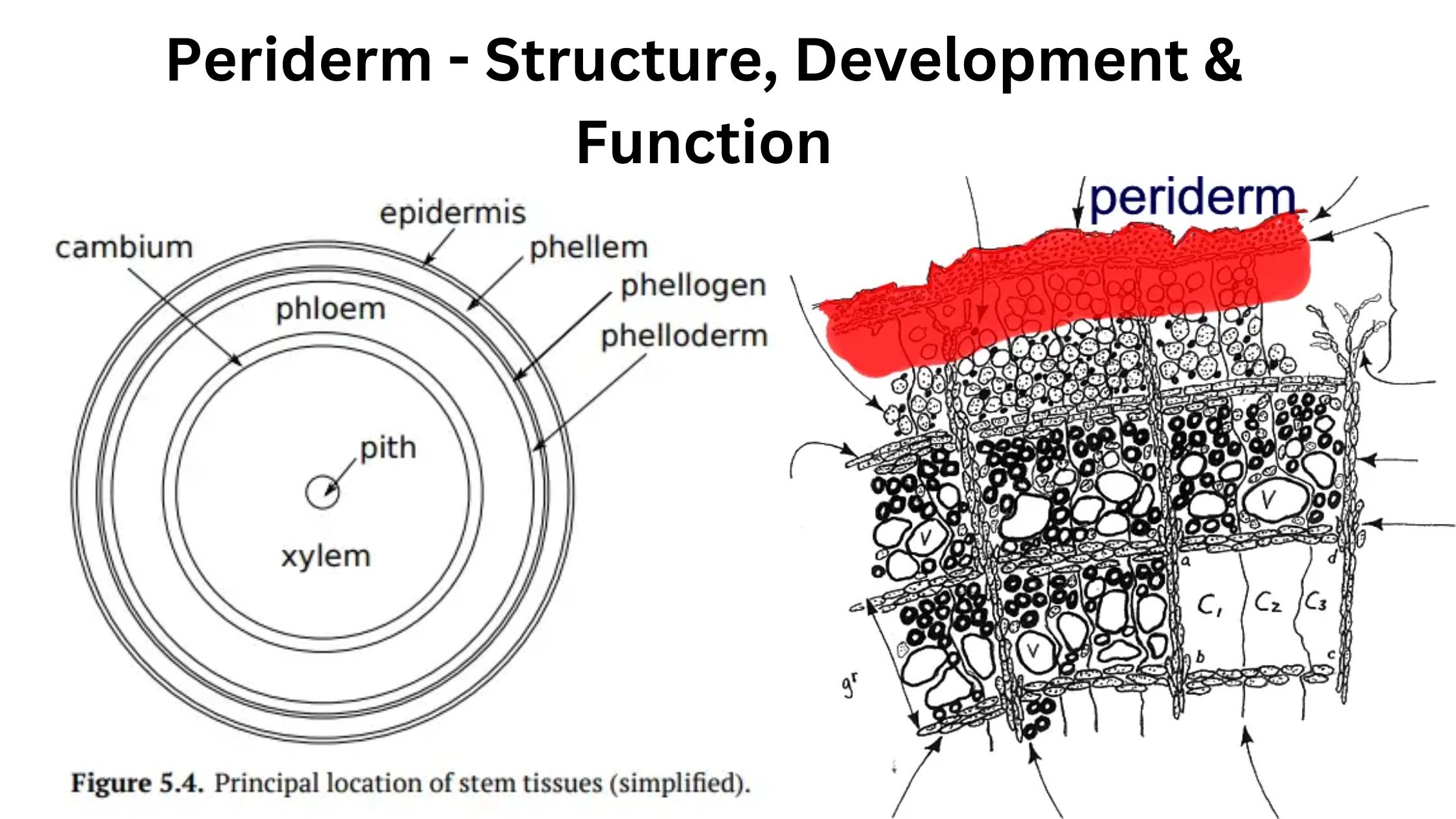
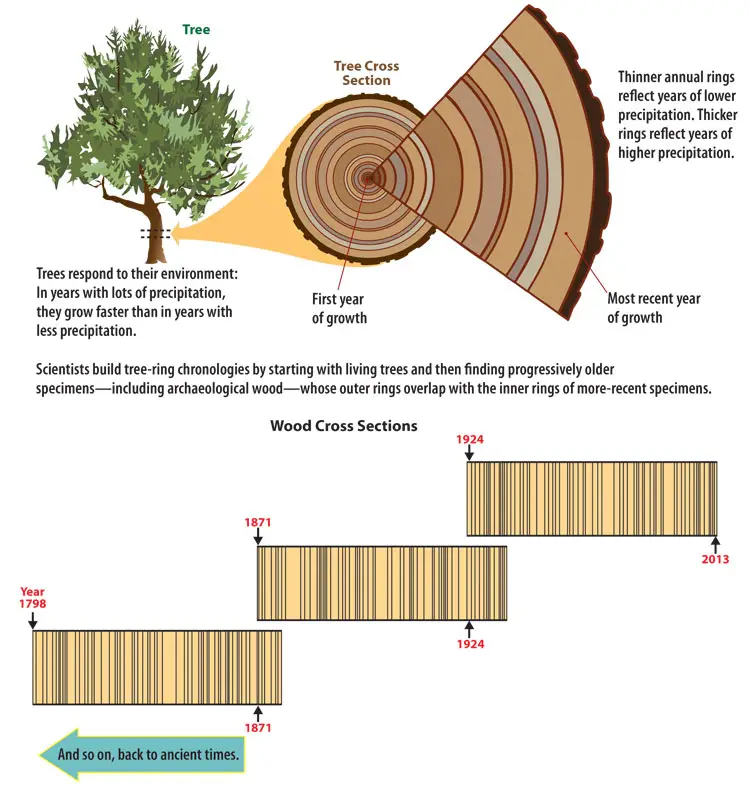
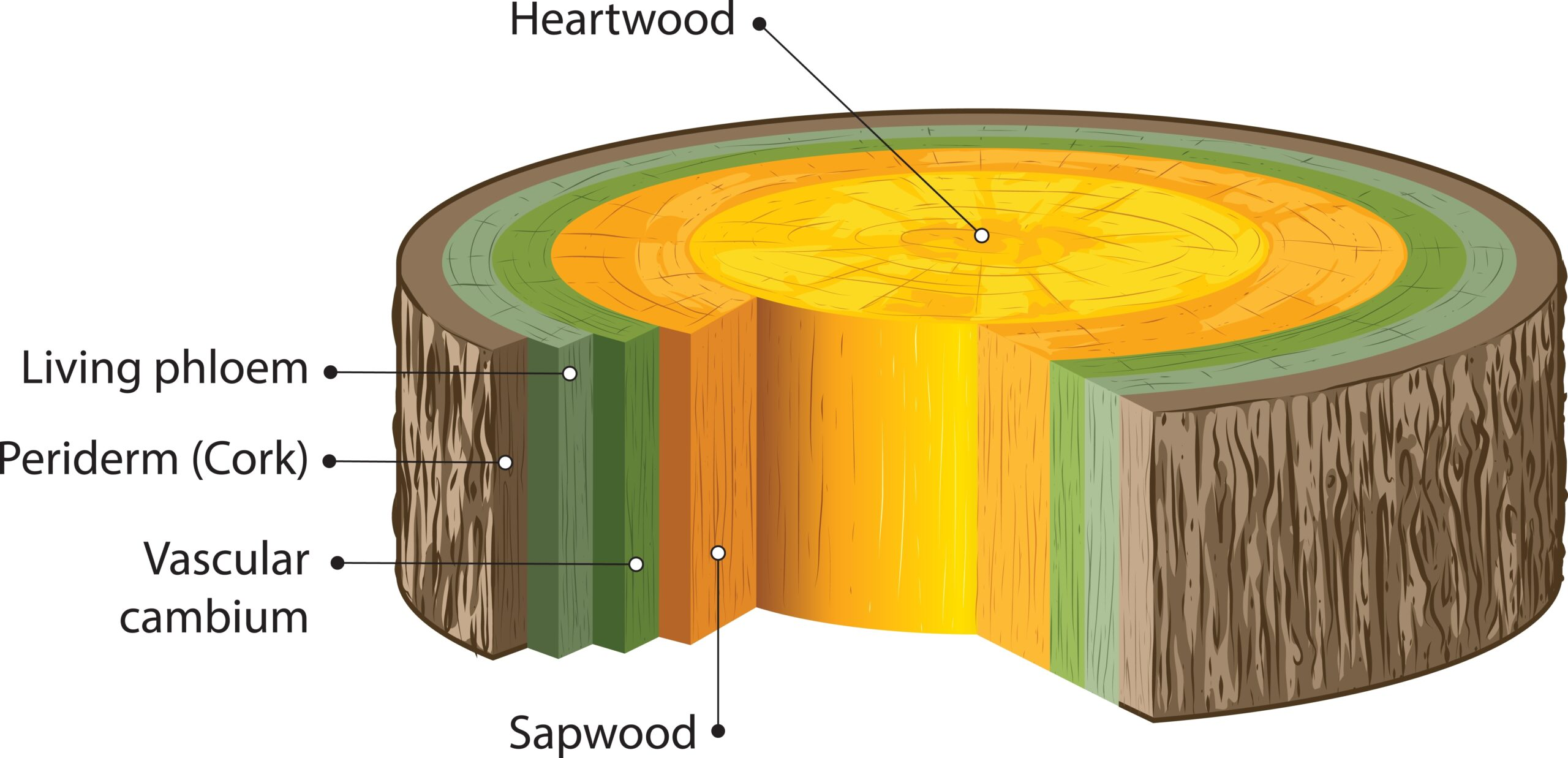
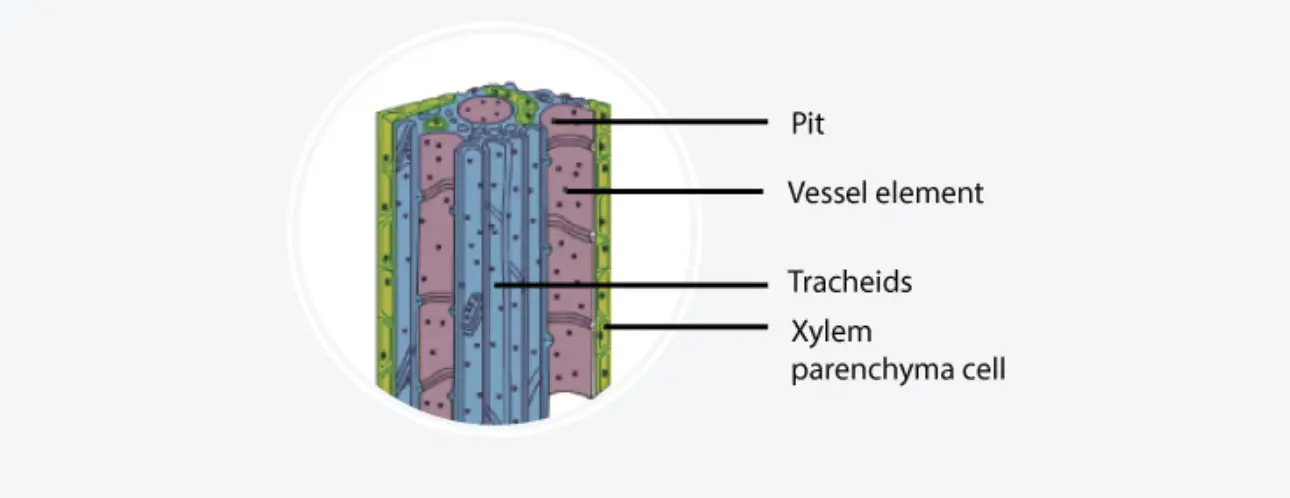
