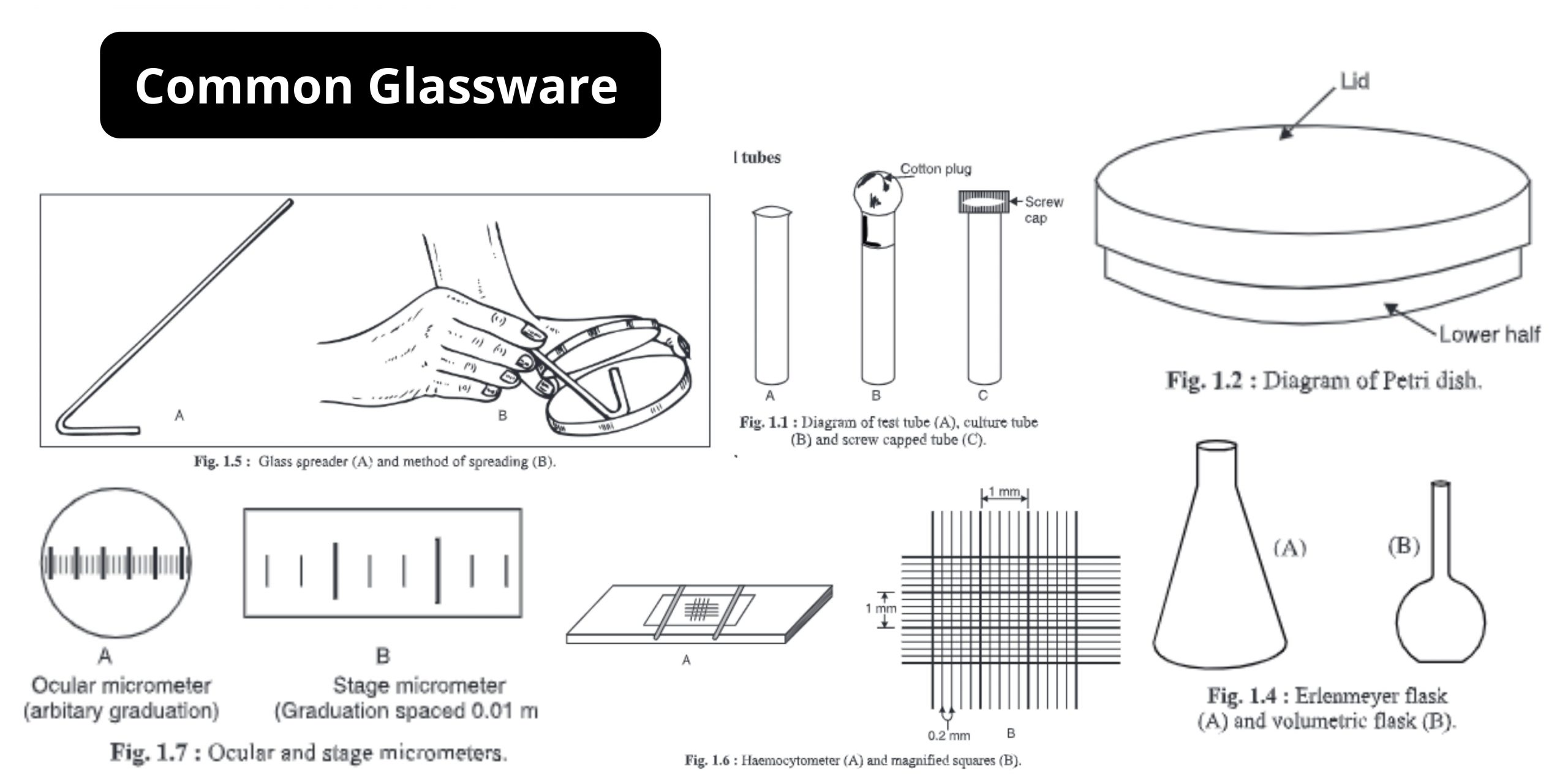
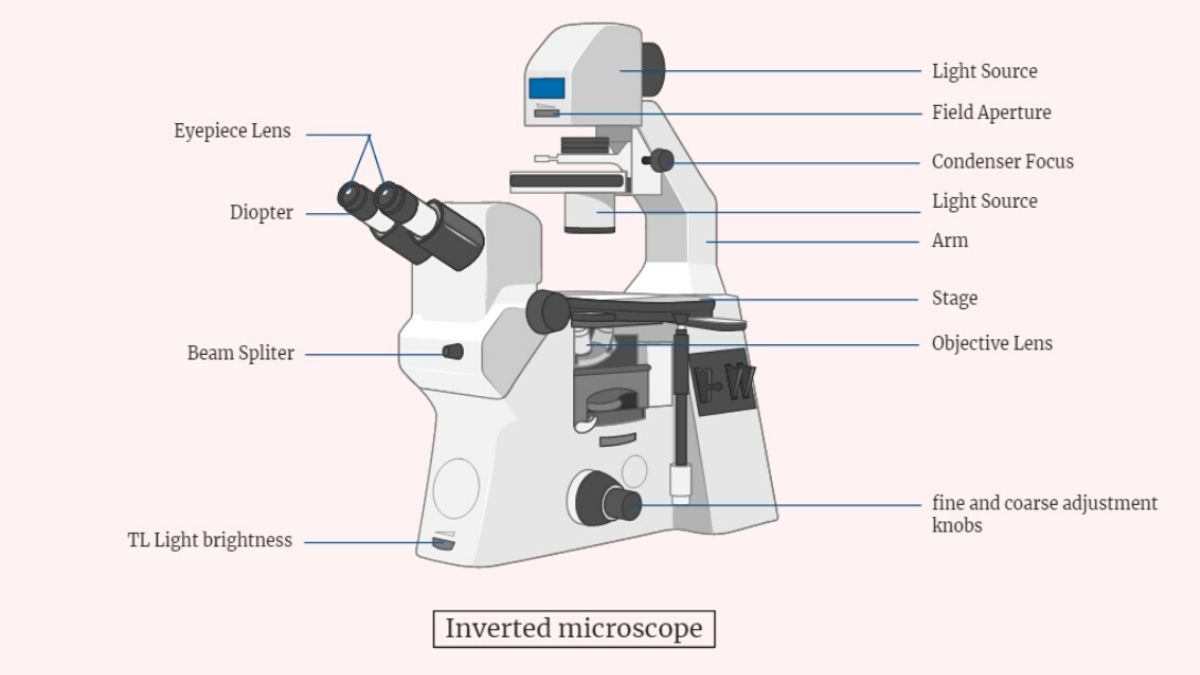
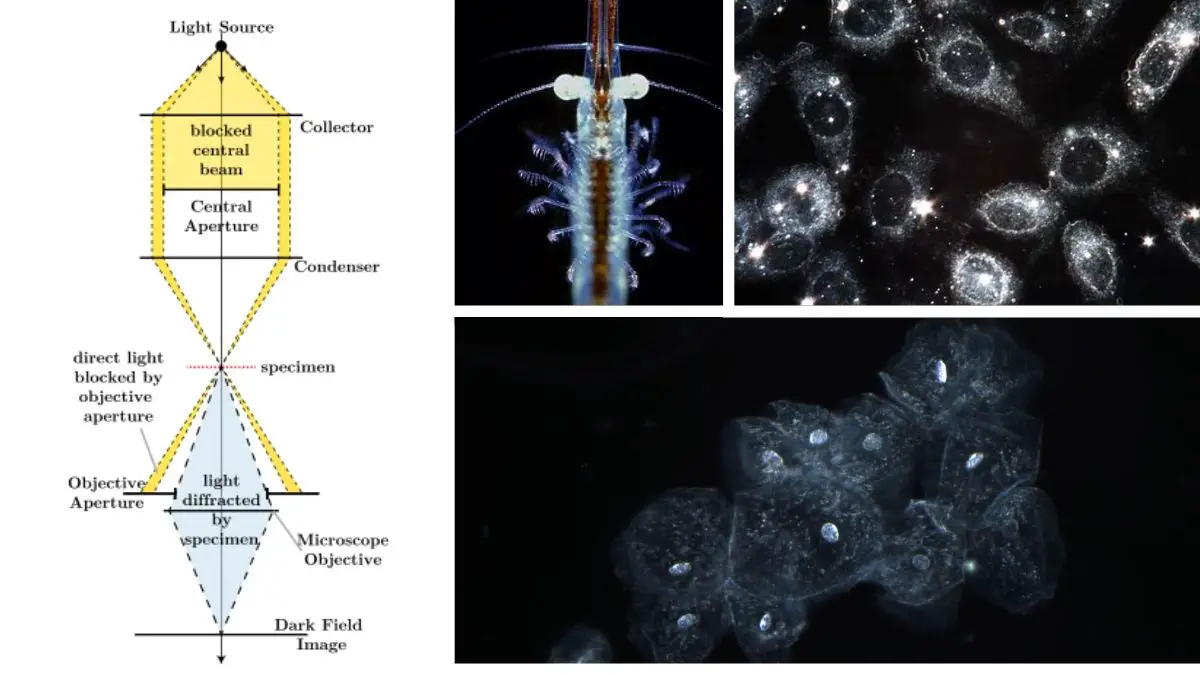
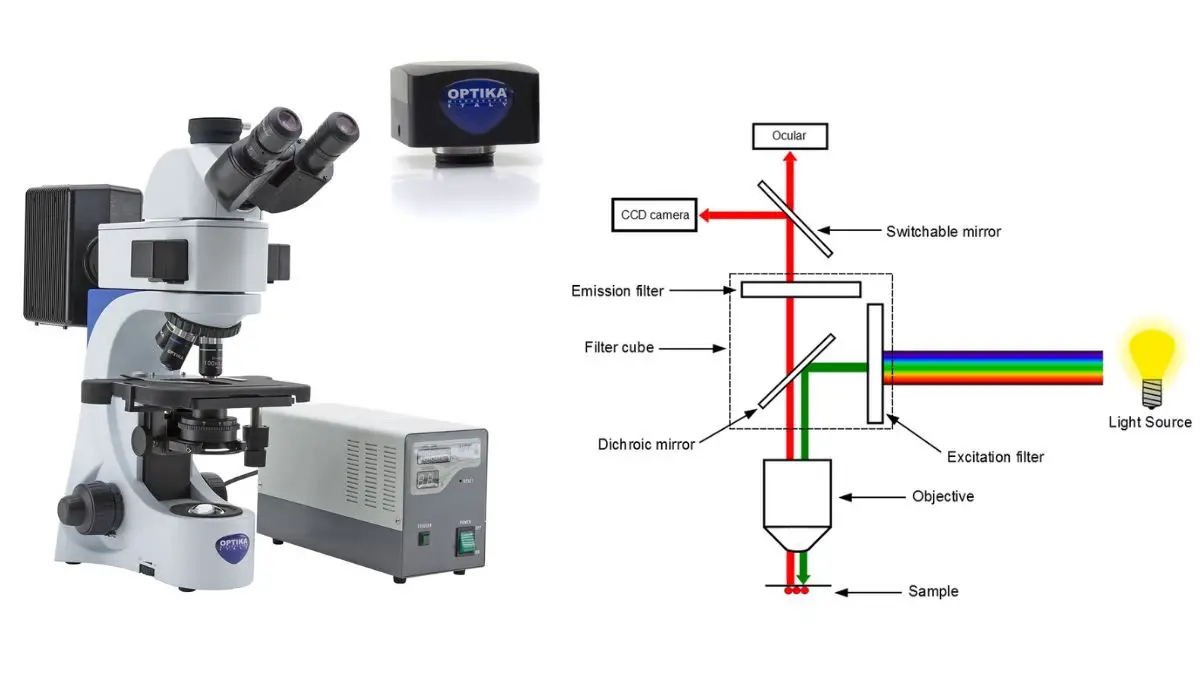
14 Common Glassware used in A Microbiology Laboratory
Microbiology laboratories require well-built rooms that are equipped with tools, glassware and equipment. Test tubes, culture tubes, Petri dishes and Erlenmeyer flasks are the most important types of glassware in a microbiological lab. 1. Test tube Usually composed of glass or transparent plastic, a test tube is a standard piece of laboratory equipment distinguished by … Read more