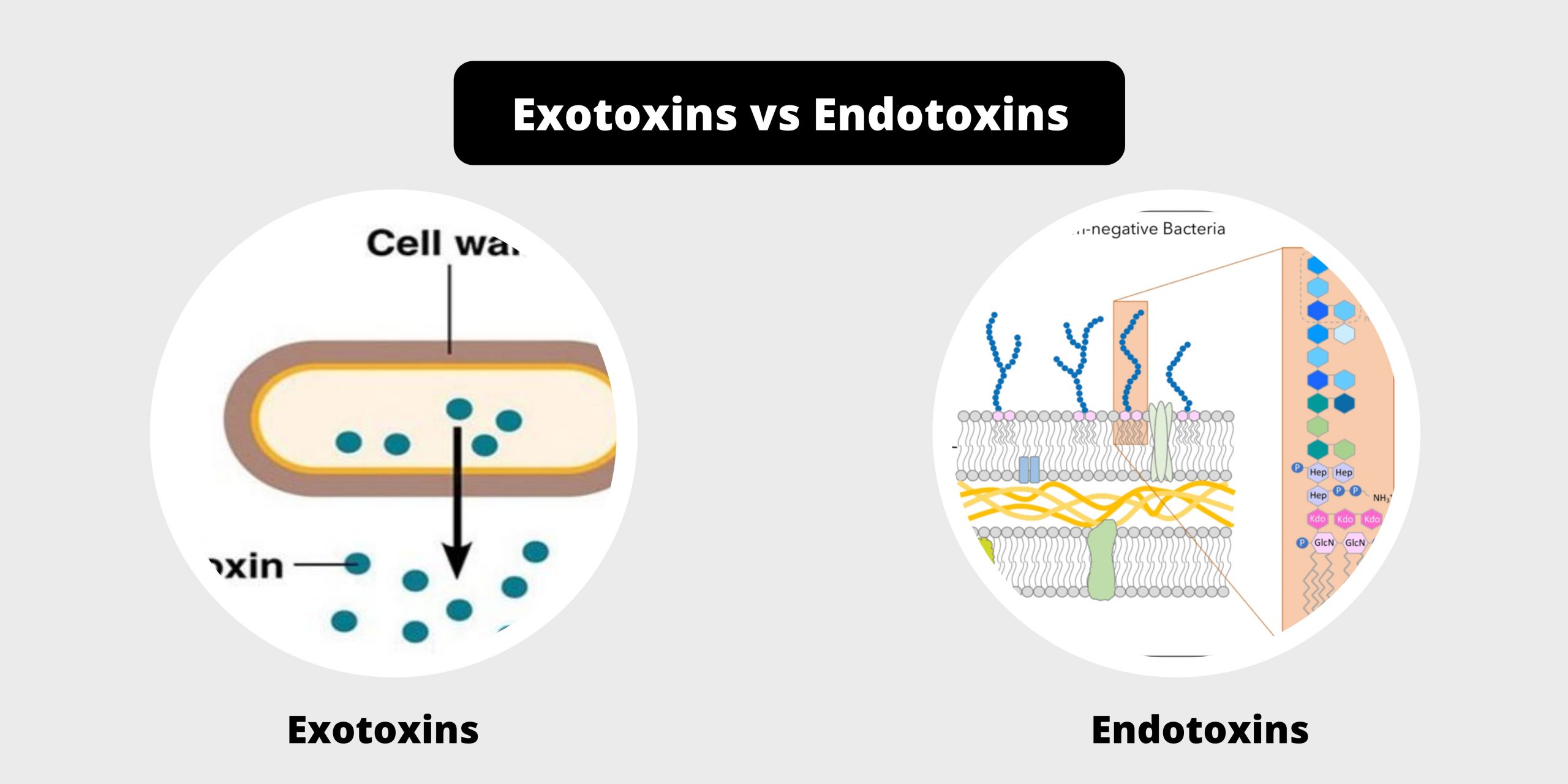
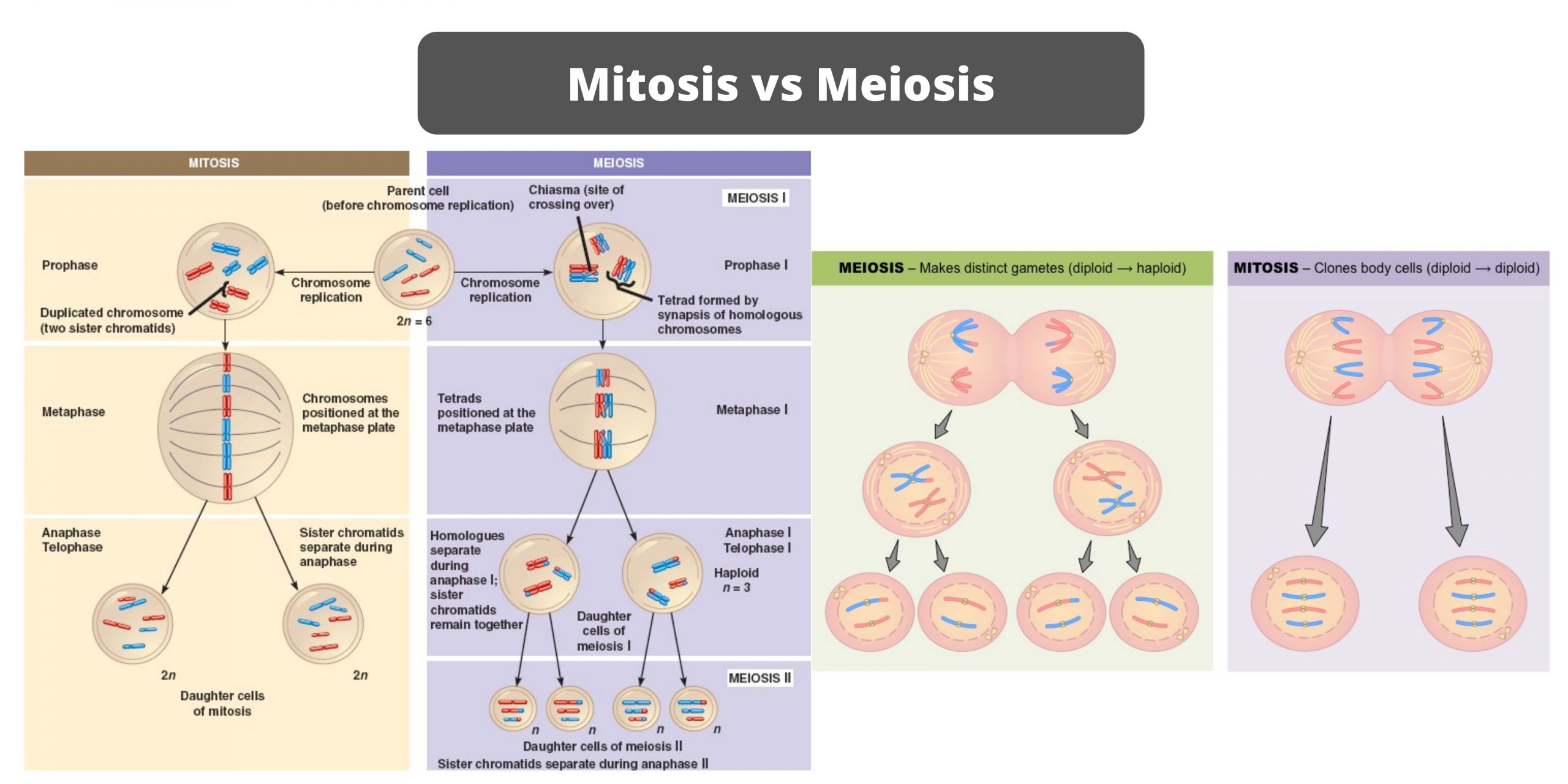
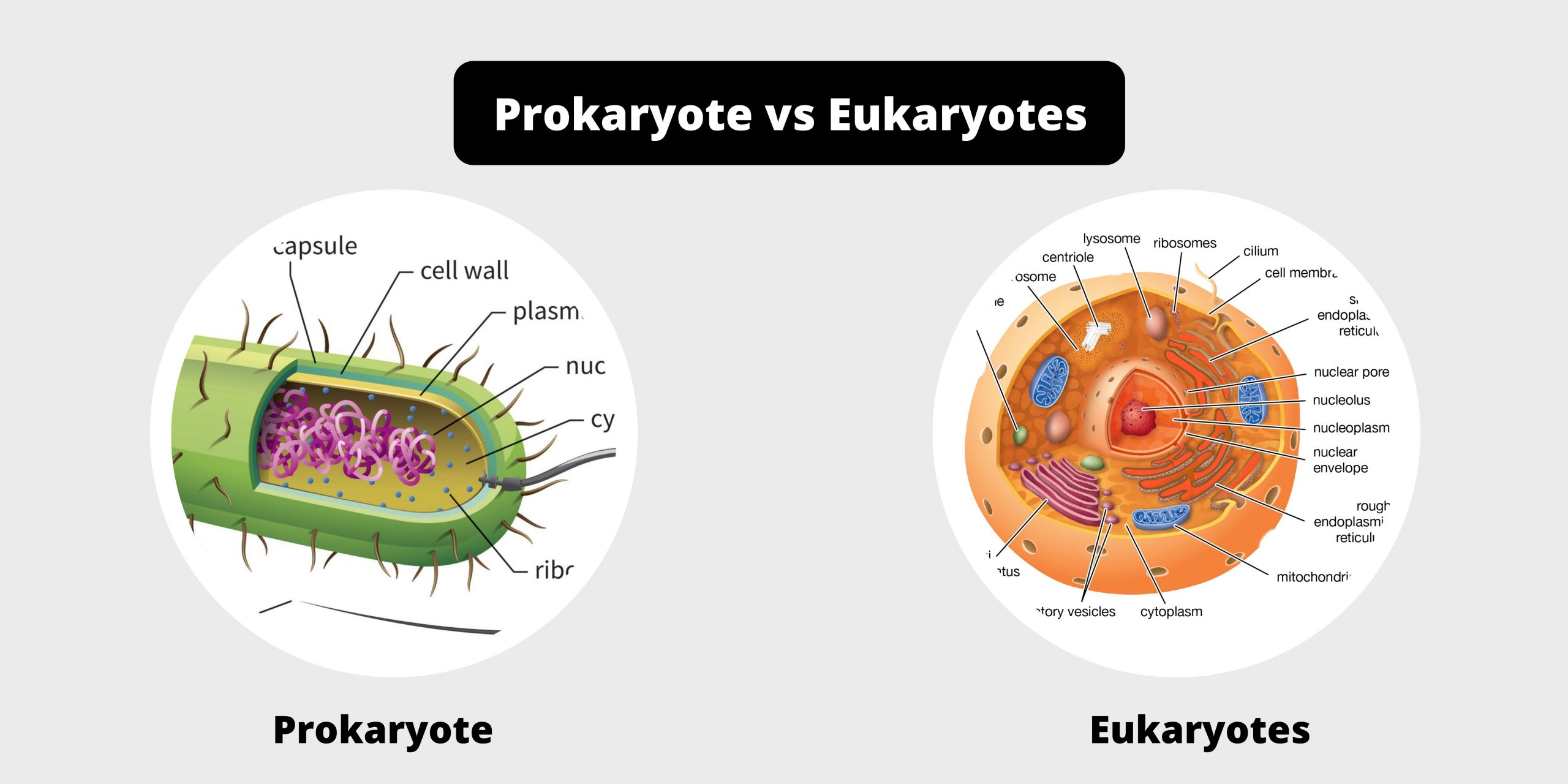
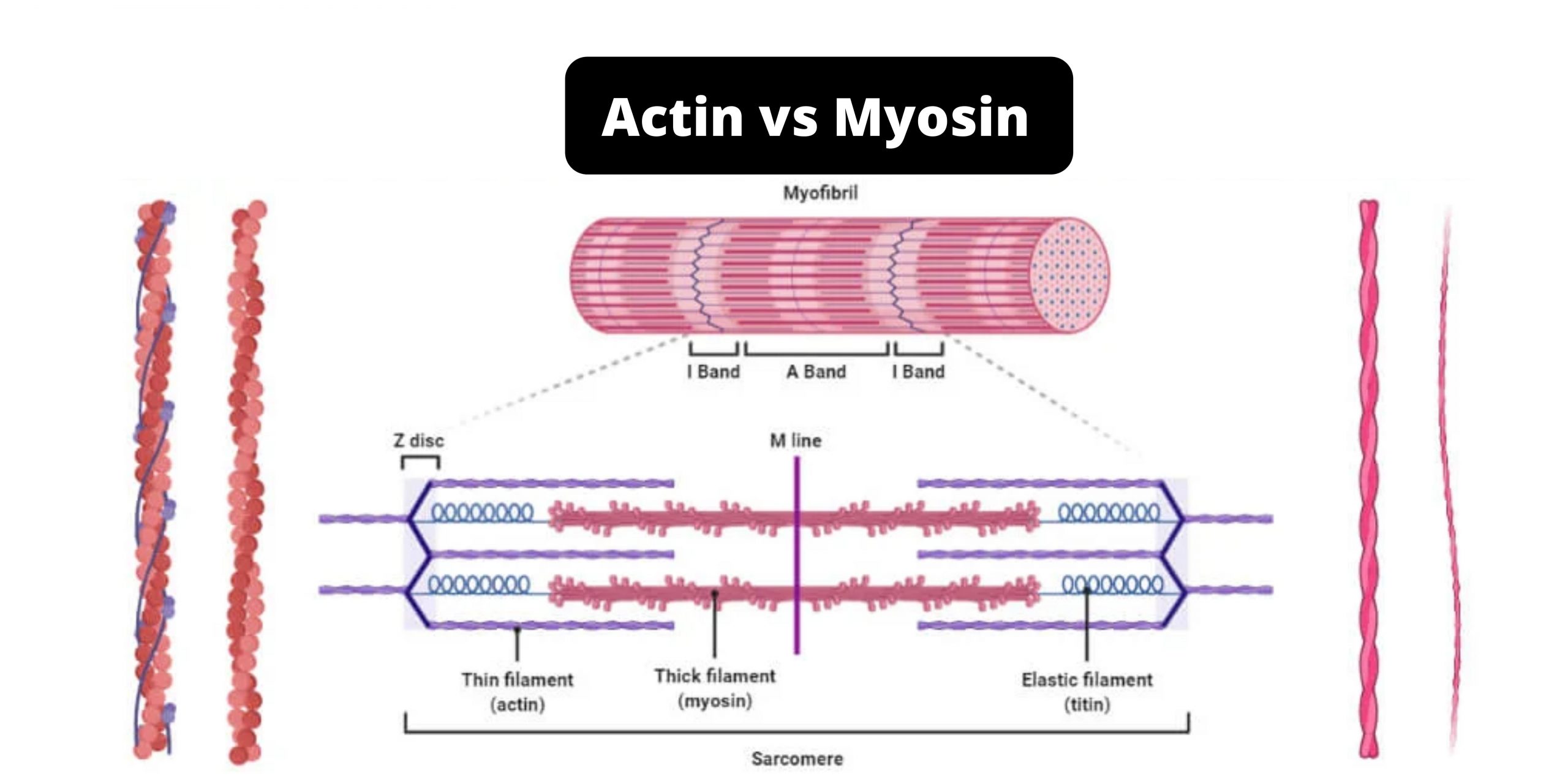