Tissues – Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
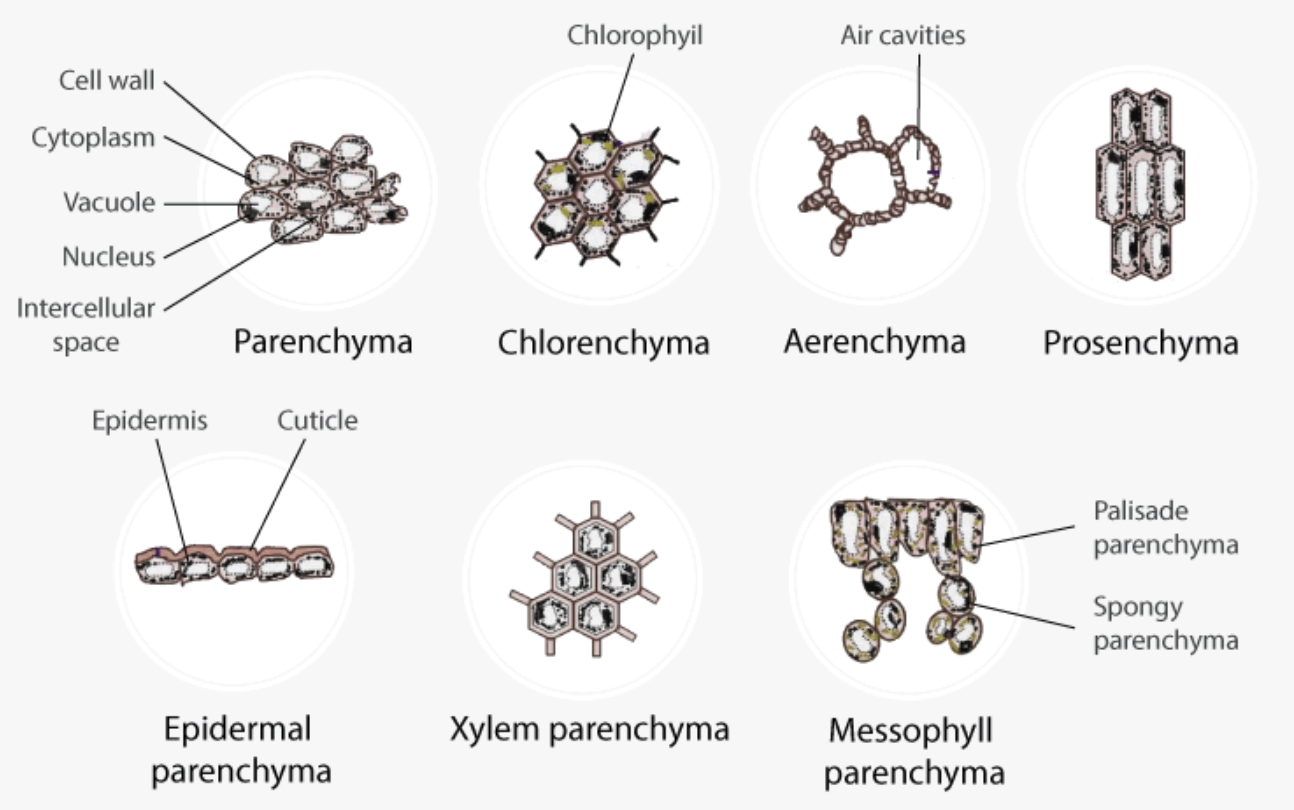
What are Tissues? Definition of Tissues Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform specific functions in an organism. They serve as the structural and functional units that form organs, playing critical roles in various biological processes. Characteristics of Tissues Location of Tissues Formation of Tissues The formation of tissues, known as … Read more