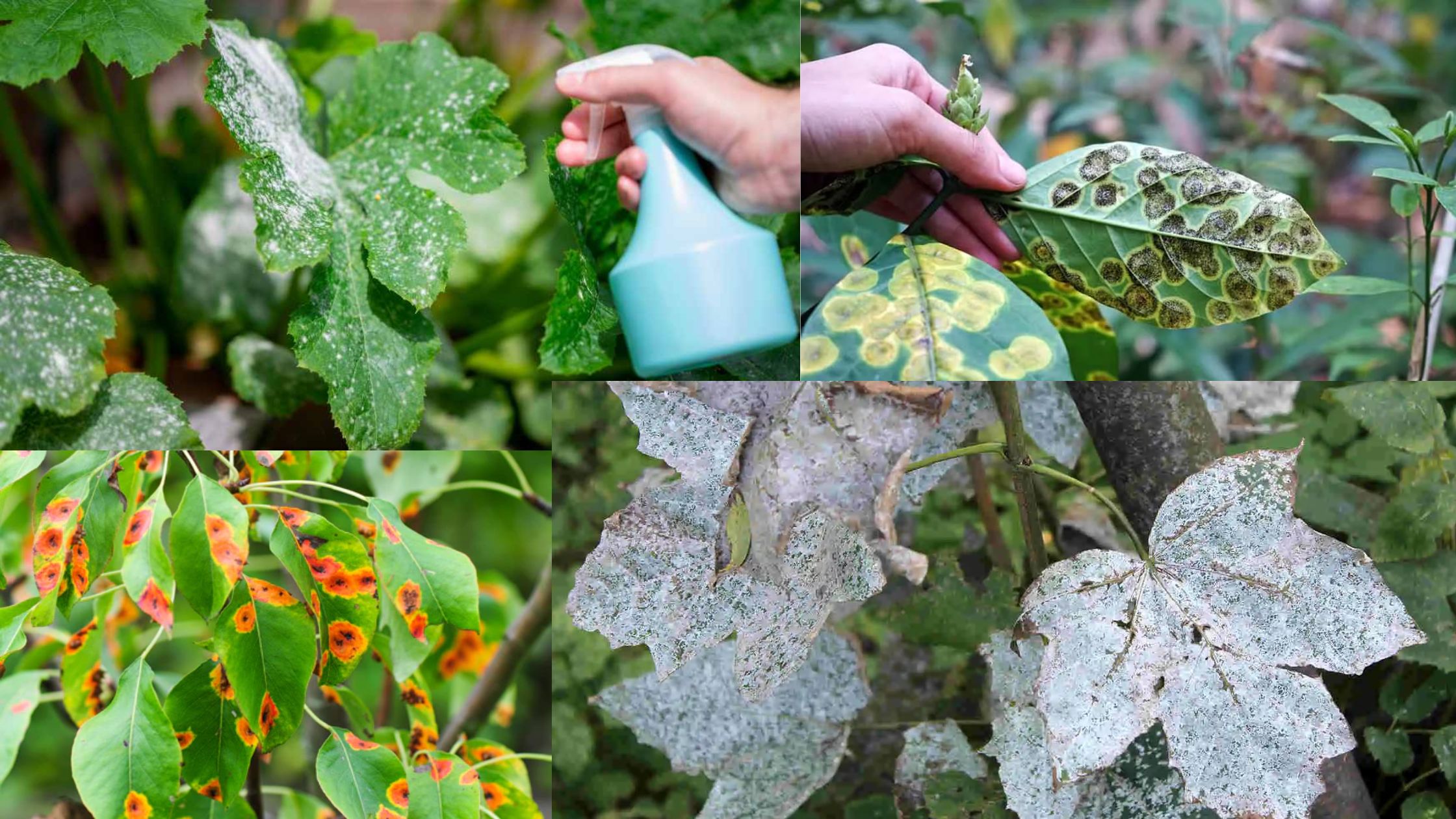
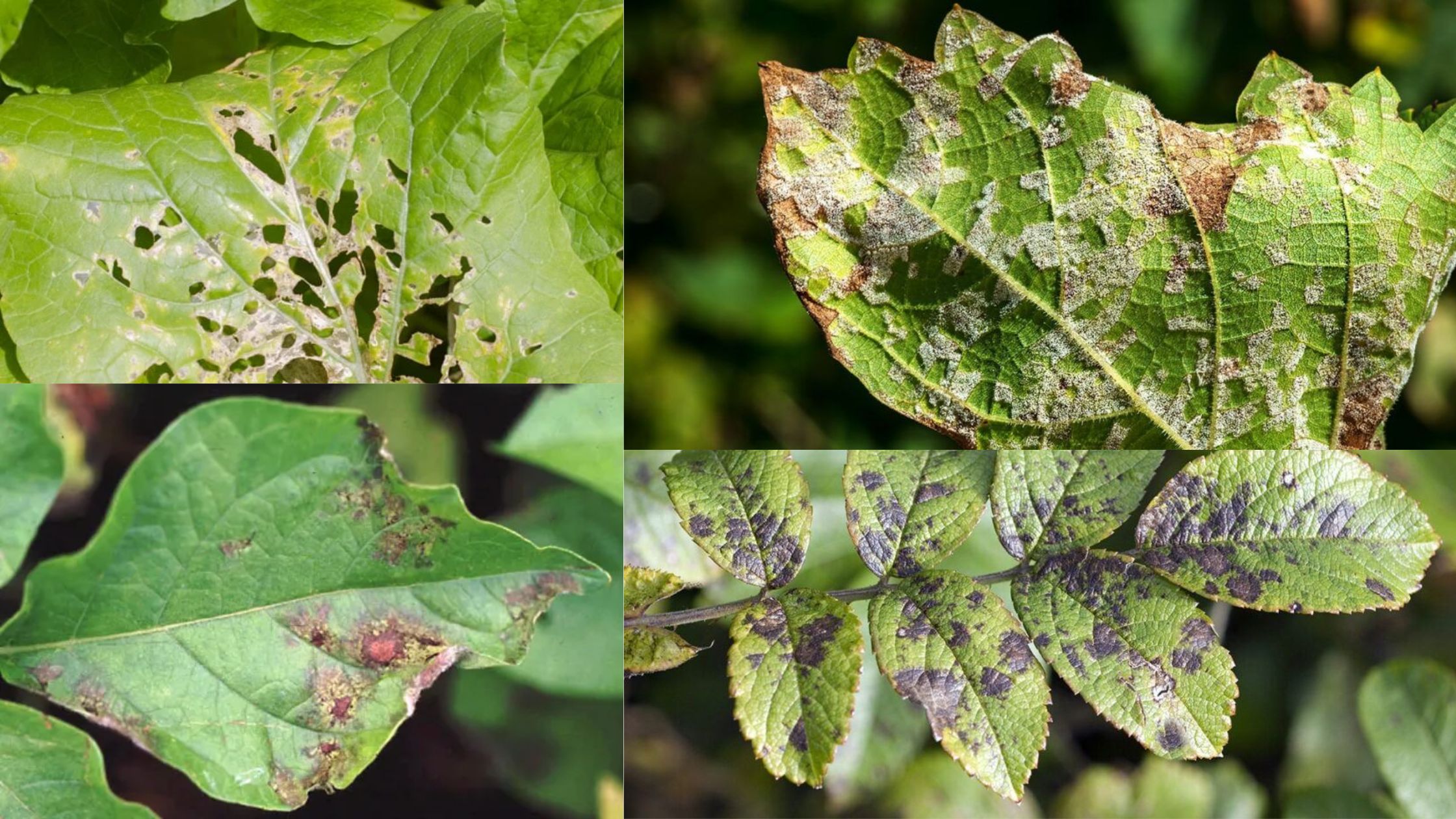
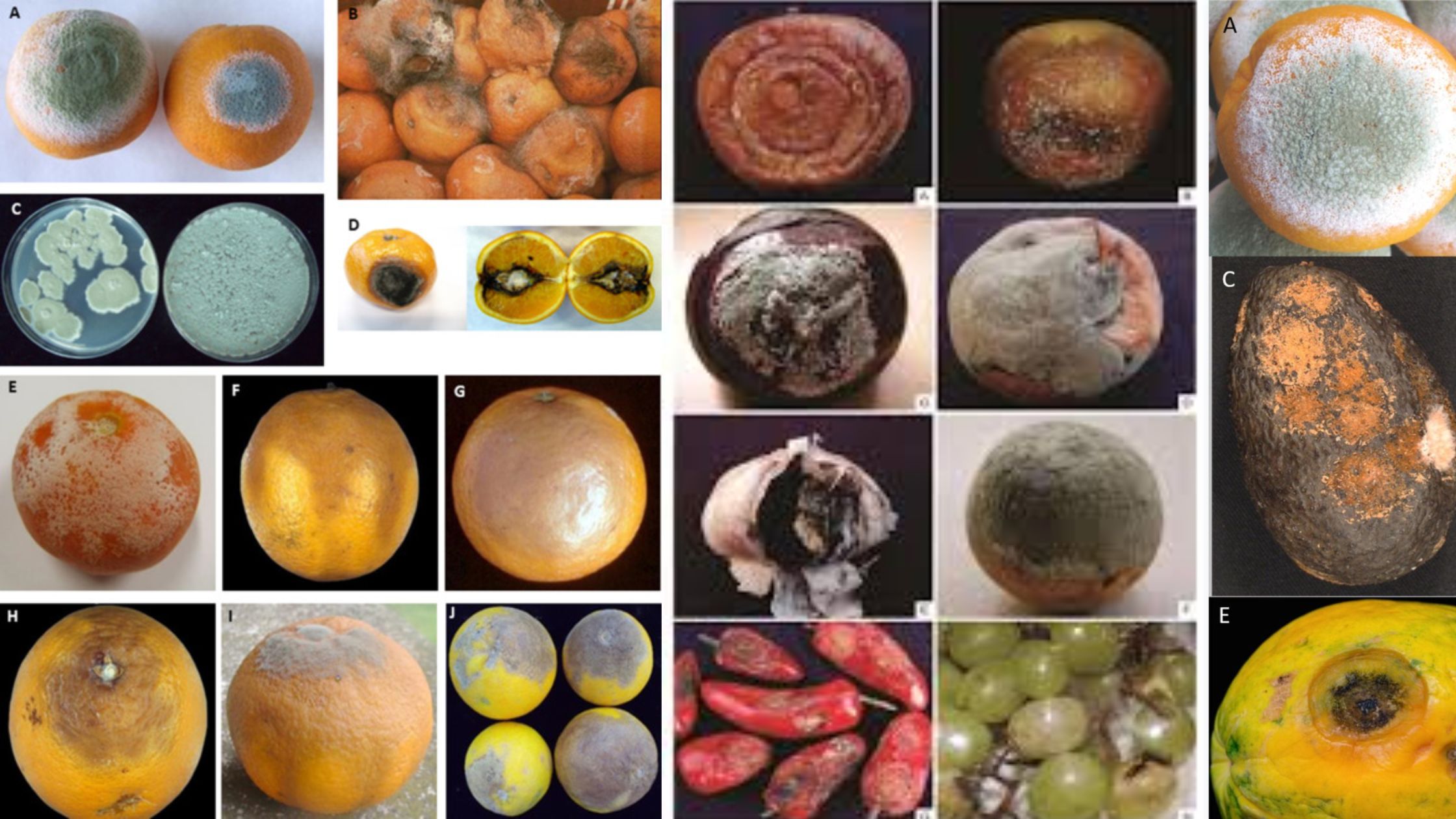
Plant Diseases – Diagnose, Control and Treatment
Diagnosis of Plant Diseases The diagnosis of plant diseases is a systematic process that requires careful observation, analysis of symptoms, and consideration of various environmental factors. An accurate diagnosis is critical for effective management and control strategies, as it enables the identification of the underlying causes of plant distress. The following steps outline the essential … Read more