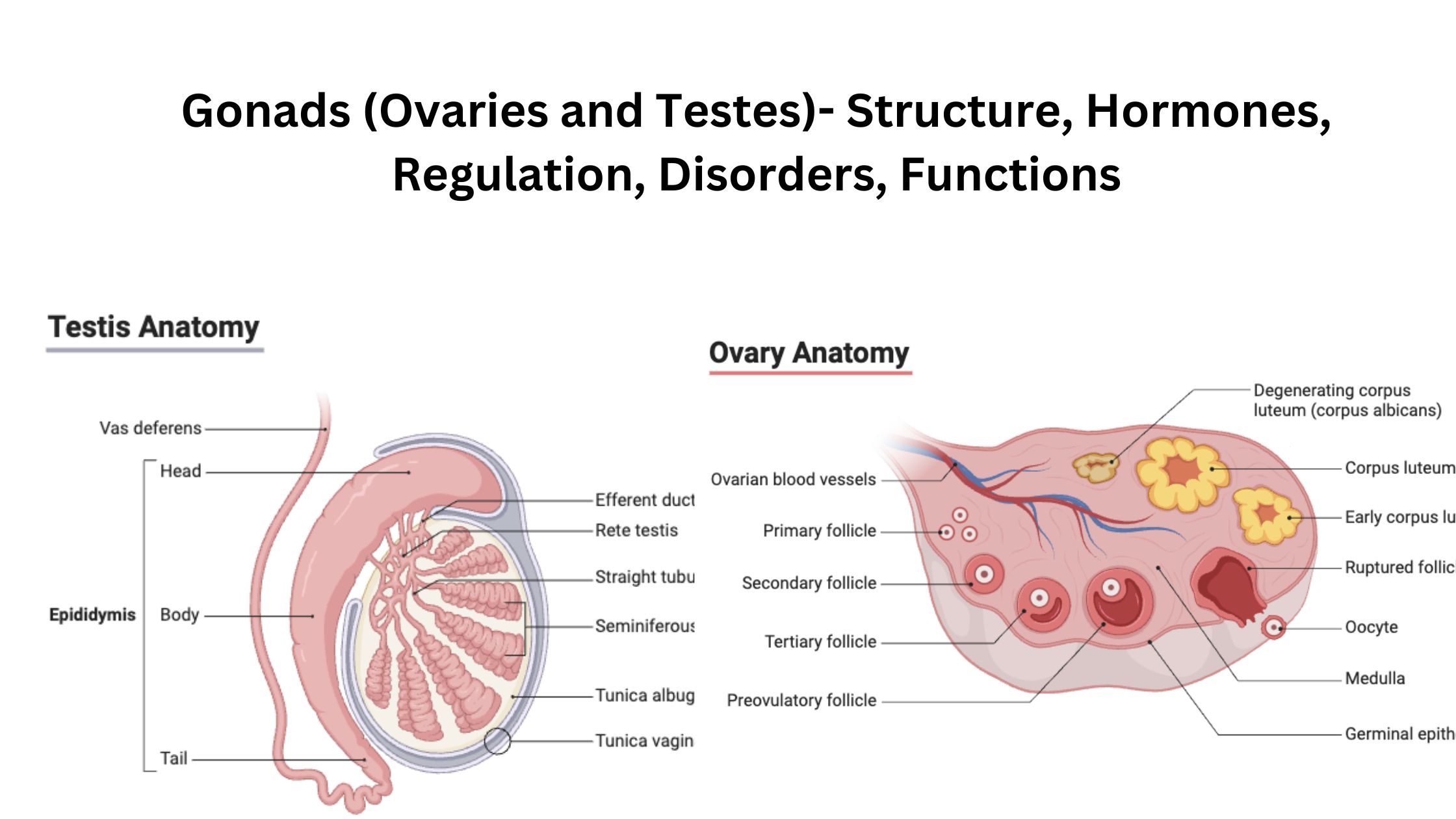
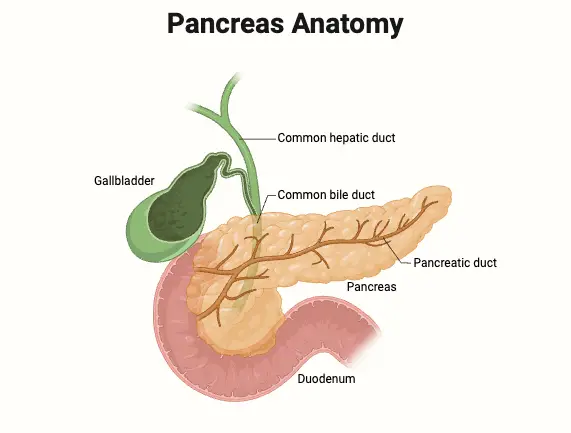
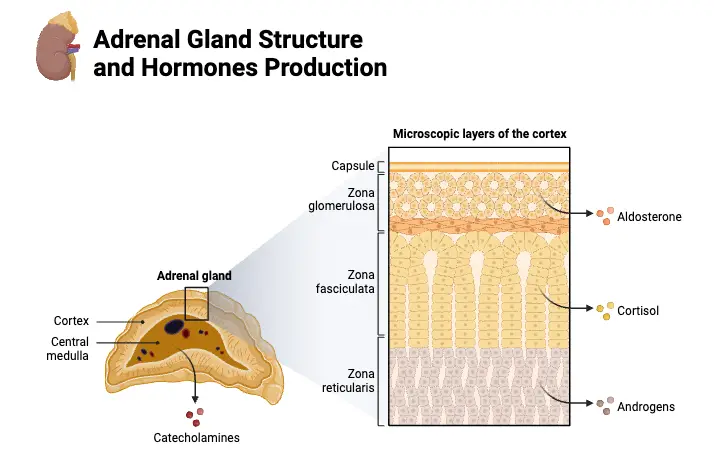
Ovaries – Definition, Structure, Hormones, Functions
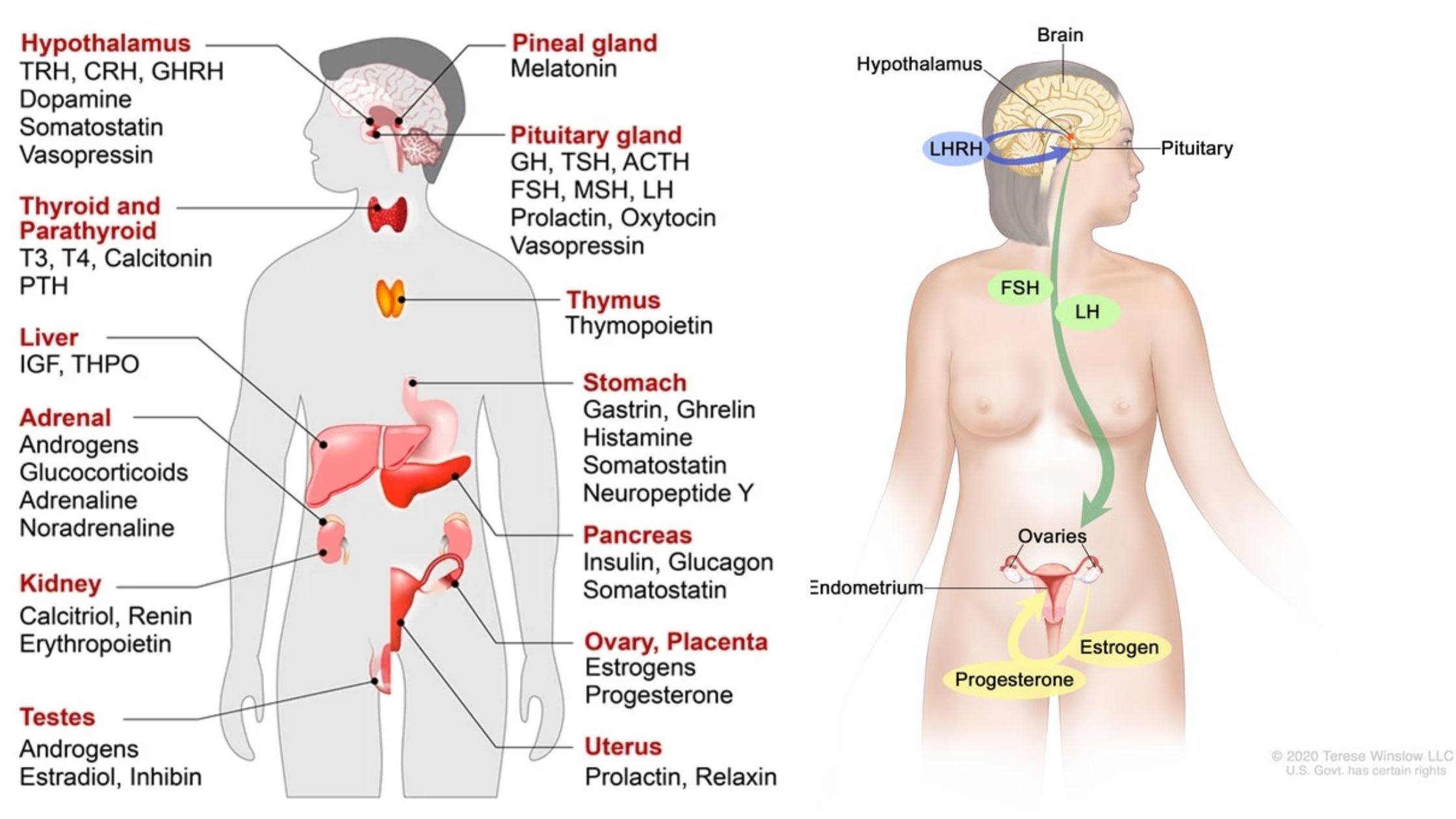
What is Ovary? Definition of Ovary The ovary is a reproductive organ in females that produces eggs and secretes hormones like estrogen and progesterone, essential for regulating the menstrual cycle and fertility. Anatomy of the Ovary The ovary is a crucial organ in the female reproductive system, responsible for producing eggs and secreting hormones essential … Read more