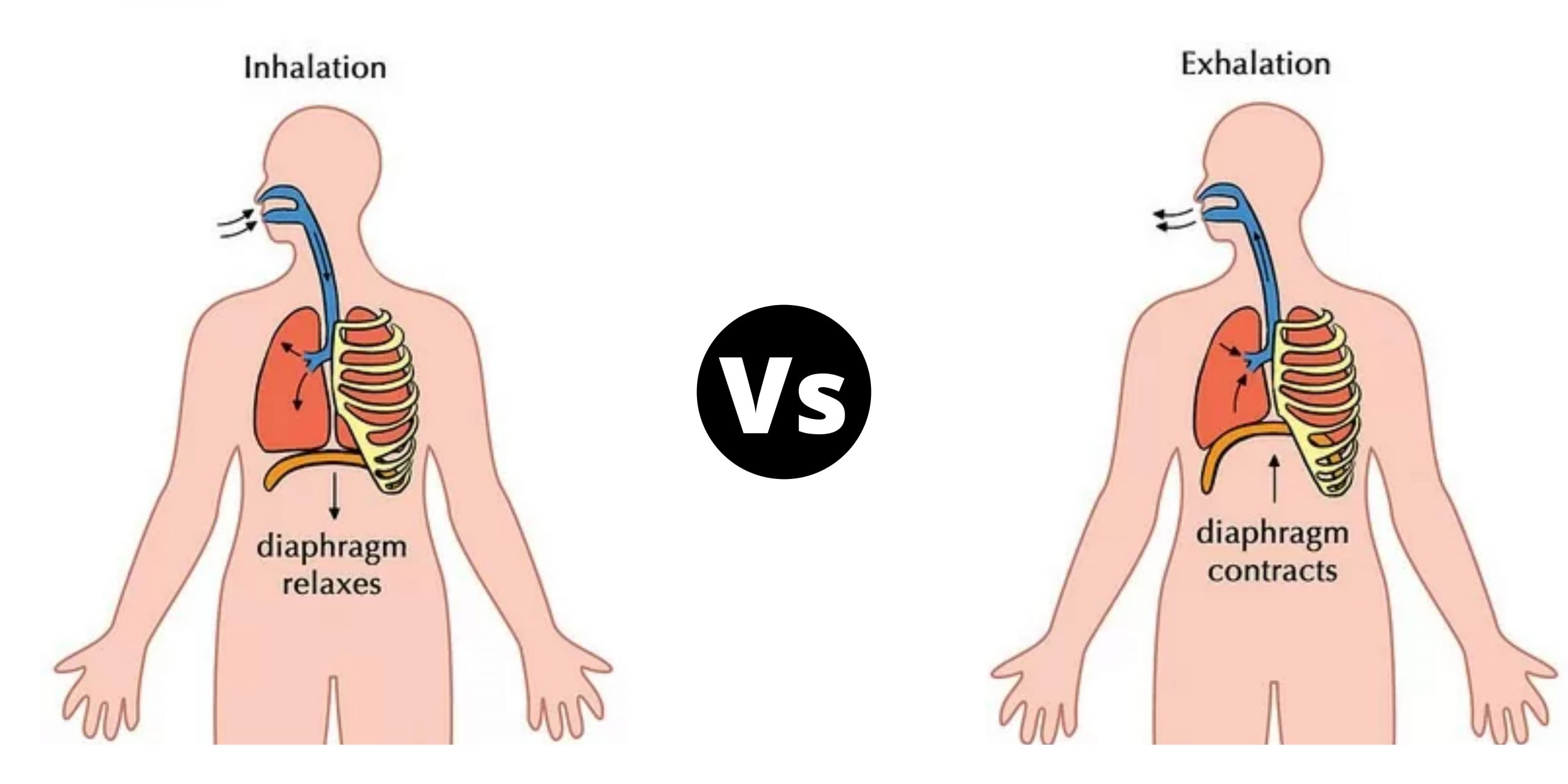
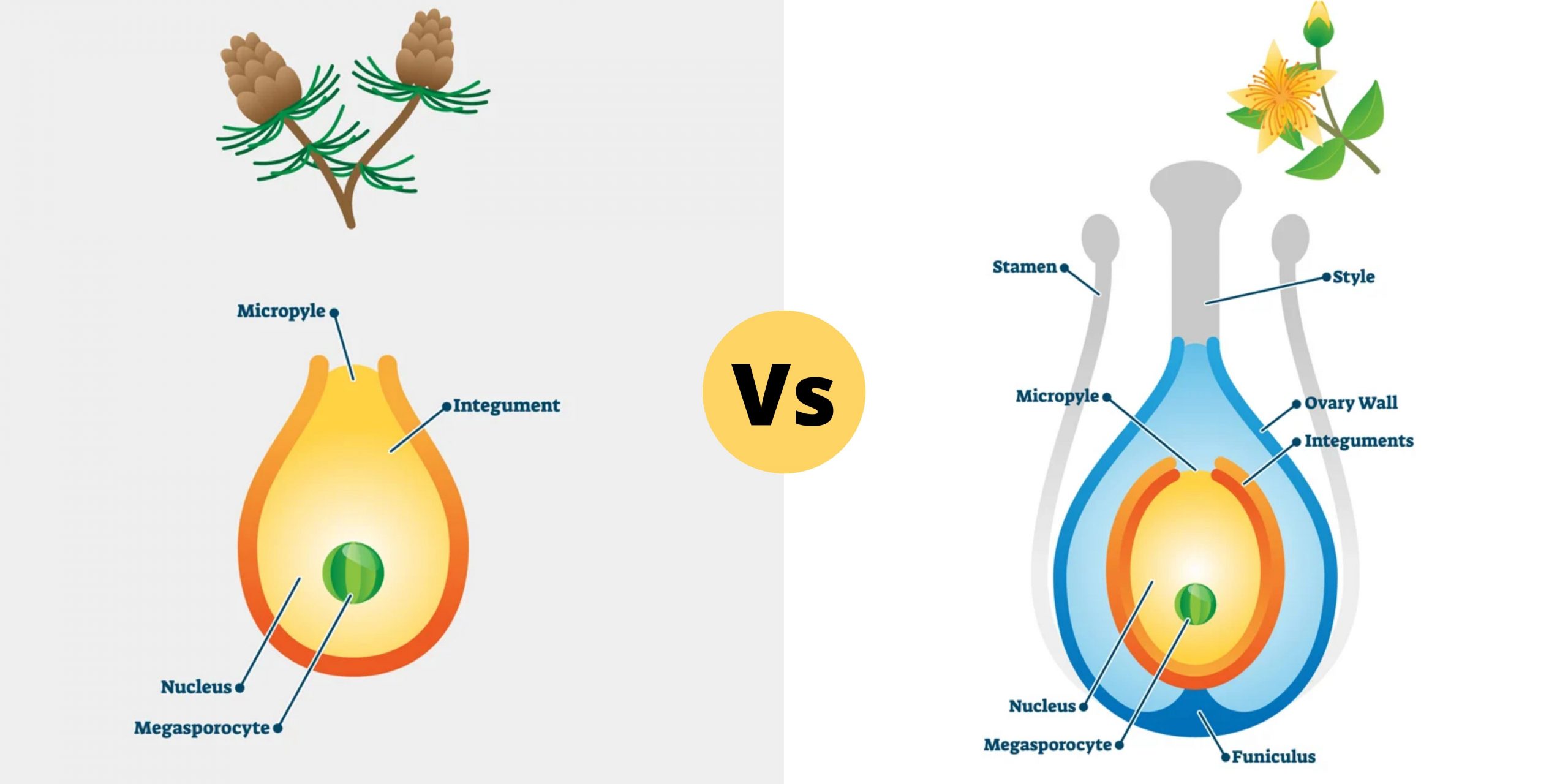
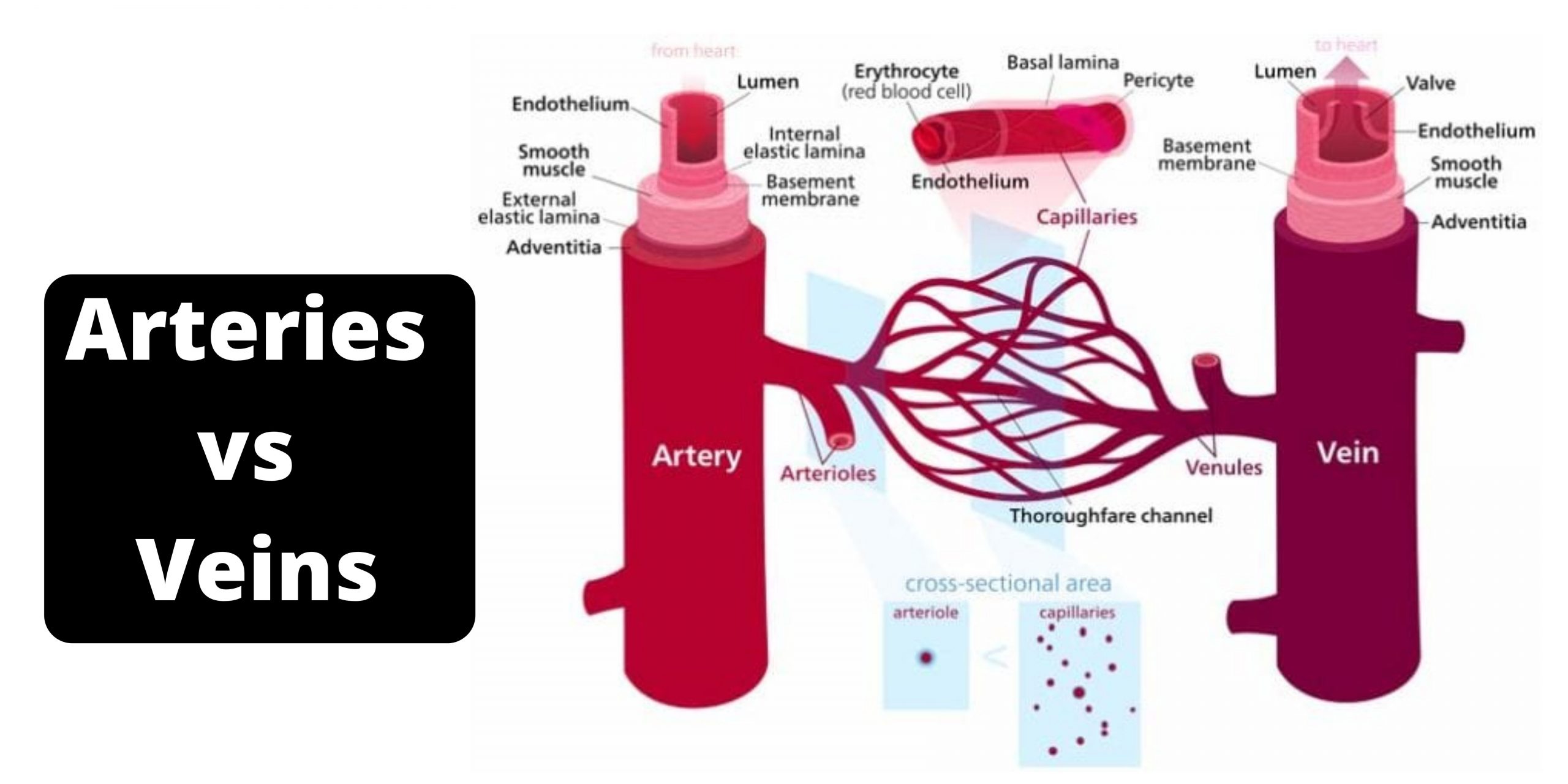
Differences Between Genomics and Proteomics
Proteomics and Genomics are two major areas of molecular biology. Genomes are the biological material that makes up an organism. It contains genes that contain the information about genetics of organisms (genetic code). The research conducted to uncover the information contained in the genome is called genomics.