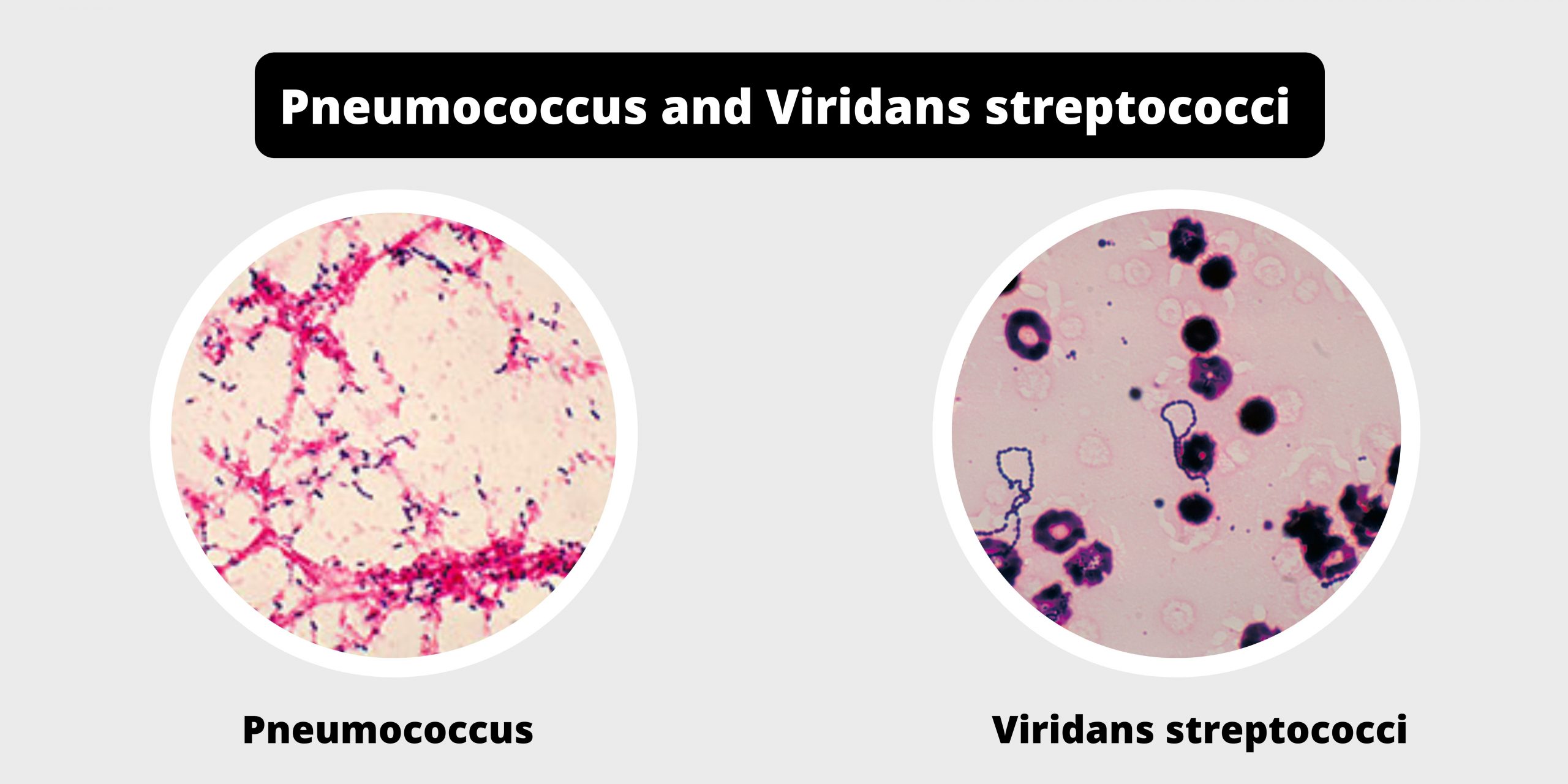
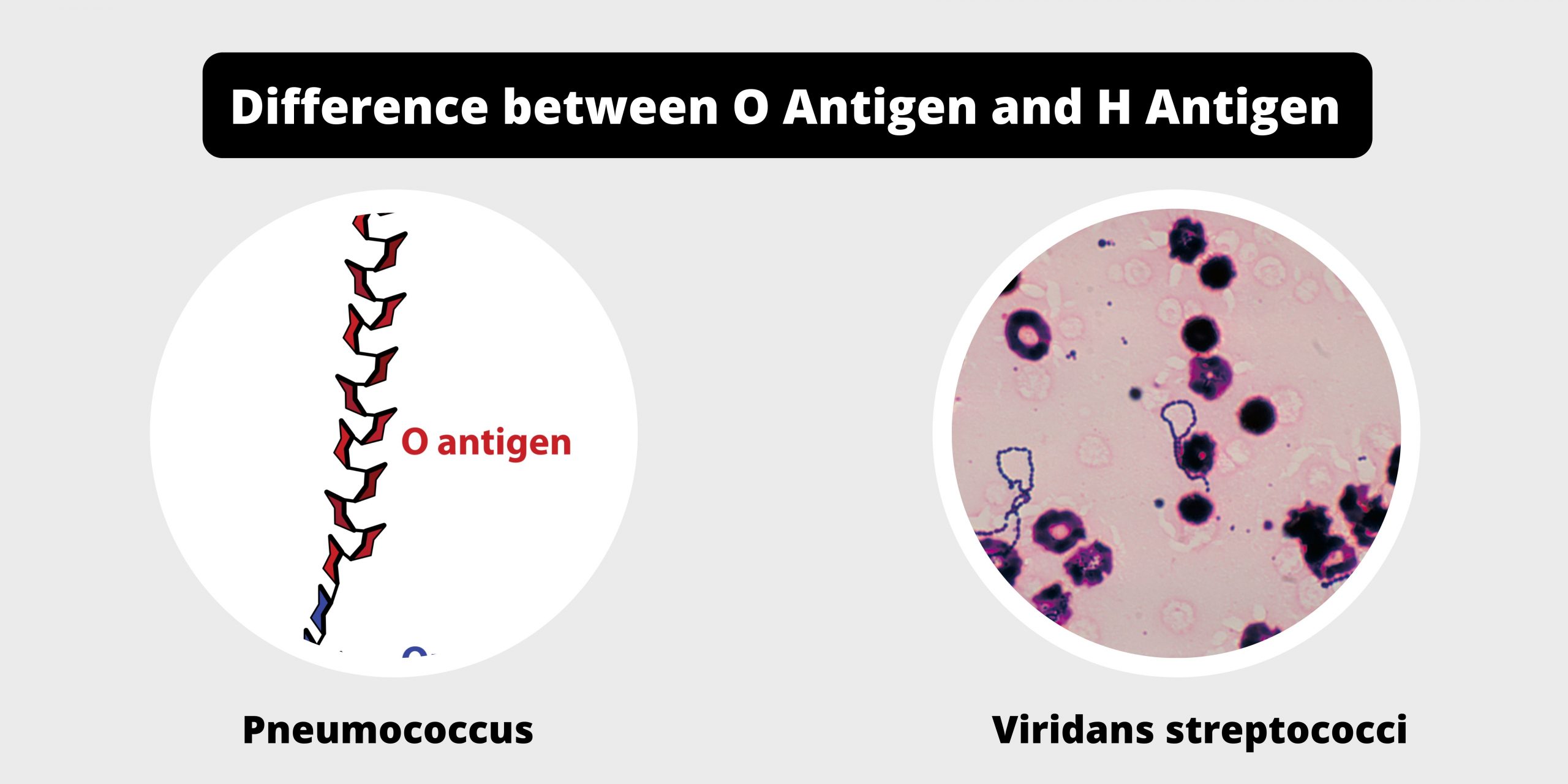
Difference between exotoxins and endotoxins – exotoxins vs endotoxins
Exotoxin is a toxins produced by bacteria. Exotoxins can cause damage to the host by damaging cells or disrupting normal cell metabolism. They are extremely powerful and could cause significant harm on the human host. Exotoxins can be released, or, as with endotoxins, they can be released when cells. Gram negative pathogens can release outer membrane vesicles with lipopolysaccharide endotoxin, as well as some viral proteins within the bounding membrane as well as other toxins in the intra-vesicular content and thus add an unimagined dimension to the widely-known membrane vesicle transport, which is extremely active in the interface between host and pathogen.